A60 (a) A car of mass 1000 kg is initially at rest. It moves along a straight road for 20s and then comes to rest again. The speed-time graph for the movement is: vims 20 10 10 15 20 bs (i) What is the total distance travelled? (ii) What resultant force acts on the car during the part of the motion represented by CD? (iii) What is the momentum of the car when it has reached its maximum speed? Use this momentum value to find the constant resultant acceler- ating force.
A60 (a) A car of mass 1000 kg is initially at rest. It moves along a straight road for 20s and then comes to rest again. The speed-time graph for the movement is: vims 20 10 10 15 20 bs (i) What is the total distance travelled? (ii) What resultant force acts on the car during the part of the motion represented by CD? (iii) What is the momentum of the car when it has reached its maximum speed? Use this momentum value to find the constant resultant acceler- ating force.
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter9: Linear Momentum And Collisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 34P: A ball of mass 250 g is thrown with an initial velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 30 with the...
Related questions
Question
Show all working explaining detailly each step.
Answer a(i), (ii) & (iii)
![(iv) During the part of the motion
represented by OB on the graph,
the constant resultant force found in
(iii) is acting on the moving car
although it is inoving through air.
Sketch a graph to show how the
driving force would have to vary with
time to produce this constant accel-
eration. Explain the shape of your
graph.
(b) If, when travelling at this maximum
speed, the 1000 kg car had struck and
remained attached to a stationary vehicle
of mass 1500 kg, with what speed would
the interlocked vehicles have travelled
immediately after collision?
Calculate the kinetic energy of the car just
prior to this collision and the kinetic
energy of the interlocked vehicles just
afterwards. Comment upon the values
obtained.
Explain how certain design features in a
modern car help to protect the driver of a
car in such a collision.
[L]](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F5a6d9c67-6f13-49d2-ac4d-2d996f90a88b%2F385ce445-d8ce-4ff7-9440-569859a74c48%2Fndqu58_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:(iv) During the part of the motion
represented by OB on the graph,
the constant resultant force found in
(iii) is acting on the moving car
although it is inoving through air.
Sketch a graph to show how the
driving force would have to vary with
time to produce this constant accel-
eration. Explain the shape of your
graph.
(b) If, when travelling at this maximum
speed, the 1000 kg car had struck and
remained attached to a stationary vehicle
of mass 1500 kg, with what speed would
the interlocked vehicles have travelled
immediately after collision?
Calculate the kinetic energy of the car just
prior to this collision and the kinetic
energy of the interlocked vehicles just
afterwards. Comment upon the values
obtained.
Explain how certain design features in a
modern car help to protect the driver of a
car in such a collision.
[L]
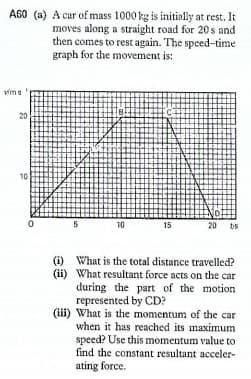
Transcribed Image Text:A60 (a) A cur of mass 1000 kg is initiolly at rest. It
moves along a straight road for 20 s and
then comes to rest again. The speed-time
graph for the movement is:
vims
20
10
10
15
20 ts
(i) What is the total distance travelled?
(ii) What resultant force acts on the car
during the part of the motion
represented by CD?
(ii) What is the momentum of the car
when it has reached its maximum
speed? Use this momentum value to
find the constant resultant acceler-
ating force.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College