According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory, an acid is any substance (molecule or ion) that can transfer a proton (H ion) to another substance, and a base is any substance that can accept a proton. Acid-base reactions are proton-transfer reactions, as follows: HA + = BH! + A acid base acid base Part D Chemical species whose formulas differ only by one proton are said to be conjugate acid- base pairs. Thus, A is the conjugate base of the acid HA, and HA is the conjugate acid of the base A Similarly, B is the conjugate base of the acid BH, and BH is the conjugate acid of the base B. The stronger the acid, the weaker the conjugate base, and the stronger the base, the weaker the conjugate acid. Among three bases, X, Y, and Z , the strongest one is Y, and the weakest one is Z . Rank their conjugate acids, HX, HY, and HZ, in order of decreasing strength. Rank the acids from strongest to weakest. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. > View Available Hint(s) Reset Help HY HX HZ Strongest acid Weakest acid O The correct ranking cannot be determined.
According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory, an acid is any substance (molecule or ion) that can transfer a proton (H ion) to another substance, and a base is any substance that can accept a proton. Acid-base reactions are proton-transfer reactions, as follows: HA + = BH! + A acid base acid base Part D Chemical species whose formulas differ only by one proton are said to be conjugate acid- base pairs. Thus, A is the conjugate base of the acid HA, and HA is the conjugate acid of the base A Similarly, B is the conjugate base of the acid BH, and BH is the conjugate acid of the base B. The stronger the acid, the weaker the conjugate base, and the stronger the base, the weaker the conjugate acid. Among three bases, X, Y, and Z , the strongest one is Y, and the weakest one is Z . Rank their conjugate acids, HX, HY, and HZ, in order of decreasing strength. Rank the acids from strongest to weakest. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. > View Available Hint(s) Reset Help HY HX HZ Strongest acid Weakest acid O The correct ranking cannot be determined.
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter16: Principles Of Chemical Reactivity: The Chemistry Of Acids And Bases
Section16.10: The Lewis Concept Of Acids And Bases
Problem 2.5ACP: To measure the relative strengths of bases stronger than OH, it is necessary to choose a solvent...
Related questions
Question
Question in image.
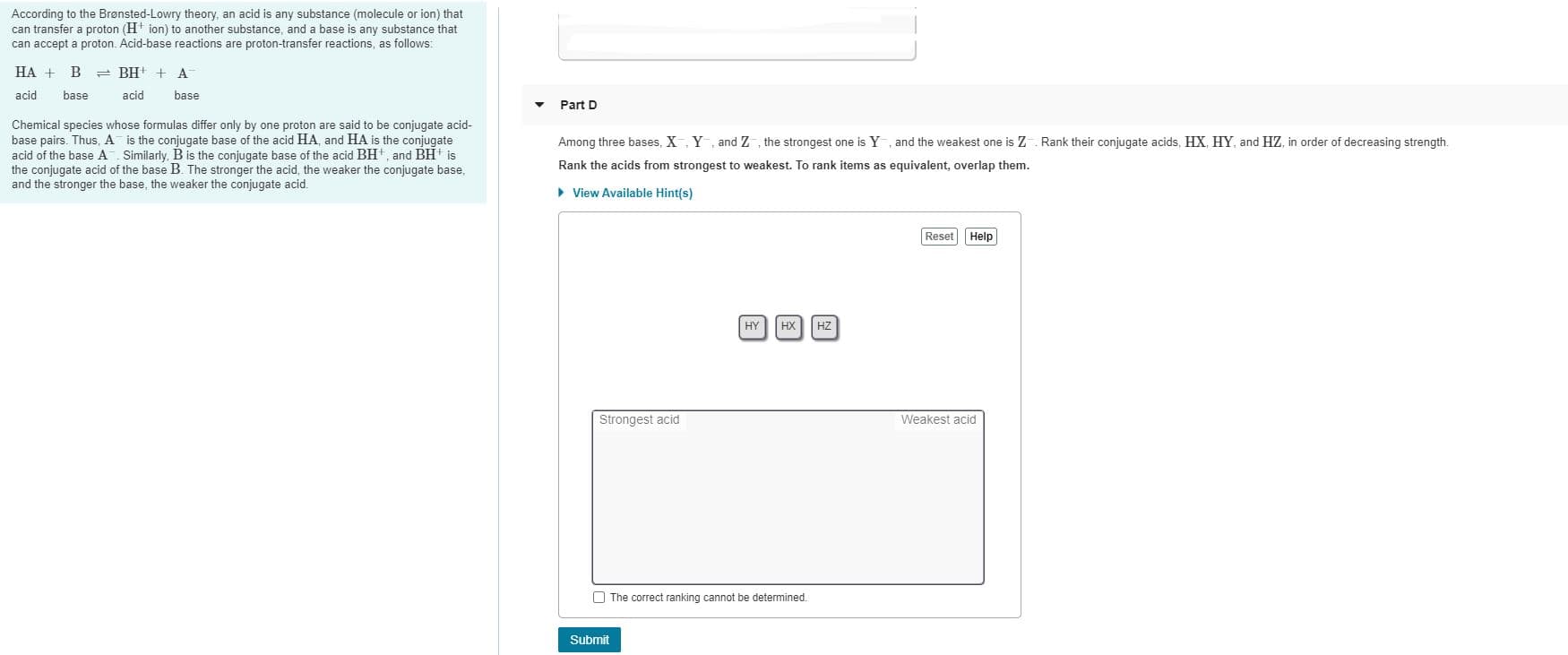
Transcribed Image Text:According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory, an acid is any substance (molecule or ion) that
can transfer a proton (H ion) to another substance, and a base is any substance that
can accept a proton. Acid-base reactions are proton-transfer reactions, as follows:
HA +
= BH! + A
acid
base
acid
base
Part D
Chemical species whose formulas differ only by one proton are said to be conjugate acid-
base pairs. Thus, A is the conjugate base of the acid HA, and HA is the conjugate
acid of the base A Similarly, B is the conjugate base of the acid BH, and BH is
the conjugate acid of the base B. The stronger the acid, the weaker the conjugate base,
and the stronger the base, the weaker the conjugate acid.
Among three bases, X, Y, and Z , the strongest one is Y, and the weakest one is Z . Rank their conjugate acids, HX, HY, and HZ, in order of decreasing strength.
Rank the acids from strongest to weakest. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
> View Available Hint(s)
Reset Help
HY
HX
HZ
Strongest acid
Weakest acid
O The correct ranking cannot be determined.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning