Air flows into the atmosphere from a nozzle and strikes a vertical plate as shown in the figure below. A horizontal force of 12 N is required to hold the plate in place. Determine the reading on the pressure gage. Assume the flow to be incompressible and frictionless. p=? 12N Area = 0.003 m? Area = 0.01 m?
Air flows into the atmosphere from a nozzle and strikes a vertical plate as shown in the figure below. A horizontal force of 12 N is required to hold the plate in place. Determine the reading on the pressure gage. Assume the flow to be incompressible and frictionless. p=? 12N Area = 0.003 m? Area = 0.01 m?
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engineering (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN:9781305084766
Author:Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:Saeed Moaveni
Chapter6: Fundamental Dimensions And Units
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 49P
Related questions
Question
Please fastttt only final asnwer needed
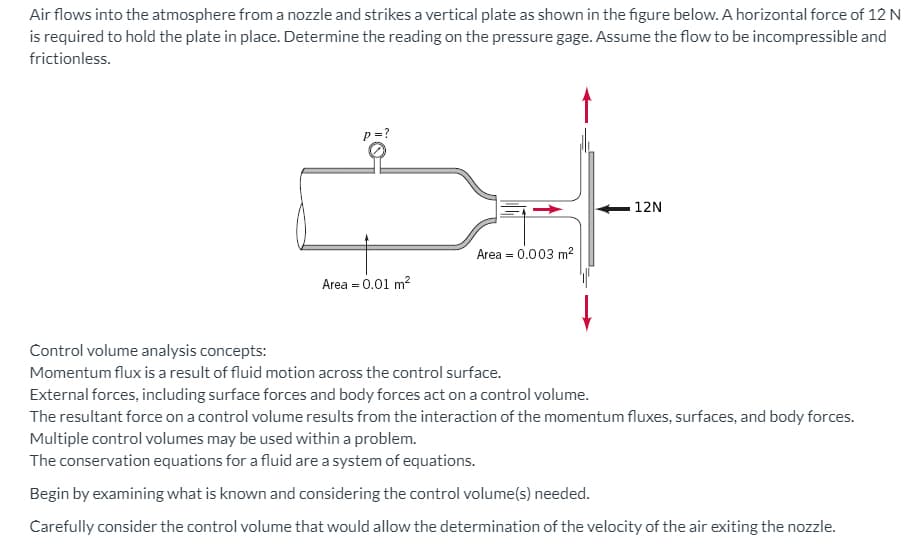
Transcribed Image Text:Air flows into the atmosphere from a nozzle and strikes a vertical plate as shown in the figure below. A horizontal force of 12 N
is required to hold the plate in place. Determine the reading on the pressure gage. Assume the flow to be incompressible and
frictionless.
p=?
12N
Area = 0.003 m2
Area = 0.01 m?
Control volume analysis concepts:
Momentum flux is a result of fluid motion across the control surface.
External forces, including surface forces and body forces act on a control volume.
The resultant force on a control volume results from the interaction of the momentum fluxes, surfaces, and body forces.
Multiple control volumes may be used within a problem.
The conservation equations for a fluid are a system of equations.
Begin by examining what is known and considering the control volume(s) needed.
Carefully consider the control volume that would allow the determination of the velocity of the air exiting the nozzle.

Transcribed Image Text:(f) What is the gage pressure of the jet traveling radially outward beyond the edges of the plate?
p= i 1.819
kPa
(g) What is the gage pressure acting on the right-hand face of the plate?
p = i 4
kPa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305084766
Author:
Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305084766
Author:
Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:
Cengage Learning