An 7.5 kg crate is pulled 5.3 m up a 30° incline by a rope angled 16 ° above the incline. The tension in the rope is 110N and the crate's coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.27. Part A You may want to review (Pages 222 - 223). How much work is done by tension, by gravity, and by the normal force? For help with math skills, you may want to review: Express your answers using two significant figures. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. The Vector Dot Product • View Available Hint(s) Wr, Wg, Wn = J Submit Part B What is the increase in thermal energy of the crate and incline? Express your answer using two significant figures.
An 7.5 kg crate is pulled 5.3 m up a 30° incline by a rope angled 16 ° above the incline. The tension in the rope is 110N and the crate's coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.27. Part A You may want to review (Pages 222 - 223). How much work is done by tension, by gravity, and by the normal force? For help with math skills, you may want to review: Express your answers using two significant figures. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. The Vector Dot Product • View Available Hint(s) Wr, Wg, Wn = J Submit Part B What is the increase in thermal energy of the crate and incline? Express your answer using two significant figures.
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter7: Work, Energy, And Energy Resources
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7PE: A shopper pushes a grocery cart 20.0 m at constant speed on level ground, against a 35.0 N...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
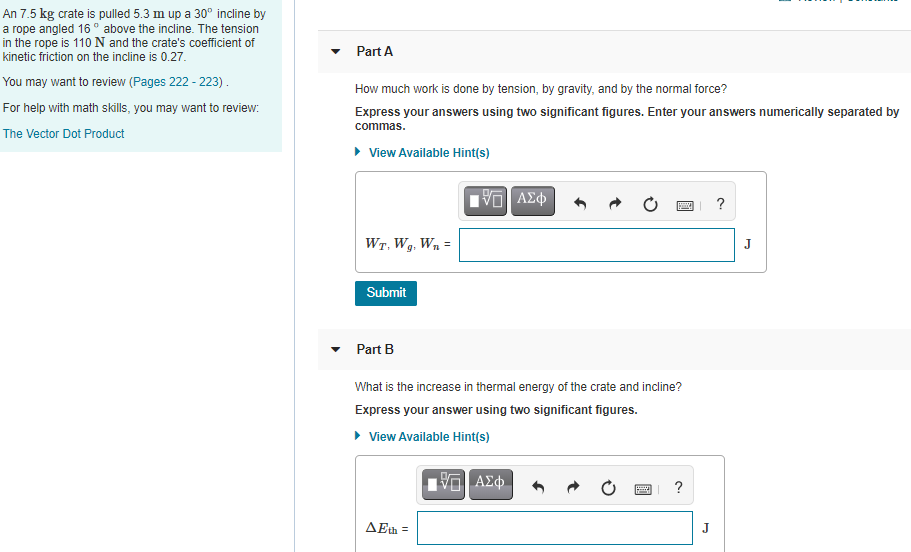
Transcribed Image Text:An 7.5 kg crate is pulled 5.3 m up a 30° incline by
a rope angled 16 ° above the incline. The tension
in the rope is 110N and the crate's coefficient of
kinetic friction on the incline is 0.27.
Part A
You may want to review (Pages 222 - 223).
How much work is done by tension, by gravity, and by the normal force?
For help with math skills, you may want to review:
Express your answers using two significant figures. Enter your answers numerically separated by
commas.
The Vector Dot Product
• View Available Hint(s)
Wr, Wg, Wn =
J
Submit
Part B
What is the increase in thermal energy of the crate and incline?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning