An infinitely long solid insulating cylinder of radius a = 2.1 cm is positioned with its symmetry axis along the z-axis as shown. The cylinder is uniformly charged with a charge density p = 28 µC/m³. Concentric with the cylinder is a cylindrical conducting shell of inner radius b = 14.9 cm, and outer radius c = 17.9 cm. The conducting shell has a linear charge density A = -0.36µC/m. R(0,d) Pa4) 1) What is E,(R), the y-component of the electric field at point R, located a distanced = 47 cm from the origin along the y-axis as shown? -12.29*10^3 N/C Submit 2) What is V(P) - V(R), the potential difference between points P and R? Point P is located at (x,y) = (47 cm, 47 cm). 2.001*10^3 V Submit 3) What is V(c) - V(a), the potentital difference between the outer surface of the conductor and the outer surface of the insulator? -1366.9 V Submit
An infinitely long solid insulating cylinder of radius a = 2.1 cm is positioned with its symmetry axis along the z-axis as shown. The cylinder is uniformly charged with a charge density p = 28 µC/m³. Concentric with the cylinder is a cylindrical conducting shell of inner radius b = 14.9 cm, and outer radius c = 17.9 cm. The conducting shell has a linear charge density A = -0.36µC/m. R(0,d) Pa4) 1) What is E,(R), the y-component of the electric field at point R, located a distanced = 47 cm from the origin along the y-axis as shown? -12.29*10^3 N/C Submit 2) What is V(P) - V(R), the potential difference between points P and R? Point P is located at (x,y) = (47 cm, 47 cm). 2.001*10^3 V Submit 3) What is V(c) - V(a), the potentital difference between the outer surface of the conductor and the outer surface of the insulator? -1366.9 V Submit
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter24: Electric Fields
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 66PQ
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:4) Defining the zero of potential to be along the z-axis (x = y = 0), what is the sign of the potential at the surface of the
insulator?
V(a) ·
Ov(a) = 0
V(a) > 0
< 0
Submit
5) The charge density of the insulating cylinder is now changed to a new value, p' and it is found that the electric field
at point P is now zero. What is the value of p'?
µC/m³ Submit
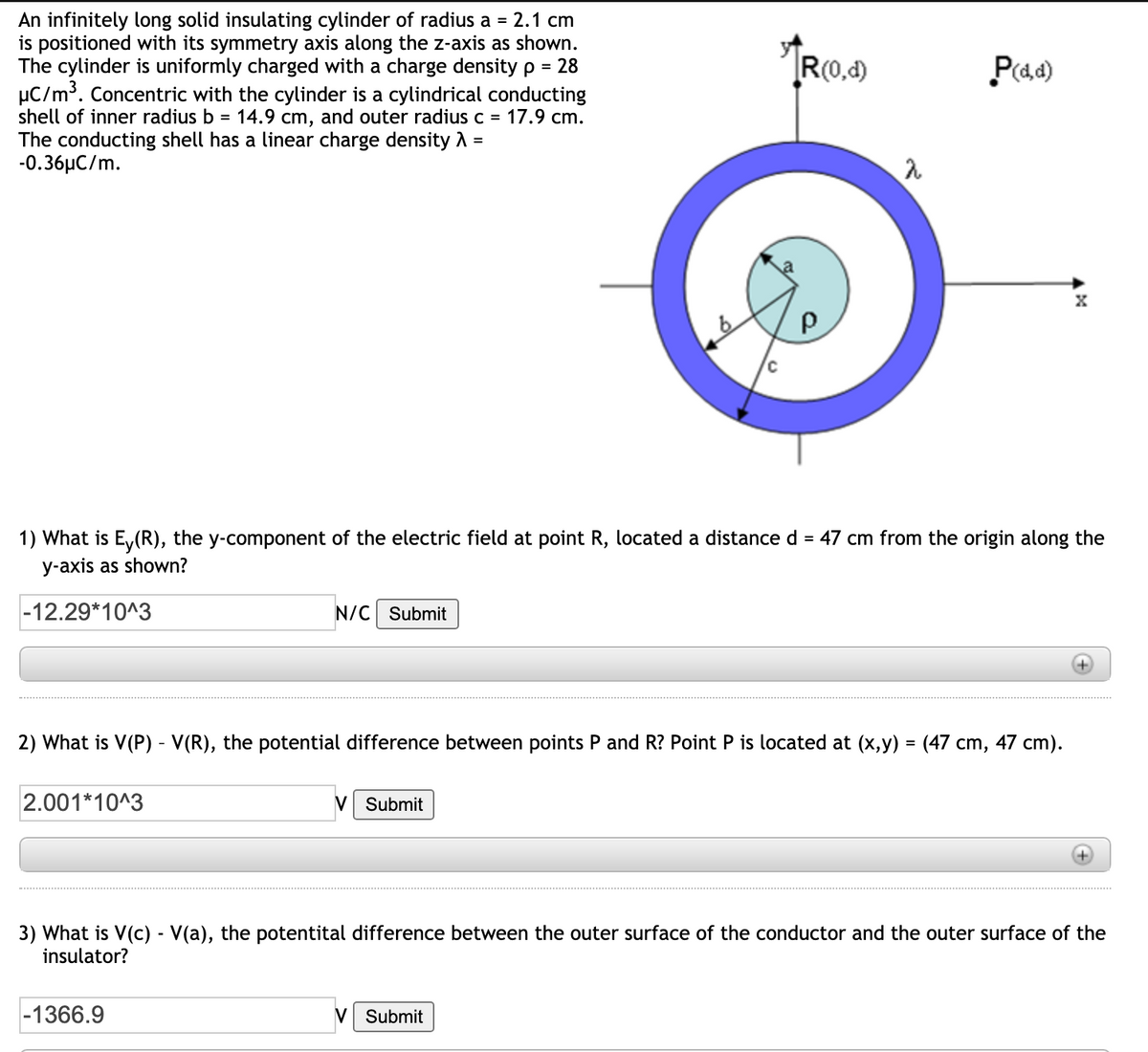
Transcribed Image Text:An infinitely long solid insulating cylinder of radius a = 2.1 cm
is positioned with its symmetry axis along the z-axis as shown.
The cylinder is uniformly charged with a charge density p = 28
µC/m³. Concentric with the cylinder is a cylindrical conducting
14.9 cm, and outer radius c = 17.9 cm.
R(0,4)
P(a4)
shell of inner radius b =
The conducting shell has a linear charge density A =
-0.36µC/m.
47 cm from the origin along the
1) What is E,(R), the y-component of the electric field at point R, located a distance d =
y-axis as shown?
|-12.29*10^3
N/C Submit
2) What is V(P) - V(R), the potential difference between points P and R? Point P is located at (x,y) = (47 cm, 47 cm).
2.001*10^3
V Submit
3) What is V(c) - V(a), the potentital difference between the outer surface of the conductor and the outer surface of the
insulator?
|-1366.9
V Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning