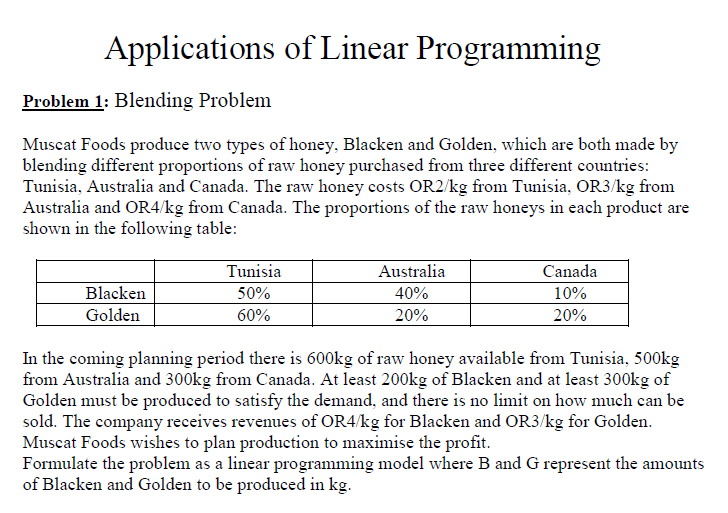
Applications of Linear Programming Problem 1: Blending Problem Muscat Foods produce two types of honey, Blacken and Golden, which are both made by blending different proportions of raw honey purchased from three different countries: Tunisia, Australia and Canada. The raw honey costs OR2/kg from Tunisia, OR3/kg from Australia and OR4/kg from Canada. The proportions of the raw honeys in each product are shown in the following table: Blacken Golden Tunisia 50% 60% Australia 40% 20% Canada 10% 20% In the coming planning period there is 600kg of raw honey available from Tunisia, 500kg from Australia and 300kg from Canada. At least 200kg of Blacken and at least 300kg of Golden must be produced to satisfy the demand, and there is no limit on how much can be sold. The company receives revenues of OR4/kg for Blacken and OR3/kg for Golden. Muscat Foods wishes to plan production to maximise the profit. Formulate the problem as a linear programming model where B and G represent the amounts of Blacken and Golden to be produced in kg.
Applications of Linear Programming Problem 1: Blending Problem Muscat Foods produce two types of honey, Blacken and Golden, which are both made by blending different proportions of raw honey purchased from three different countries: Tunisia, Australia and Canada. The raw honey costs OR2/kg from Tunisia, OR3/kg from Australia and OR4/kg from Canada. The proportions of the raw honeys in each product are shown in the following table: Blacken Golden Tunisia 50% 60% Australia 40% 20% Canada 10% 20% In the coming planning period there is 600kg of raw honey available from Tunisia, 500kg from Australia and 300kg from Canada. At least 200kg of Blacken and at least 300kg of Golden must be produced to satisfy the demand, and there is no limit on how much can be sold. The company receives revenues of OR4/kg for Blacken and OR3/kg for Golden. Muscat Foods wishes to plan production to maximise the profit. Formulate the problem as a linear programming model where B and G represent the amounts of Blacken and Golden to be produced in kg.
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter4: Linear Programming Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 73P
Related questions
Question
100%
Please formulate the LP with clear steps
Transcribed Image Text:Applications of Linear Programming
Problem 1: Blending Problem
Muscat Foods produce two types of honey, Blacken and Golden, which are both made by
blending different proportions of raw honey purchased from three different countries:
Tunisia, Australia and Canada. The raw honey costs OR2/kg from Tunisia, OR3/kg from
Australia and OR4/kg from Canada. The proportions of the raw honeys in each product are
shown in the following table:
Blacken
Golden
Tunisia
50%
60%
Australia
40%
20%
Canada
10%
20%
In the coming planning period there is 600kg of raw honey available from Tunisia, 500kg
from Australia and 300kg from Canada. At least 200kg of Blacken and at least 300kg of
Golden must be produced to satisfy the demand, and there is no limit on how much can be
sold. The company receives revenues of OR4/kg for Blacken and OR3/kg for Golden.
Muscat Foods wishes to plan production to maximise the profit.
Formulate the problem as a linear programming model where B and G represent the amounts
of Blacken and Golden to be produced in kg.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,