As the price level rises, the cost of borrowing money will (remain the same, fall, rise), causing the quantity of output demanded to (remain the same, fall, rise). This phenomenon is known as the (exchange rate, interest rate, wealth) effect. When an economy’s price level rises, ceteris paribus, the domestic price level relative to the price level in other countries will (rise, fall). This means that domestic exports will be relatively (less, more) expensive than before, while foreign imports will be relatively (less, more) expensive than they were previously. The number of domestic products purchased by foreigners (exports) will therefore (remain the same, fall, rise), and the number of foreign products purchased by domestic consumers and firms (imports) will (remain the same, fall, rise). Net exports will therefore(remain the same, fall, rise), causing the quantity of domestic output demanded to(remain the same, fall, rise). This phenomenon is known as the (interest rate, open economy, wealth) effec
As the price level rises, the cost of borrowing money will (remain the same, fall, rise), causing the quantity of output demanded to (remain the same, fall, rise). This phenomenon is known as the (exchange rate, interest rate, wealth) effect. When an economy’s price level rises, ceteris paribus, the domestic price level relative to the price level in other countries will (rise, fall). This means that domestic exports will be relatively (less, more) expensive than before, while foreign imports will be relatively (less, more) expensive than they were previously. The number of domestic products purchased by foreigners (exports) will therefore (remain the same, fall, rise), and the number of foreign products purchased by domestic consumers and firms (imports) will (remain the same, fall, rise). Net exports will therefore(remain the same, fall, rise), causing the quantity of domestic output demanded to(remain the same, fall, rise). This phenomenon is known as the (interest rate, open economy, wealth) effec
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter26: The Neoclassical Perspective
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21P: Use Table 26.3 to answer the following questions. Sketch an aggregate supply and aggregate demand...
Related questions
Question
As the price level rises, the cost of borrowing money will (remain the same, fall, rise), causing the quantity of output demanded to (remain the same, fall, rise). This phenomenon is known as the (exchange rate, interest rate, wealth) effect.
When an economy’s price level rises, ceteris paribus, the domestic price level relative to the price level in other countries will (rise, fall). This means that domestic exports will be relatively (less, more) expensive than before, while foreign imports will be relatively (less, more) expensive than they were previously. The number of domestic products purchased by foreigners (exports) will therefore (remain the same, fall, rise), and the number of foreign products purchased by domestic consumers and firms (imports) will (remain the same, fall, rise). Net exports will therefore(remain the same, fall, rise), causing the quantity of domestic output demanded to(remain the same, fall, rise). This phenomenon is known as the (interest rate, open economy, wealth) effect.

Transcribed Image Text:As the price level rises, the cost of borrowing money will
causing the quantity of output demanded to
. This phenomenon is known as the
effect.
When an economy's price level rises, ceteris paribus, the domestic price level relative to the price level in other countries will
This means that
domestic exports will be relatively
previously. The number of domestic products purchased by foreigners (exports) will therefore
expensive than before, while foreign imports will be relatively
expensive than they were
and the number of foreign
products purchased by domestic consumers and firms (imports) will
Net exports will therefore
causing the quantity of domestic output demanded to
. This phenomenon is known as the
effect.
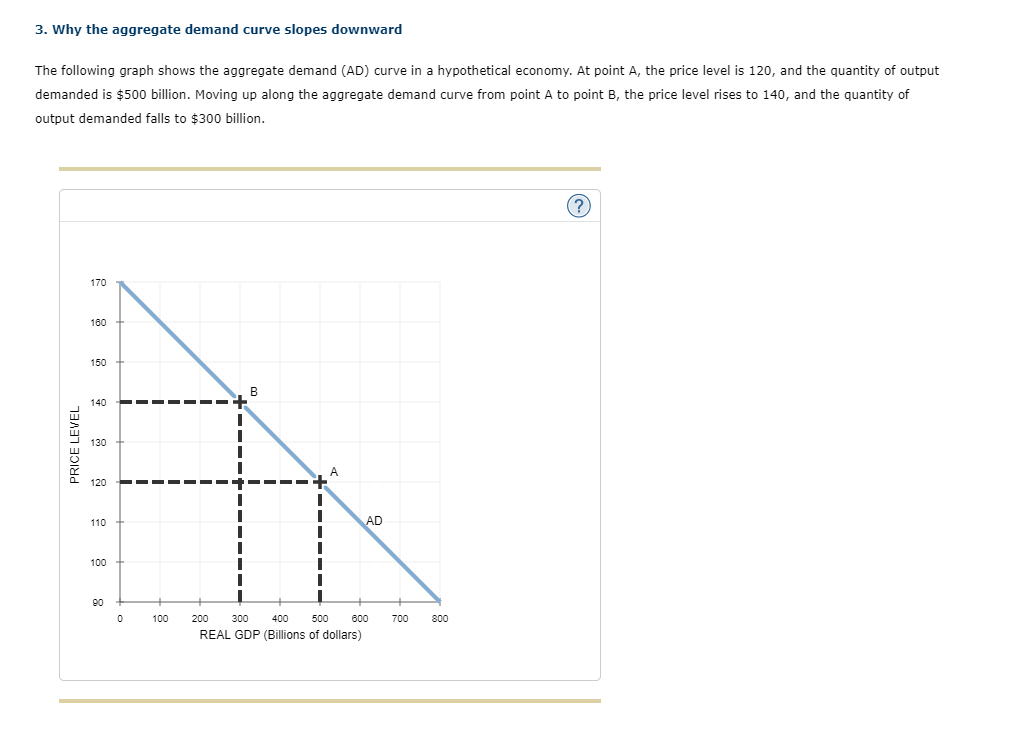
Transcribed Image Text:3. Why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward
The following graph shows the aggregate demand (AD) curve in a hypothetical economy. At point A, the price level is 120, and the quantity of output
demanded is $500 billion. Moving up along the aggregate demand curve from point A to point B, the price level rises to 140, and the quantity of
output demanded falls to $300 billion.
170
180
150
B
140
130
A
120
110
AD
100
90
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
REAL GDP (Billions of dollars)
PRICE LEVEL
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning