8. a) As you know, the largest mass extinction in the history of life on earth was the Permian extinction that occurred about 252 million years ago. The therapsids are often described as “mammal-like reptiles”. If the Permian extinction had caused the extinction of the therapsids, would mammals as we know them now have evolved? Why or why not? 8. b) Many lines of evidence, including biochemical evidence, show that living birds are direct descendants of dinosaurs. A number of dinosaur lineages had feathered dinosaurs, not just the lineage that includes living birds. Do you think that is it justified to believe that all feathered dinosaurs had behaviors known from living birds? Such behaviors of birds include colonial nesting, sexual displays by males using feathers, males moving to display their ornamental feathers to female mates. Give a brief reason for your answer. 8. c) A number of scientists believe that the Permian extinction was caused by huge volcanic lava flows (from the Siberian traps) that may have caused low oxygen concentrations compared to the high oxygen levels in the Permian. Does this low oxygen level after the Permian extinction make it likely that dinosaurs, especially large ones, did not evolve immediately after the Permian extinction (252 million years ago)? Why or why not?
8. a) As you know, the largest mass extinction in the history of life on earth was the Permian extinction that occurred about 252 million years ago. The therapsids are often described as “mammal-like reptiles”. If the Permian extinction had caused the extinction of the therapsids, would mammals as we know them now have evolved? Why or why not? 8. b) Many lines of evidence, including biochemical evidence, show that living birds are direct descendants of dinosaurs. A number of dinosaur lineages had feathered dinosaurs, not just the lineage that includes living birds. Do you think that is it justified to believe that all feathered dinosaurs had behaviors known from living birds? Such behaviors of birds include colonial nesting, sexual displays by males using feathers, males moving to display their ornamental feathers to female mates. Give a brief reason for your answer. 8. c) A number of scientists believe that the Permian extinction was caused by huge volcanic lava flows (from the Siberian traps) that may have caused low oxygen concentrations compared to the high oxygen levels in the Permian. Does this low oxygen level after the Permian extinction make it likely that dinosaurs, especially large ones, did not evolve immediately after the Permian extinction (252 million years ago)? Why or why not?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Chapter1: The Human Body: An Orientation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,...
Related questions
Question
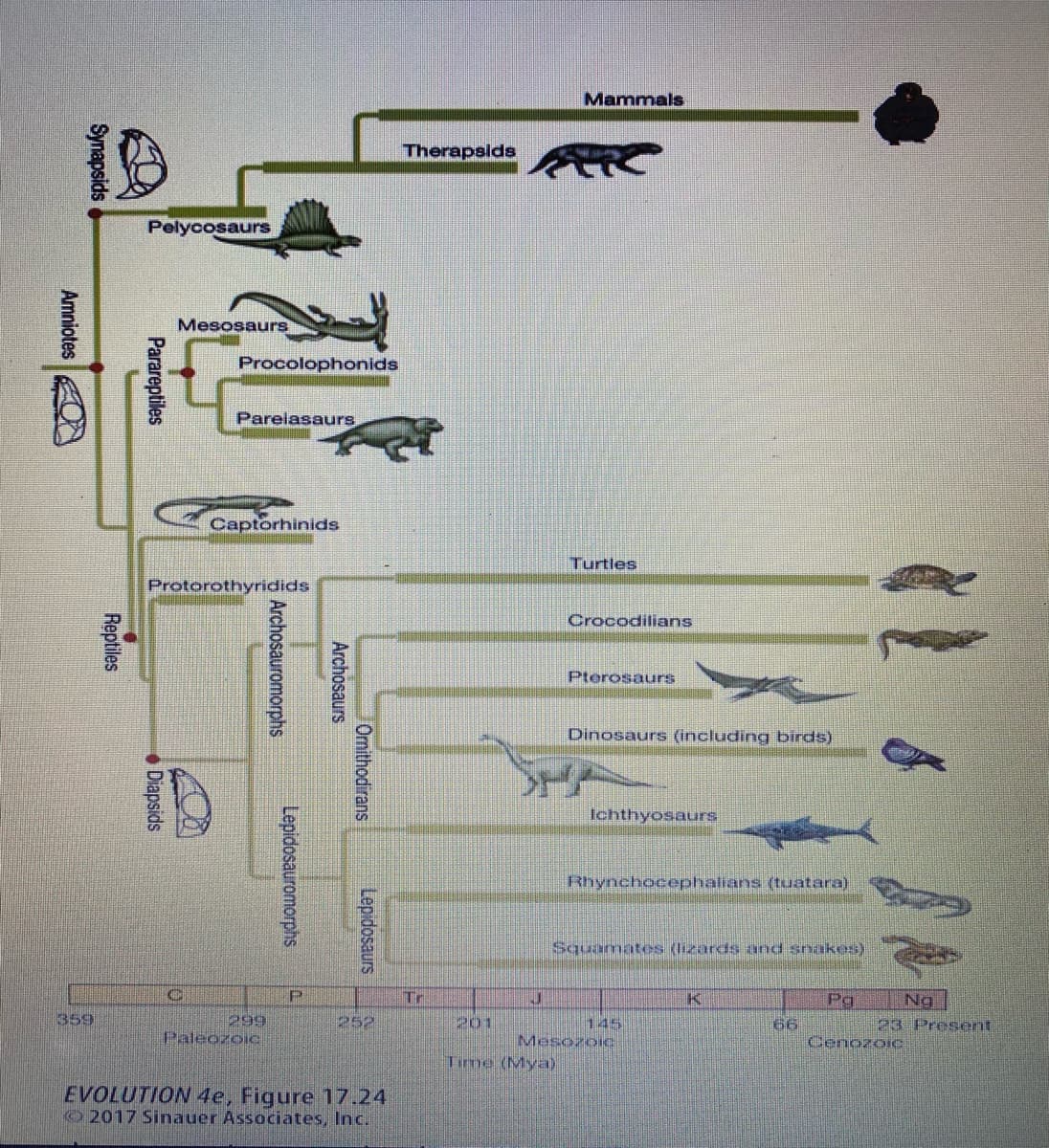
Hello, I need help answering number 8 a, b, & c using the phylogeny below. Pls & thank you!
8. a) As you know, the largest mass extinction in the history of life on earth was the Permian
extinction that occurred about 252 million years ago. The therapsids are often described as “mammal-like reptiles”.
If the Permian extinction had caused the extinction of the therapsids, would mammals as we know them now have evolved? Why or why not?
8. b) Many lines of evidence, including biochemical evidence, show that living birds are direct descendants of dinosaurs.
A number of dinosaur lineages had feathered dinosaurs, not just the lineage that includes living birds. Do you think that is it justified to believe that all feathered dinosaurs had behaviors known from living birds? Such behaviors of birds include colonial nesting, sexual displays by males using feathers, males moving to display their ornamental feathers to female mates. Give a brief reason for your answer.
8. c) A number of scientists believe that the Permian extinction was caused by huge volcanic lava flows (from the Siberian traps) that may have caused low oxygen concentrations compared to the high oxygen levels in the Permian. Does this low oxygen level after the Permian extinction make it likely that dinosaurs, especially large ones, did not evolve immediately after the Permian extinction (252 million years ago)? Why or why not?
Photos reference:
Futuyma, D. J., & Kirkpatrick, M. (2017). Chapter 17 The History of Life. In Evolution (4th ed., pp. 430-467). Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates.
![FIGURE 17.24 Phylogenetic relation-
ships and temporal duration (thick bars)
of major groups of amniote vertebrates.
Some authors define "reptiles" as one
of the two major lineages of amniotes,
the other being the synapsids, which
includes mammals. (After (53].)](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F65ea5826-21bc-4fd3-a7b6-320e00c383f2%2F87ac3ebf-5668-4cc4-b699-7a91073a094c%2F4vlj93b_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:FIGURE 17.24 Phylogenetic relation-
ships and temporal duration (thick bars)
of major groups of amniote vertebrates.
Some authors define "reptiles" as one
of the two major lineages of amniotes,
the other being the synapsids, which
includes mammals. (After (53].)
Transcribed Image Text:Mammals
ID
Pelycosaurs
Mesosaurs
Procolophonids
Parelasaurs
Captorhinids
Turtles
Protorothyridids
Crocodilians
Pterosaurs
Dinosaurs (including birds)
Ichthyosaurs
Rhynchocephalians (tuatara)
Squamates (lizards and snakes)
Tr
Ng
23 Present
Pg
359
299
Paleozoic
252
201
145
Mesozoic
66
Cenozoic
Time (Mya)
EVOLUTION 4e, Figure 17.24
2017 Sinauer Associates, Inc.
Omithodirans
Lepidosaurs
Archosaurs
Archosauromorphs
Lepidosauromorphs
Parareptiles
Diapsids
Reptiles
Synapsids
Amniotes
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:
9780135168059
Author:
Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, Jon
Publisher:
Pearson Education, Inc.,

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:
9780135168059
Author:
Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, Jon
Publisher:
Pearson Education, Inc.,

Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative Approach
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:
9780078024283
Author:
Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa Bidle
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy…
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:
9780321927040
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON