Assigned chemical agent: How does this agent specifically destroy microbial cells? Propose a hypothesis as to which organism will resist the most disinfectants, and why:
Assigned chemical agent: How does this agent specifically destroy microbial cells? Propose a hypothesis as to which organism will resist the most disinfectants, and why:
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative and Clinical Competencies (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305964792
Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Chapter42: Basic Microbiology
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2CR
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Evaluation of Antiseptics and Disinfectants
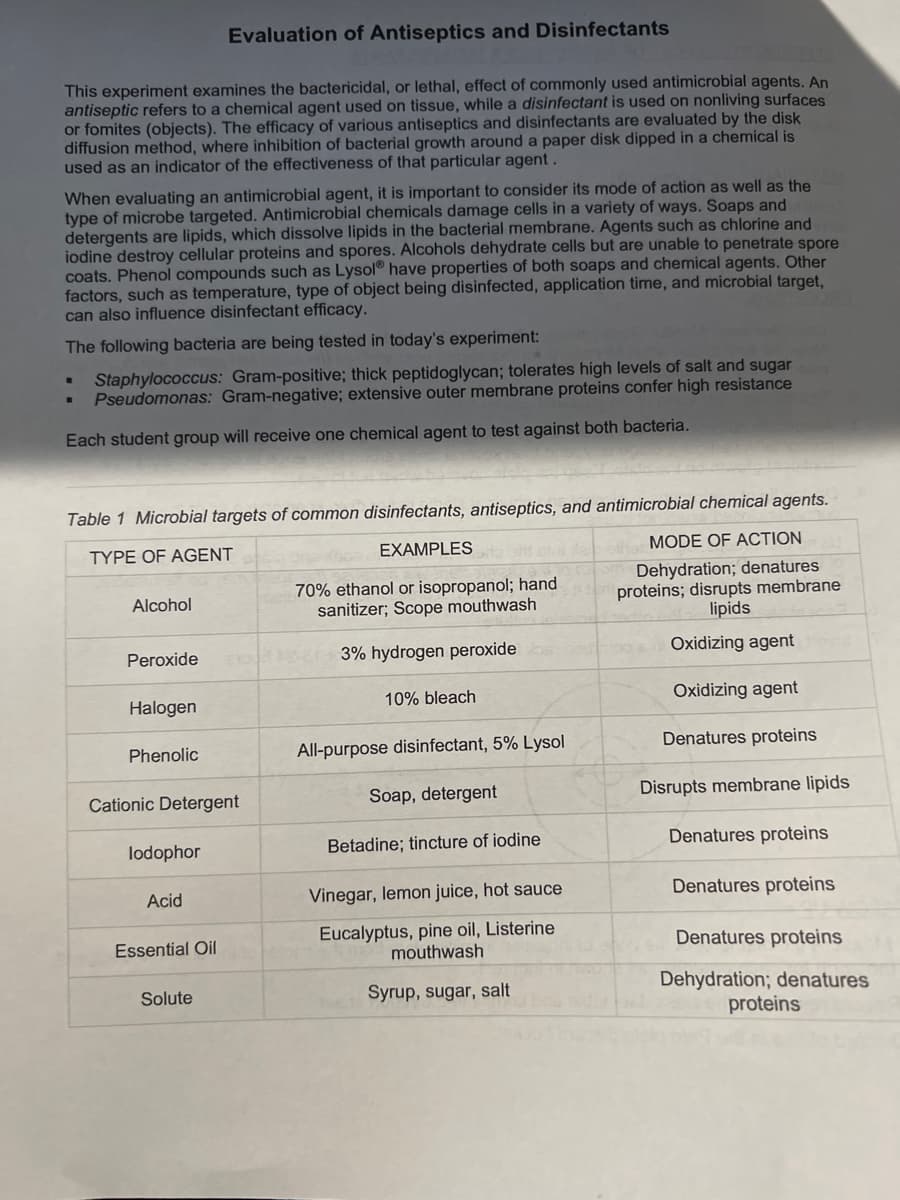
This experiment examines the bactericidal, or lethal, effect of commonly used antimicrobial agents. An
antiseptic refers to a chemical agent used on tissue, while a disinfectant is used on nonliving surfaces
or fomites (objects). The efficacy of various antiseptics and disinfectants are evaluated by the disk
diffusion method, where inhibition of bacterial growth around a paper disk dipped in a chemical is
used as an indicator of the effectiveness of that particular agent.
When evaluating an antimicrobial agent, it is important to consider its mode of action as well as the
type of microbe targeted. Antimicrobial chemicals damage cells in a variety of ways. Soaps and
detergents are lipids, which dissolve lipids in the bacterial membrane. Agents such as chlorine and
iodine destroy cellular proteins and spores. Alcohols dehydrate cells but are unable to penetrate spore
coats. Phenol compounds such as Lysol® have properties of both soaps and chemical agents. Other
factors, such as temperature, type of object being disinfected, application time, and microbial target,
can also influence disinfectant efficacy.
The following bacteria are being tested in today's experiment:
Staphylococcus: Gram-positive; thick peptidoglycan; tolerates high levels of salt and sugar
Pseudomonas: Gram-negative; extensive outer membrane proteins confer high resistance
Each student group will receive one chemical agent to test against both bacteria.
Table 1 Microbial targets of common disinfectants, antiseptics, and antimicrobial chemical agents.
TYPE OF AGENT
EXAMPLES
MODE OF ACTION
70% ethanol or isopropanol; hand
sanitizer; Scope mouthwash
Dehydration; denatures
proteins; disrupts membrane
lipids
Alcohol
Peroxide
3% hydrogen peroxide
Oxidizing agent
Halogen
10% bleach
Oxidizing agent
Phenolic
All-purpose disinfectant, 5% Lysol
Denatures proteins
Cationic Detergent
Soap, detergent
Disrupts membrane lipids
lodophor
Betadine; tincture of iodine
Denatures proteins
Acid
Vinegar, lemon juice, hot sauce
Denatures proteins
Eucalyptus, pine oil, Listerine
mouthwash
Essential Oil
Denatures proteins
Dehydration; denatures
proteins
Solute
Syrup, sugar, salt

Transcribed Image Text:After reading the experiment, consider the mode of action of the chemlcal agent
and review the properties of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in your text. Use this information
to propose a testable hypothesis regarding which organism will resist the most disinfectants, and why.
Assigned chemical agent:
How does this agent specifically destroy microbial cells?
Propose a hypothesis as to which organism will resist the most disinfectants, and why:
Predict the specific experimental results that you should observe to support this hypothesis:
Identify the:
Independent variable, which is manipulated by the experimenter:
Dependent variable, the outcome that cannot be manipulated by the experimenter:
Control treatment, comparative benchmark which lacks the independent variable:
Controlled variables, or factors that might affect the outcome which must be standardized; be
specific – use "incubation time for plates" rather than simply “time"
1.
2.
3.
4.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a…
Nursing
ISBN:
9781305964792
Author:
Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a…
Nursing
ISBN:
9781305964792
Author:
Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

