Assume a length of axon membrane of about 0.10 m is excited by an action potential (length excited = nerve speed x pulse duration = 50.0 m/s x 0.0020 s = 0.10 m). In the resting state, the outer surface of the axon wall is charged positively with K* ions and the inner wall has an equal and opposite charge of negative organic ions, as shown in the figure below. Model the axon as a parallel-plate capacitor and take C = KE A/d and Q = CAV to investigate the charge as follows. Use typical values for a cylindrical axon of cell wall thickness d = 1.6 x 10-8 m, axon radius r = 1.7 x 101 um, and cell-wall dielectric constant K = 2.3. External fluid Positive charge layer { Axon wall membrane d Negative charge layer Internal fluid + Axon radius = r
Assume a length of axon membrane of about 0.10 m is excited by an action potential (length excited = nerve speed x pulse duration = 50.0 m/s x 0.0020 s = 0.10 m). In the resting state, the outer surface of the axon wall is charged positively with K* ions and the inner wall has an equal and opposite charge of negative organic ions, as shown in the figure below. Model the axon as a parallel-plate capacitor and take C = KE A/d and Q = CAV to investigate the charge as follows. Use typical values for a cylindrical axon of cell wall thickness d = 1.6 x 10-8 m, axon radius r = 1.7 x 101 um, and cell-wall dielectric constant K = 2.3. External fluid Positive charge layer { Axon wall membrane d Negative charge layer Internal fluid + Axon radius = r
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter18: Direct-Current Circuits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 43P: Assume a length of axon membrane of about 0.10 m is excited by an action potential (length excited =...
Related questions
Question
100%
please help

Transcribed Image Text:(a) Calculate the positive charge on the outside of a 0.10-m piece of axon when it is not conducting an electric pulse. (Assume an initial potential difference
-2
of 7.0 x 10 v.)
C
How many K* ions are on the outside of the axon assuming an initial potential difference of 7.0 x 10-2 v?
K* ions
Is this a large charge per unit area? Hint: Calculate the charge per unit area in terms of electronic charge e per angstrom squared (Å<). An atom has a cross
section of about 1 Å2 (1 Å = 10-10 m). (Compare to normal atomic spacing of one atom every few Å.)
Yes
No
(b) How much positive charge must flow through the cell membrane to reach the excited state of +3.0 × 10¬2
V from the resting state of –7.0 x 10-2 v?
How many sodium ions (Na+) is this?
Nat ions
(c) If it takes 2.0 ms for the NaT ions to enter the axon, what is the average current in the axon wall in this process?
µA
-2
(d) How much energy does it take to raise the potential of the inner axon wall to +3.0 x 10 v, starting from the resting potential of -7.0 x 10-2 v?
(Assume that no energy is required to first raise the potential to 0 V from the resting potential of –7.0 x 10-2 V.)
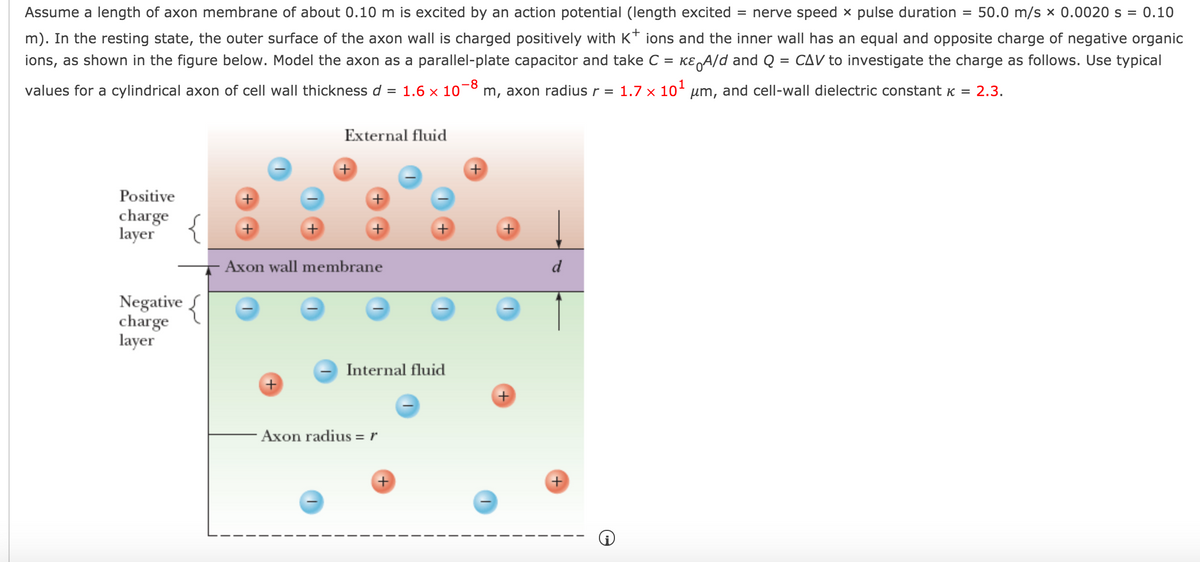
Transcribed Image Text:Assume a length of axon membrane of about 0.10 m is excited by an action potential (length excited = nerve speed x pulse duration =
50.0 m/s x 0.0020 s = 0.10
m). In the resting state, the outer surface of the axon wall is charged positively with K* ions and the inner wall has an equal and opposite charge of negative organic
ions, as shown in the figure below. Model the axon as a parallel-plate capacitor and take C = KE A/d and Q = CAV to investigate the charge as follows. Use typical
values for a cylindrical axon of cell wall thickness d = 1.6 x 10
-8
m, axon radius r = 1.7 x 10- um, and cell-wall dielectric constant K = 2.3.
External fluid
Positive
charge
layer
+
Axon wall membrane
d
Negative {
charge
layer
Internal fluid
Axon radius =r
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning