Chapter6: Gauss's Law
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 19CQ: The conductor in the preceding figure has an excess charge of 5.0C . If a 2.0C point charge is...
Related questions
Question
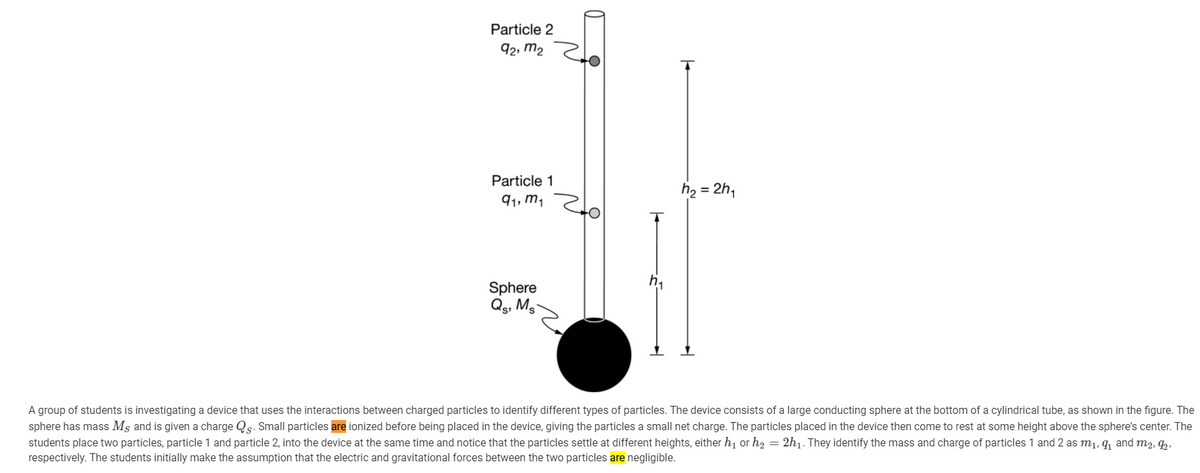
Transcribed Image Text:Particle 2
92, m2
Particle 1
= 2h,
91, m1
Sphere
Qg, Mg-
A group of students is investigating a device that uses the interactions between charged particles to identify different types of particles. The device consists of a large conducting sphere at the bottom of a cylindrical tube, as shown in the figure. The
sphere has mass Ms and is given a charge Qs. Small particles are ionized before being placed in the device, giving the particles a small net charge. The particles placed in the device then come to rest at some height above the sphere's center. The
students place two particles, particle 1 and particle 2, into the device at the same time and notice that the particles settle at different heights, either h, or h2 = 2h1. They identify the mass and charge of particles 1 and 2 as m1, q, and m2, ,
respectively. The students initially make the assumption that the electric and gravitational forces between the two particles are negligible.

Transcribed Image Text:(b) Do the sphere and particle 1 have like charges or opposite charges?
Like charges
Opposite charges
Justify your claim.
Expert Solution
Step 1

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

