B. y = Ce2x_ C. y = c,e2x (5D3 + 3D2 – 32D + 12)y = 0 A. y = c1e-2x + c2e¬0.4x + c3e3x + Cze-0.4x + Cze3* B. y = c¡e2x + c2e0.2x + C3e¬3x + Cze-3x C. y = c1e2* + c2e0.4% + C3e¬3* + Cze" D. y = ce-2x + c2e¬0.2x + C3e3x -3x + Cze + Cze3¤
B. y = Ce2x_ C. y = c,e2x (5D3 + 3D2 – 32D + 12)y = 0 A. y = c1e-2x + c2e¬0.4x + c3e3x + Cze-0.4x + Cze3* B. y = c¡e2x + c2e0.2x + C3e¬3x + Cze-3x C. y = c1e2* + c2e0.4% + C3e¬3* + Cze" D. y = ce-2x + c2e¬0.2x + C3e3x -3x + Cze + Cze3¤
Algebra for College Students
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285195780
Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Chapter13: Conic Sections
Section13.1: Circles
Problem 48PS
Related questions
Question
Answer the following homogeneous linear differential equations.
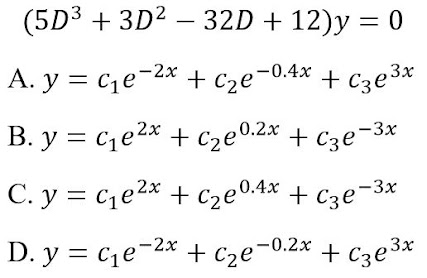
Transcribed Image Text:(5D3 + 3D2 — 32D + 12)у — 0
|
A. y = ce-2x + cze¬0.4x + C3e3*
+ Cze
B. y = c,e2* + cze0.2x
+ Cze-3x
C. y = ce2* + cze0.4* + C3e°
-3*
+ Cze0.4x
+ Cze*
%3D
D. y = ce-2* + cze¬02
-0.2x + Cze³*
+ Cze3*
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra for College Students
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195780
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning