B3-QRT63: PERSON IN AN ELEVATOR-SCALE READING 11. person who weighs 500 N is standing on a scale in an elevator. The elevator is identical in all cases. The velocity and acceleration of the elevators at the instant shown are given. A レ=3m/s wv 2 m/s v= 3 m/s v= 1 m/s a=2 m/s? a=2 m/s2 a = 0 a=2 m/s2 F H. v33 m/s v = 3 m/s v= 3 m/s レ=0 a=2 m/s2 a=2 m/s2 a = 0 a= 9.8 m/s2 (a) List the cases where the scale reading is greater than 500 N. Explain your reasoning. (b) List the cases where the scale reading is less than 500 N. Explain your reasoning. (c) List the cases when the scale reading is equal to the scale reading of 500 N. Explain your reasoning. E
B3-QRT63: PERSON IN AN ELEVATOR-SCALE READING 11. person who weighs 500 N is standing on a scale in an elevator. The elevator is identical in all cases. The velocity and acceleration of the elevators at the instant shown are given. A レ=3m/s wv 2 m/s v= 3 m/s v= 1 m/s a=2 m/s? a=2 m/s2 a = 0 a=2 m/s2 F H. v33 m/s v = 3 m/s v= 3 m/s レ=0 a=2 m/s2 a=2 m/s2 a = 0 a= 9.8 m/s2 (a) List the cases where the scale reading is greater than 500 N. Explain your reasoning. (b) List the cases where the scale reading is less than 500 N. Explain your reasoning. (c) List the cases when the scale reading is equal to the scale reading of 500 N. Explain your reasoning. E
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter4: Forces In One Dimension
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6STP
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
A person who weighs 500 N is standing on a scale in an elevator. The elevator is identical in all cases. The velocity and acceleration of the elevators a the instant shown are given.
a)
b)
c)
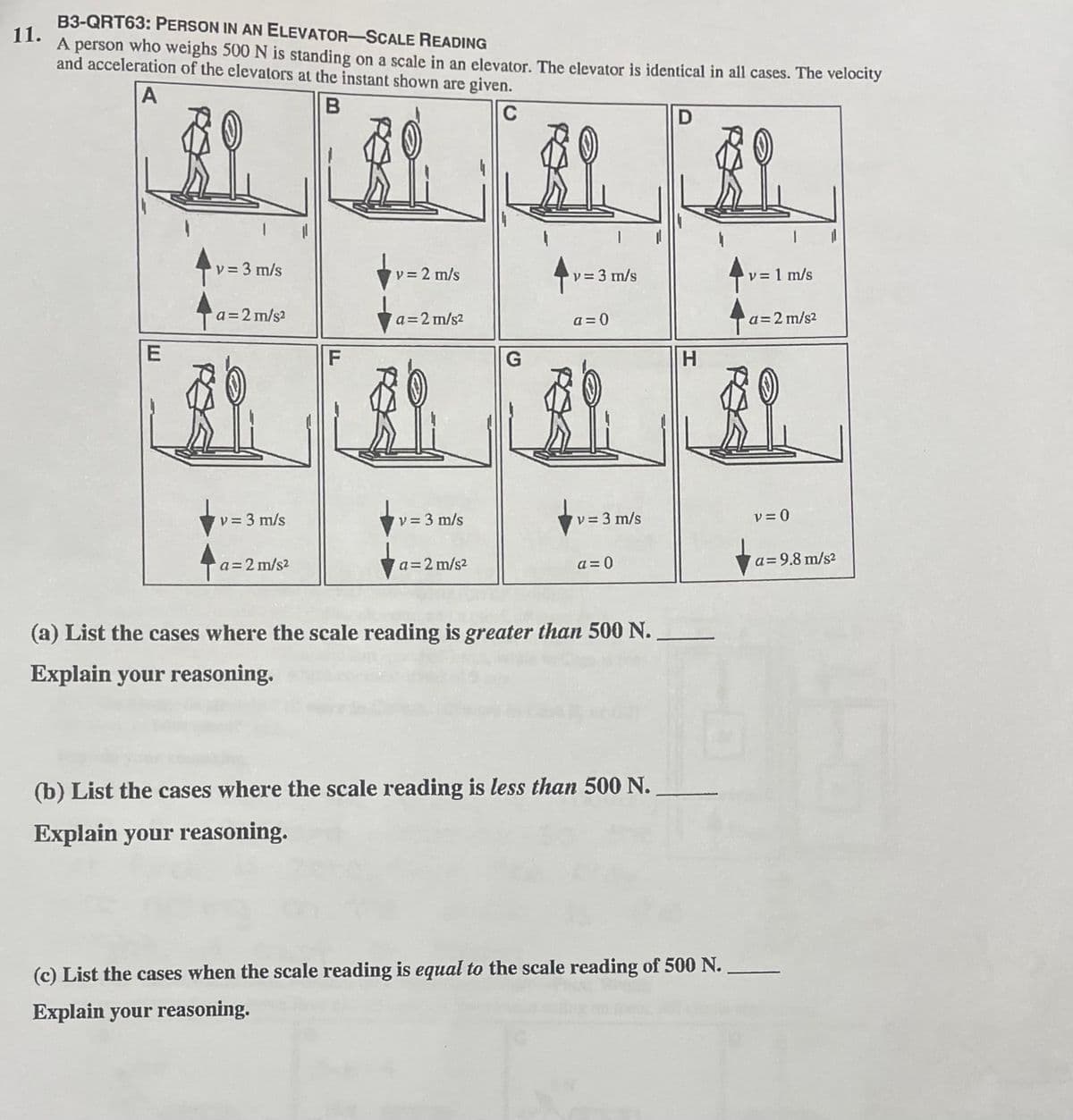
Transcribed Image Text:B3-QRT63: PERSON IN AN ELEVATOR-SCALE READING
11.
A person who weighs 500 N is standing on a scale in an elevator. The elevator is identical in all cases. The velocity
and acceleration of the elevators at the instant shown are given.
A
C
D
v = 3 m/s
v = 2 m/s
v= 3 m/s
v = 1 m/s
%3D
a = 2 m/s?
a=2 m/s?
a = 0
a=2 m/s2
H.
v= 3 m/s
v = 3 m/s
v = 3 m/s
v = 0
a=2 m/s2
a = 0
a=9.8 m/s?
a=2 m/s2
(a) List the cases where the scale reading is greater than 500 N.
Explain your reasoning.
(b) List the cases where the scale reading is less than 500 N.
Explain your reasoning.
(c) List the cases when the scale reading is equal to the scale reading of 500 N.
Explain your reasoning.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill