c) Now suppose that instead of using a sales tax the mayor decides to use an income tax of 5% or $100 per person. Write out the new budget constraint in recalculate the demand functions. d) Does the mayor achieve her desired tax revenue? e) Calculate the utility under this scenario. which tax are residents better off under?
c) Now suppose that instead of using a sales tax the mayor decides to use an income tax of 5% or $100 per person. Write out the new budget constraint in recalculate the demand functions. d) Does the mayor achieve her desired tax revenue? e) Calculate the utility under this scenario. which tax are residents better off under?
Principles of Microeconomics
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter12: The Design Of The Tax System
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4PA
Related questions
Question
The question is in the attached image. Please note to only complete sections D and E. ignore a,b and c
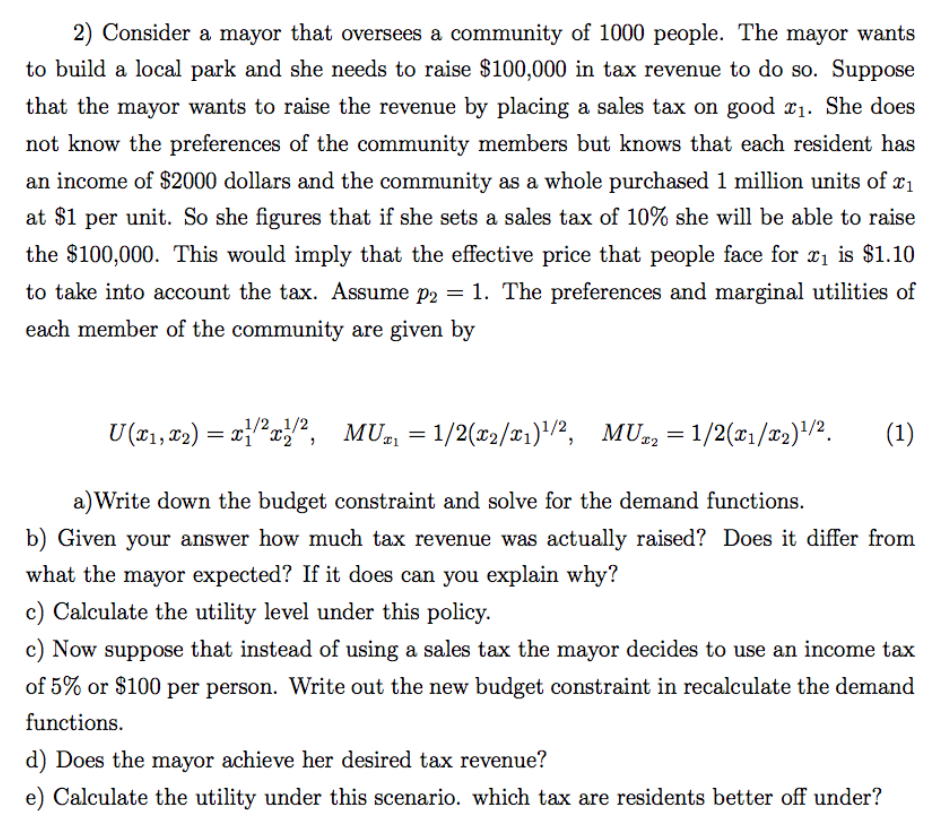
Transcribed Image Text:2) Consider a mayor that oversees a community of 1000 people. The mayor wants
to build a local park and she needs to raise $100,000 in tax revenue to do so. Suppose
that the mayor wants to raise the revenue by placing a sales tax on good ¤1. She does
not know the preferences of the community members but knows that each resident has
an income of $2000 dollars and the community as a whole purchased 1 million units of x1
at $1 per unit. So she figures that if she sets a sales tax of 10% she will be able to raise
the $100,000. This would imply that the effective price that people face for xı is $1.10
to take into account the tax. Assume p2 = 1. The preferences and marginal utilities of
each member of the community are given
U (®1, 22) = x}"x", MU-, =1/2(x2/&1)!/2,
„1/21/2
MUz2 = 1/2(x1/x2)/2.
(1)
a)Write down the budget constraint and solve for the demand functions.
b) Given your answer how much tax revenue was actually raised? Does it differ from
what the mayor expected? If it does can you explain why?
c) Calculate the utility level under this policy.
c) Now suppose that instead of using a sales tax the mayor decides to use an income tax
of 5% or $100 per person. Write out the new budget constraint in recalculate the demand
functions.
d) Does the mayor achieve her desired tax revenue?
e) Calculate the utility under this scenario. which tax are residents better off under?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning