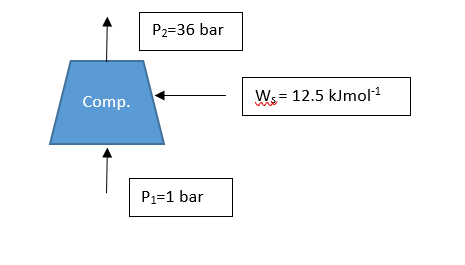
Carbon dioxide gas enters a water-cooled compressor at conditions P1 = 1 bar and T1 = 10 °C, and is discharged at conditions P2 = 36 bar and T2 = 90 °C. The entering CO2 flows through a 10-cm-diameter pipe with an average velocity of 10 m⋅s−1, and is discharged through a 3-cm-diameter pipe. The power supplied to the compressor is 12.5 kJ.mol−1. What is the heat-transfer rate from the compressor?
Carbon dioxide gas enters a water-cooled compressor at conditions P1 = 1 bar and T1 = 10 °C, and is discharged at conditions P2 = 36 bar and T2 = 90 °C. The entering CO2 flows through a 10-cm-diameter pipe with an average velocity of 10 m⋅s−1, and is discharged through a 3-cm-diameter pipe. The power supplied to the compressor is 12.5 kJ.mol−1. What is the heat-transfer rate from the compressor?
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Chapter7: Tubing And Piping
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2RQ: The size of 1/2 in. would refer to the ______regard to copper tubing used in plumbing and heating....
Related questions
Question
Carbon dioxide gas enters a water-cooled compressor at conditions P1 = 1 bar and T1 = 10 °C, and is discharged at conditions P2 = 36 bar and T2 = 90 °C. The entering CO2 flows through a 10-cm-diameter pipe with an average velocity of 10 m⋅s−1, and is discharged through a 3-cm-diameter pipe. The power supplied to the compressor is 12.5 kJ.mol−1. What is the heat-transfer rate from the compressor?
H1 = 21.71 kJ.mol−1 V1 = 23.40 L.mol−1
H2 = 23.78 kJ.mol−1 V2 = 0.7587 L.mol−1
Transcribed Image Text:P2=36 bar
W = 12.5 kJmol1
Comp.
P1=1 bar
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning