Cellular Metabolism Extension Examine the diagram and answer the questions below. GLYCOLYSIS glycine, serine, alanine, cysteine, threonine pyruvate asparagine acetyl CoA aspartate phenylalanine tyrosine L-malate fumarate fatty acyl CoA from fatty acids leucine, lysine, tryptophan, isocitrate .. CO₂ alpha ketoglutarate succinyl CoA CO₂ glutamate glutamine histidine, proline, arginine 4) In the diagram above, identify all the amino acids and underline or highlight in blue. 5) In the diagram above, identify all the carbon-containing molecules of normal glucose catabolism and underline or highlight in red. 6) In the diagram above, identify the molecule names related to fatty acids and underline o highlight in yellow In the diagram above, the dashed line arrows symbolize reactions that are caused when one of the reactions in this diagram is disrupted. Q Using the internet, look up each disorder below and label it on the diagram in green. Draw an X over the reaction (arrow) that is disrupted and write the name of the disorder beside the X. 7. Phenylketonuria (PKU) 8. Maple Syrup Urine Disease 9. "polygamist Down's" or Fumarase deficiency 10. Medium-chain-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency. 1) Define catabolism: 2) Define anabolism: 3) Define metabolism: CO oxaloacetate succinate valine, isoleucine, methionine, cholesterol, odd chain fatty acids citrate Normal Glucose Catabolism Catabolism of other molecules
Cellular Metabolism Extension Examine the diagram and answer the questions below. GLYCOLYSIS glycine, serine, alanine, cysteine, threonine pyruvate asparagine acetyl CoA aspartate phenylalanine tyrosine L-malate fumarate fatty acyl CoA from fatty acids leucine, lysine, tryptophan, isocitrate .. CO₂ alpha ketoglutarate succinyl CoA CO₂ glutamate glutamine histidine, proline, arginine 4) In the diagram above, identify all the amino acids and underline or highlight in blue. 5) In the diagram above, identify all the carbon-containing molecules of normal glucose catabolism and underline or highlight in red. 6) In the diagram above, identify the molecule names related to fatty acids and underline o highlight in yellow In the diagram above, the dashed line arrows symbolize reactions that are caused when one of the reactions in this diagram is disrupted. Q Using the internet, look up each disorder below and label it on the diagram in green. Draw an X over the reaction (arrow) that is disrupted and write the name of the disorder beside the X. 7. Phenylketonuria (PKU) 8. Maple Syrup Urine Disease 9. "polygamist Down's" or Fumarase deficiency 10. Medium-chain-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency. 1) Define catabolism: 2) Define anabolism: 3) Define metabolism: CO oxaloacetate succinate valine, isoleucine, methionine, cholesterol, odd chain fatty acids citrate Normal Glucose Catabolism Catabolism of other molecules
Basic Clinical Laboratory Techniques 6E
6th Edition
ISBN:9781133893943
Author:ESTRIDGE
Publisher:ESTRIDGE
Chapter6: Basic Clinical Chemistry
Section6.5: Blood Glucose And Hemoglobin A1c
Problem 20RQ
Related questions
Question
Can u help solve questions 7-11? Please and thank you
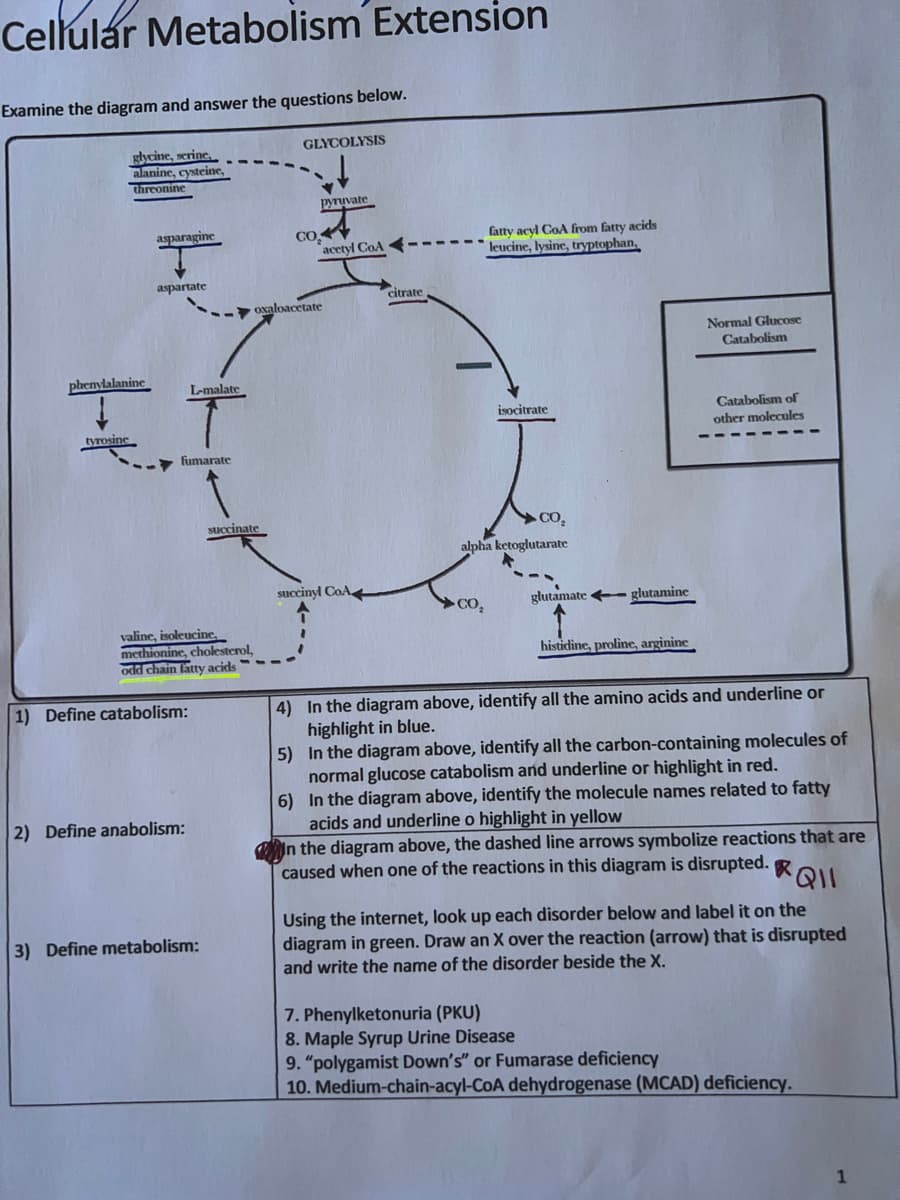
Transcribed Image Text:Cellular Metabolism Extension
Examine the diagram and answer the questions below.
GLYCOLYSIS
glycine, serine,
alanine, cysteine,
threonine
pyruvate
asparagine
acetyl CoA
aspartate
phenylalanine
tyrosine
L-malate
fumarate
fatty acyl CoA from fatty acids
leucine, lysine, tryptophan,
isocitrate
..
CO₂
alpha ketoglutarate
succinyl CoA
CO₂
glutamate glutamine
histidine, proline, arginine
4) In the diagram above, identify all the amino acids and underline or
highlight in blue.
5)
In the diagram above, identify all the carbon-containing molecules of
normal glucose catabolism and underline or highlight in red.
6)
In the diagram above, identify the molecule names related to fatty
acids and underline o highlight in yellow
In the diagram above, the dashed line arrows symbolize reactions that are
caused when one of the reactions in this diagram is disrupted. Q
Using the internet, look up each disorder below and label it on the
diagram in green. Draw an X over the reaction (arrow) that is disrupted
and write the name of the disorder beside the X.
7. Phenylketonuria (PKU)
8. Maple Syrup Urine Disease
9. "polygamist Down's" or Fumarase deficiency
10. Medium-chain-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency.
1) Define catabolism:
2) Define anabolism:
3) Define metabolism:
CO
oxaloacetate
succinate
valine, isoleucine,
methionine, cholesterol,
odd chain fatty acids
citrate
Normal Glucose
Catabolism
Catabolism of
other molecules
1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

