Ch21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions of Acid Halides, Acid Anhydrides - Hydrolysis: Conversion into Carboxylic Acids RCOCI + H₂O RCO₂H + HCI - Conversion to Esters RCOCI + R'OH → RCO₂R' + HCI obs H₂O - Reduction (hydride attack, LiAIH4): Conversion into Alcohols (final product) CI 1) LIAIH4 2) H - Reaction with Grignard reagents, R-MgBr (1 equv. to ketone, or excess to alcohol) Reactions of Esters - Hydrolysis: Conversion of Esters into Carboxylic Acids by Aqueous Base (mechanism!) - Hydrolysis: Conversion of Esters into Carboxylic Acids by Aqueous Acid (mechanism!) NaOH, H₂O HCI, H₂O (A) (B)
Ch21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions of Acid Halides, Acid Anhydrides - Hydrolysis: Conversion into Carboxylic Acids RCOCI + H₂O RCO₂H + HCI - Conversion to Esters RCOCI + R'OH → RCO₂R' + HCI obs H₂O - Reduction (hydride attack, LiAIH4): Conversion into Alcohols (final product) CI 1) LIAIH4 2) H - Reaction with Grignard reagents, R-MgBr (1 equv. to ketone, or excess to alcohol) Reactions of Esters - Hydrolysis: Conversion of Esters into Carboxylic Acids by Aqueous Base (mechanism!) - Hydrolysis: Conversion of Esters into Carboxylic Acids by Aqueous Acid (mechanism!) NaOH, H₂O HCI, H₂O (A) (B)
Chapter21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
Section21.SE: Something Extra
Problem 75AP: One frequently used method for preparing methyl esters is by reaction of carboxylic acids with...
Related questions
Question
Please complete boxed reactions. Thanks. P.s. this is not graded work but a study guide.
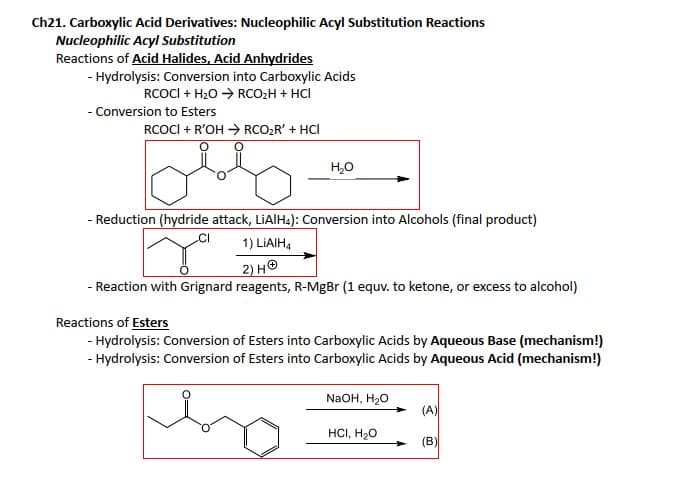
Transcribed Image Text:Ch21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
Reactions of Acid Halides, Acid Anhydrides
- Hydrolysis: Conversion into Carboxylic Acids
RCOCI+ H₂O → RCO₂H + HCI
- Conversion to Esters
RCOCI + R'OH → RCO₂R' + HCI
H₂O
- Reduction (hydride attack, LiAlH4): Conversion into Alcohols (final product)
1) LIAIH4
+
2) H
- Reaction with Grignard reagents, R-MgBr (1 equv. to ketone, or excess to alcohol)
Reactions of Esters
- Hydrolysis: Conversion of Esters into Carboxylic Acids by Aqueous Base (mechanism!)
- Hydrolysis: Conversion of Esters into Carboxylic Acids by Aqueous Acid (mechanism!)
NaOH, H₂O
HCI, H₂O
(A)
(B)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285869759
Author:
Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning