Chapter 10 Homework Depreciation by Three Methods; Partial Years Perdue Company purchased equipment on April 1 for $270,000. The equipment was expected to have a useful life of three years or 18,000 operating hours, and a residual value of $9,000. The equipment was used for 7,500 hours during Year 1, 5,500 hours in Year 2, 4,000 hours in Year 3, and 1,000 hours in Year 4. Required: Determine the amount of depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, and Year 4, by (a) the straight-line method, (b) units-of-activity method, and (c) the double-declining-balance method. Note: FOR DECLINING BALANCE ONLY, round the answer for each year to the nearest whole dollar. a. Straight-line method Year Amount Year 1 87,000 X Year 2 %24 87,000 Year 3 87,000 Year 4 b. Units-of-activity method Year Amount Year 1 $ 108,750 Year 2 79,750 V Year 3 58,000 Year 4 14,500 c. Double-declining-balance Method Year Amount Year 1 $ 179,982 x Year 2 %24 59,998 X Year 3 %24 19,994 Year 4 6,664 Feedback Check My Work a. Asset cost minus residual value equals depreciable cost. Sum the yearly depreciation to determine total depreciation. b. Annual units-of-activity depreciation allocates the cost of the asset equally over the units produced (hours). c. The double-declining rate is two times the straight-line rate. Book value is the asset cost minus accumulated depreciation. Compare the total depreciation for all methods over the time period. Recall that straight-line depreciation allocates the depreciable cost of the asset equally over the period of use, while double-declining method is an accelerated method.
Chapter 10 Homework Depreciation by Three Methods; Partial Years Perdue Company purchased equipment on April 1 for $270,000. The equipment was expected to have a useful life of three years or 18,000 operating hours, and a residual value of $9,000. The equipment was used for 7,500 hours during Year 1, 5,500 hours in Year 2, 4,000 hours in Year 3, and 1,000 hours in Year 4. Required: Determine the amount of depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, and Year 4, by (a) the straight-line method, (b) units-of-activity method, and (c) the double-declining-balance method. Note: FOR DECLINING BALANCE ONLY, round the answer for each year to the nearest whole dollar. a. Straight-line method Year Amount Year 1 87,000 X Year 2 %24 87,000 Year 3 87,000 Year 4 b. Units-of-activity method Year Amount Year 1 $ 108,750 Year 2 79,750 V Year 3 58,000 Year 4 14,500 c. Double-declining-balance Method Year Amount Year 1 $ 179,982 x Year 2 %24 59,998 X Year 3 %24 19,994 Year 4 6,664 Feedback Check My Work a. Asset cost minus residual value equals depreciable cost. Sum the yearly depreciation to determine total depreciation. b. Annual units-of-activity depreciation allocates the cost of the asset equally over the units produced (hours). c. The double-declining rate is two times the straight-line rate. Book value is the asset cost minus accumulated depreciation. Compare the total depreciation for all methods over the time period. Recall that straight-line depreciation allocates the depreciable cost of the asset equally over the period of use, while double-declining method is an accelerated method.
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter11: Depreciation, Depletion, Impairment, And Disposal
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20E: (Appendix 11.1) Depreciation for Financial Statements and Income Tax Purposes Dinkle Company...
Related questions
Question
About half of the answers I get back from this website are incorrect. Here are the answers I was given. I need the correct answers instead. I shouldn't have to use up more questions just to get the right answer.
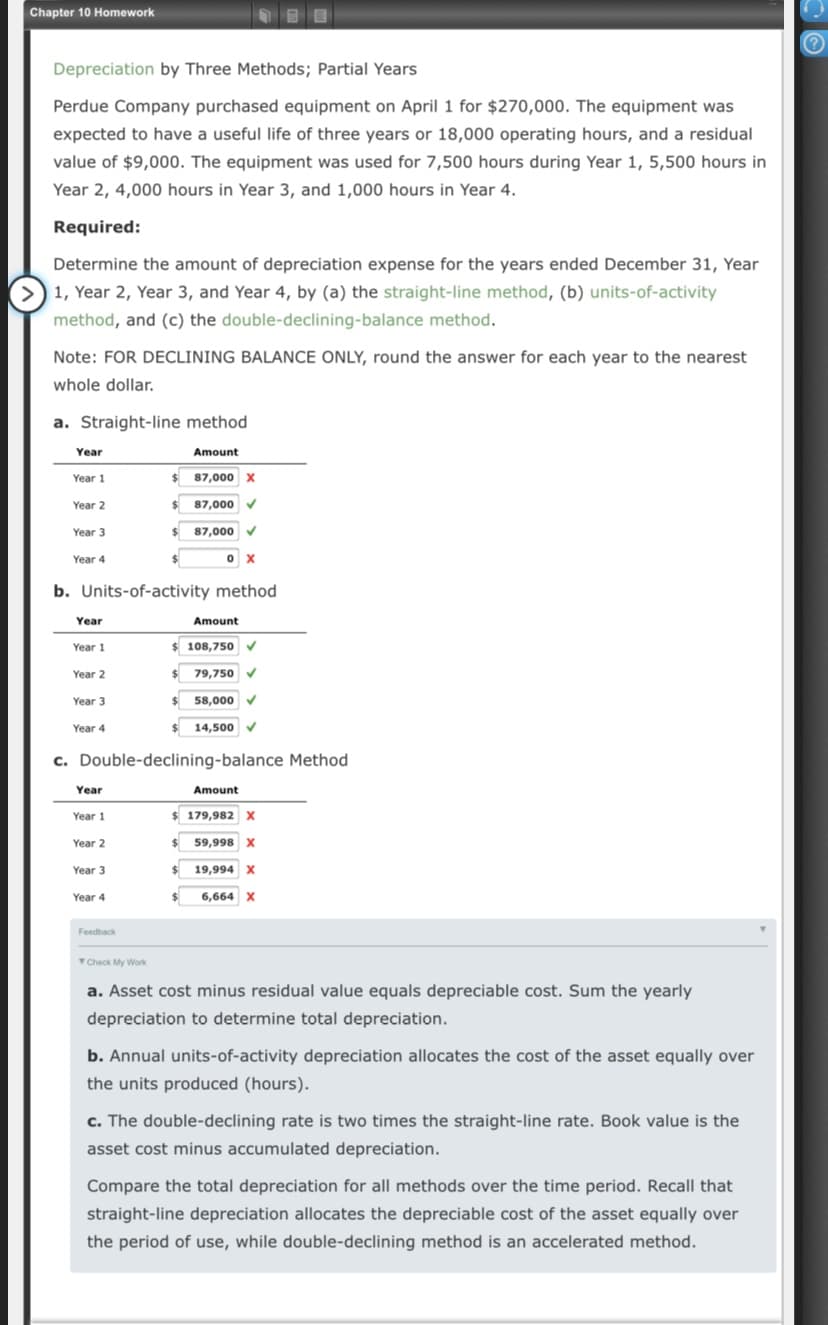
Transcribed Image Text:Chapter 10 Homework
Depreciation by Three Methods; Partial Years
Perdue Company purchased equipment on April 1 for $270,000. The equipment was
expected to have a useful life of three years or 18,000 operating hours, and a residual
value of $9,000. The equipment was used for 7,500 hours during Year 1, 5,500 hours in
Year 2, 4,000 hours in Year 3, and 1,000 hours in Year 4.
Required:
Determine the amount of depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, Year
1, Year 2, Year 3, and Year 4, by (a) the straight-line method, (b) units-of-activity
method, and (c) the double-declining-balance method.
Note: FOR DECLINING BALANCE ONLY, round the answer for each year to the nearest
whole dollar.
a. Straight-line method
Year
Amount
Year 1
87,000 X
Year 2
%24
87,000
Year 3
87,000
Year 4
b. Units-of-activity method
Year
Amount
Year 1
$ 108,750
Year 2
79,750 V
Year 3
58,000
Year 4
14,500
c. Double-declining-balance Method
Year
Amount
Year 1
$ 179,982 x
Year 2
%24
59,998 X
Year 3
%24
19,994
Year 4
6,664
Feedback
Check My Work
a. Asset cost minus residual value equals depreciable cost. Sum the yearly
depreciation to determine total depreciation.
b. Annual units-of-activity depreciation allocates the cost of the asset equally over
the units produced (hours).
c. The double-declining rate is two times the straight-line rate. Book value is the
asset cost minus accumulated depreciation.
Compare the total depreciation for all methods over the time period. Recall that
straight-line depreciation allocates the depreciable cost of the asset equally over
the period of use, while double-declining method is an accelerated method.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning