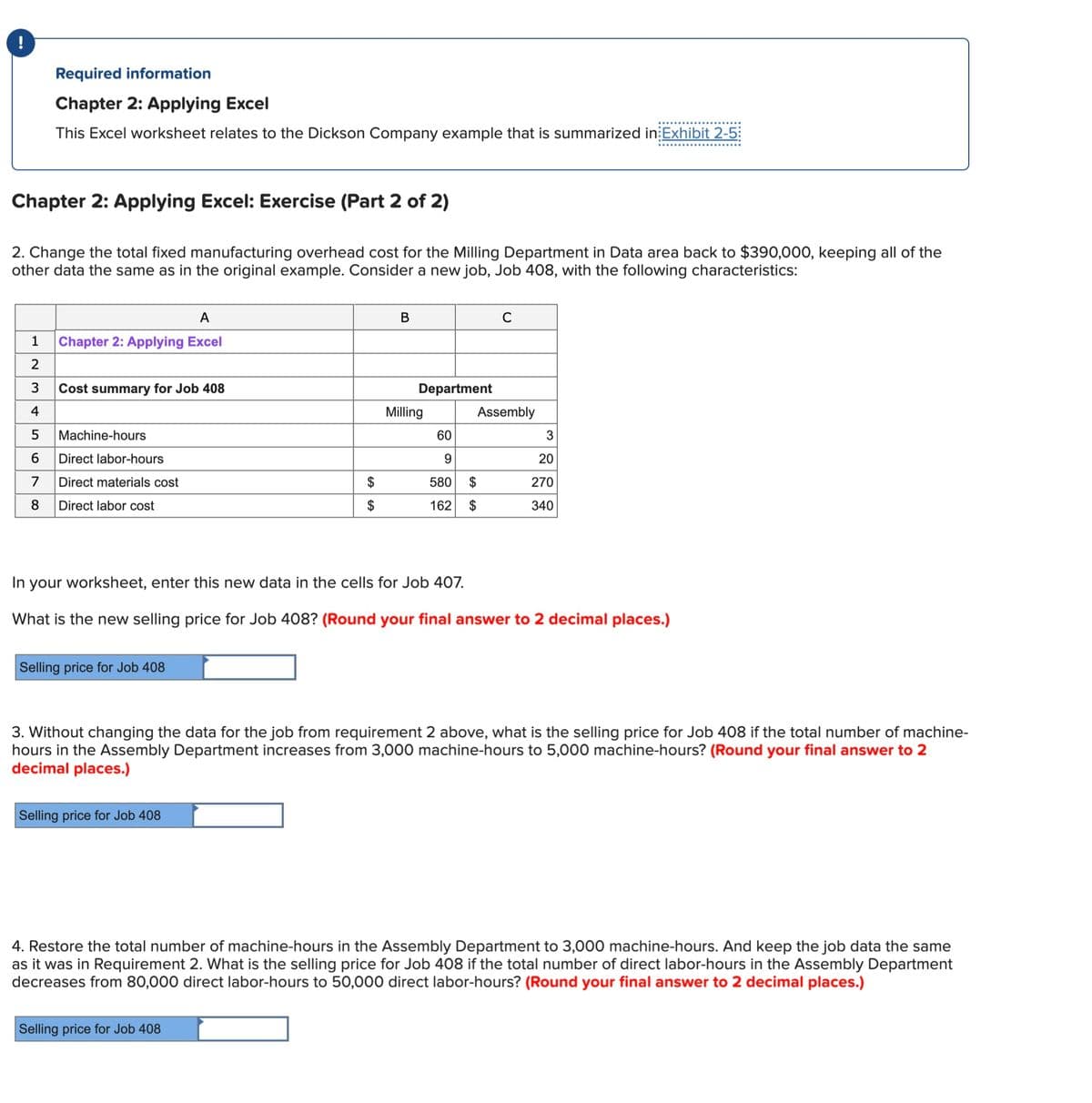
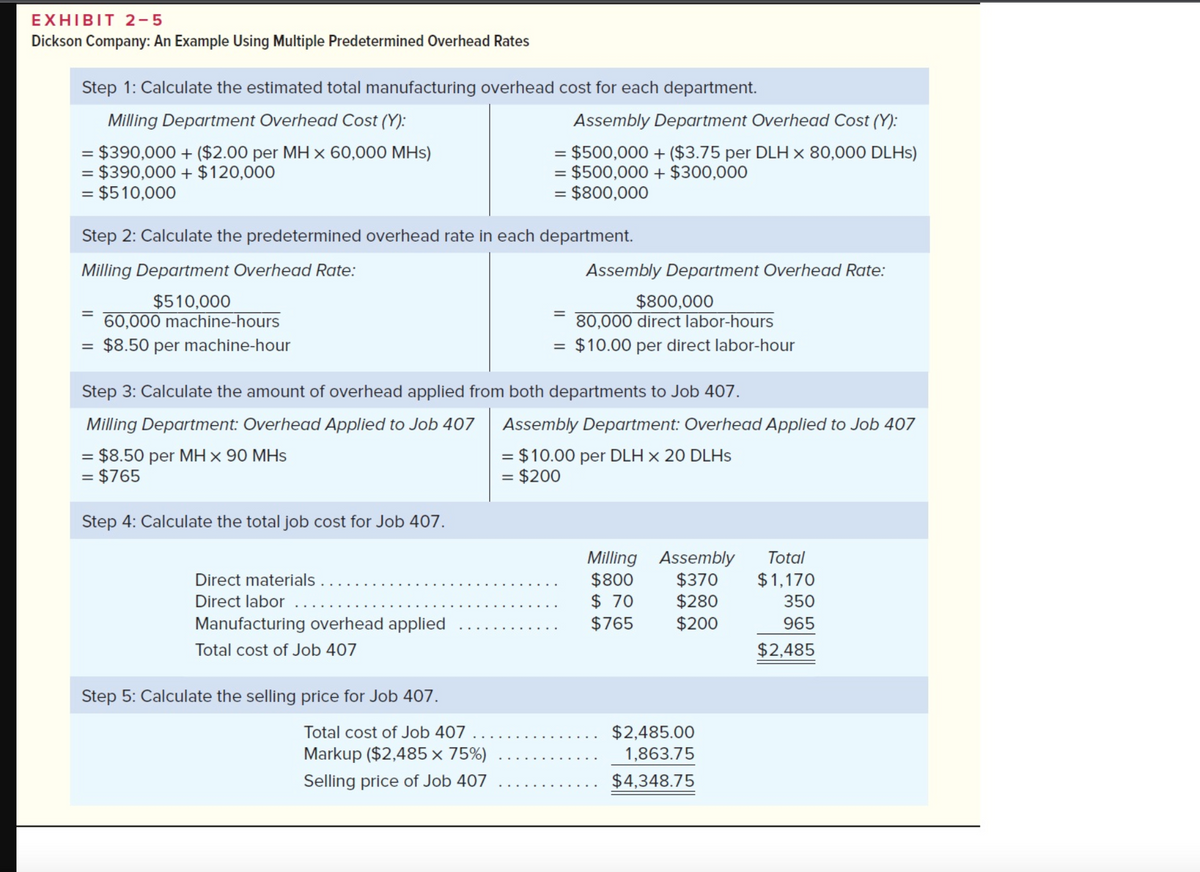
Chapter 2: Applying Excel: Exercise (Part 2 of 2) 2. Change the total fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the Milling Department in Data area back to $390,000, keeping all of the other data the same as in the original example. Consider a new job, Job 408, with the following characteristics: 1 2 3 4 A Chapter 2: Applying Excel Cost summary for Job 408 5 6 7 8 Direct labor cost Machine-hours Direct labor-hours Direct materials cost Selling price for Job 408 $ $ Selling price for Job 408 B Department Selling price for Job 408 Milling C Assembly 60 9 580 $ 162 $ In your worksheet, enter this new data in the cells for Job 407. What is the new selling price for Job 408? (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) 3 20 270 340 3. Without changing the data for the job from requirement 2 above, what is the selling price for Job 408 if the total number of machine- hours in the Assembly Department increases from 3,000 machine-hours to 5,000 machine-hours? (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) 4. Restore the total number of machine-hours in the Assembly Department to 3,000 machine-hours. And keep the job data the same as it was in Requirement 2. What is the selling price for Job 408 if the total number of direct labor-hours in the Assembly Department decreases from 80,000 direct labor-hours to 50,000 direct labor-hours? (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.)
Process Costing
Process costing is a sort of operation costing which is employed to determine the value of a product at each process or stage of producing process, applicable where goods produced from a series of continuous operations or procedure.
Job Costing
Job costing is adhesive costs of each and every job involved in the production processes. It is an accounting measure. It is a method which determines the cost of specific jobs, which are performed according to the consumer’s specifications. Job costing is possible only in businesses where the production is done as per the customer’s requirement. For example, some customers order to manufacture furniture as per their needs.
ABC Costing
Cost Accounting is a form of managerial accounting that helps the company in assessing the total variable cost so as to compute the cost of production. Cost accounting is generally used by the management so as to ensure better decision-making. In comparison to financial accounting, cost accounting has to follow a set standard ad can be used flexibly by the management as per their needs. The types of Cost Accounting include – Lean Accounting, Standard Costing, Marginal Costing and Activity Based Costing.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps




