Consider the following equilibrium: 2NH₂ (g) N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) AG = 34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 2.49 atm of ammonia (NH3) and 4.30 atm of nitrogen (N₂) at 973. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N, tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N, will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H₂? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N, will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. O rise O fall O yes O no x10 X
Consider the following equilibrium: 2NH₂ (g) N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) AG = 34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 2.49 atm of ammonia (NH3) and 4.30 atm of nitrogen (N₂) at 973. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N, tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N, will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H₂? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N, will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. O rise O fall O yes O no x10 X
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter13: Fundamental Equilibrium Concepts
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 90E: In a 3.0-L vessel, the following equilibrium partial pressures are measured: N2, 190 torr; H2, 317...
Related questions
Question
100%
I am trying to help my child with homework and I am unsure how to explain this. Please help.
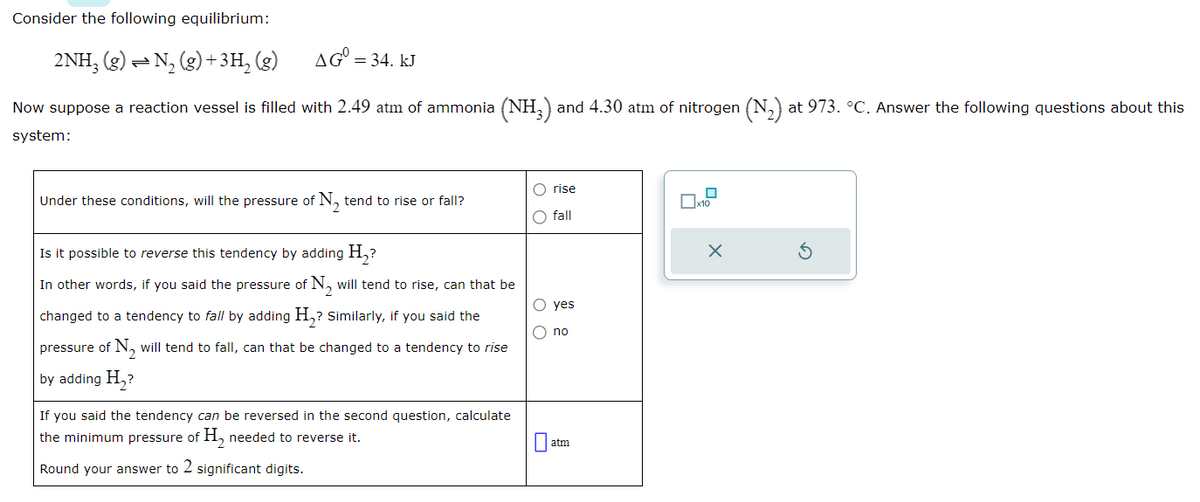
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following equilibrium:
2NH3(g) = N₂(g) + 3H₂(g)
Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 2.49 atm of ammonia (NH3) and 4.30 atm of nitrogen (N₂) at 973. °C. Answer the following questions about this
system:
AG = 34. kJ
Under these conditions, will the pressure of N₂ tend to rise or fall?
Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂?
In other words, if you said the pressure of N₂ will tend to rise, can that be
changed to a tendency to fall by adding H₂? Similarly, if you said the
pressure of N₂ will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise
by adding H₂?
If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate
the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it.
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
O rise
O fall
O yes
O no
atm
0
x10
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning