Consider the following reaction CH3CH2CO,CH2CH3 (g) H20 (g) CH;CH,CO>H (g) CH;CH2OH (g) Kp = 0.236 at 398 K a) A reaction mixture initially contains a CH3CH2CO2CH2CH3 with a partial pressure of 1255 mbar and a H2O with partial pressure of 1255 mbar at 398 K. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of each of the products and reactants. Hint: The x is small assumption is not valid here because K is close to unity. There is another way to avoid the quadratic equation. b) What is Ke at 398 K?
Consider the following reaction CH3CH2CO,CH2CH3 (g) H20 (g) CH;CH,CO>H (g) CH;CH2OH (g) Kp = 0.236 at 398 K a) A reaction mixture initially contains a CH3CH2CO2CH2CH3 with a partial pressure of 1255 mbar and a H2O with partial pressure of 1255 mbar at 398 K. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of each of the products and reactants. Hint: The x is small assumption is not valid here because K is close to unity. There is another way to avoid the quadratic equation. b) What is Ke at 398 K?
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter17: Spontaneity, Entropy, And Free Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 121CP: If wet silver carbonate is dried in a stream of hot air. the air must have a certain concentration...
Related questions
Question
CONSIDER THE FOLLOWING REACTION IN THE IMAGE BELOW
a) A reaction mixture initially contains a CHaCH2CO2CH2CH3 with a partial pressure of 1255 mbar and a H20 with
partial pressure of 1255 mbar at 398 K. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of each of the products and
reactants.
Hint: The x is small assumption is not valid here because K is close to unity. There is another way to avoid the
quadratic equation.
b) What is Ke at 398 K?
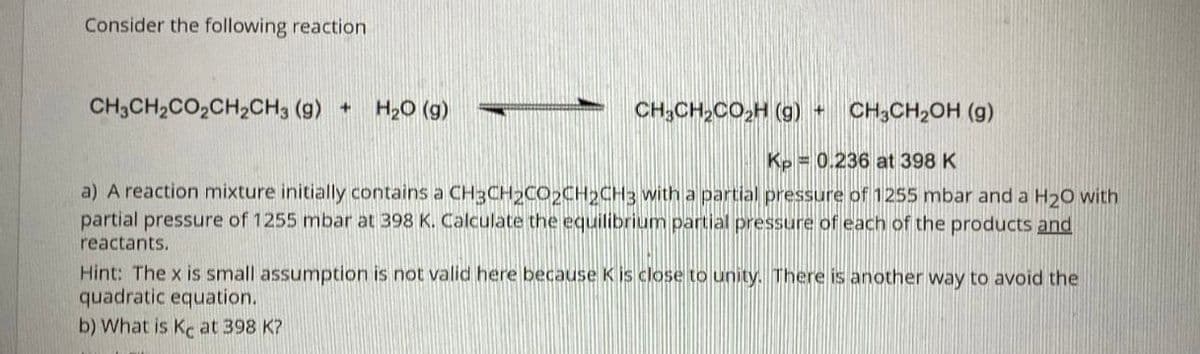
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following reaction
CH3CH2CO,CH2CH3 (g) +
H20 (g)
CH;CH,CO,H (g) +
CH;CH,OH (g)
Kp = 0.236 at 398 K
a) A reaction mixture initially contains a CH3CH2CO2CH2CH3 with a partial pressure of 1255 mbar and a H20 with
partial pressure of 1255 mbar at 398 K. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of each of the products and
reactants.
Hint: The x is small assumption is not valid here because K is close to unity. There is another way to avoid the
quadratic equation.
b) What is Kc at 398 K?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning