Consider the network shown below with the given link costs. Initially each node knows only its neighbors and cost of the links to them. The distance-vector routing (DV) algorithm is used to compute the least cost paths for all source-destination pairs. The network connectivity and link costs are stable. The routing updates occur in rounds. In an update round, each node updates all of its neighbors with the nodes it currently knows after the previous round and the distances to them. Match each of the statements or questions in the left column with the most appropriate response from the right column. V -W 9
Consider the network shown below with the given link costs. Initially each node knows only its neighbors and cost of the links to them. The distance-vector routing (DV) algorithm is used to compute the least cost paths for all source-destination pairs. The network connectivity and link costs are stable. The routing updates occur in rounds. In an update round, each node updates all of its neighbors with the nodes it currently knows after the previous round and the distances to them. Match each of the statements or questions in the left column with the most appropriate response from the right column. V -W 9
Operations Research : Applications and Algorithms
4th Edition
ISBN:9780534380588
Author:Wayne L. Winston
Publisher:Wayne L. Winston
Chapter20: Queuing Theory
Section20.10: Exponential Queues In Series And Open Queuing Networks
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
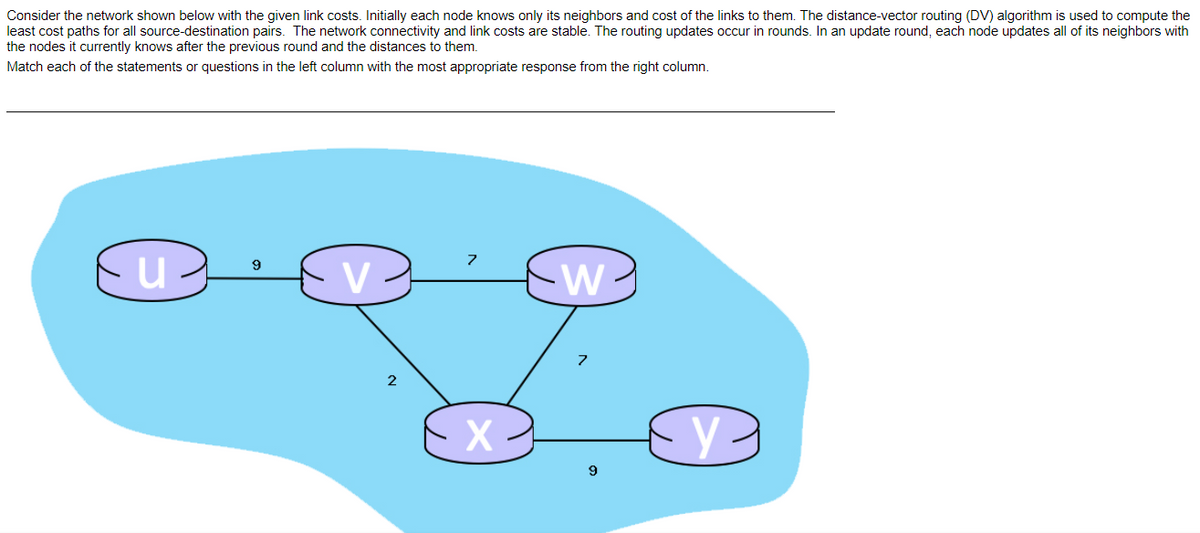
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the network shown below with the given link costs. Initially each node knows only its neighbors and cost of the links to them. The distance-vector routing (DV) algorithm is used to compute the
least cost paths for all source-destination pairs. The network connectivity and link costs are stable. The routing updates occur in rounds. In an update round, each node updates all of its neighbors with
the nodes it currently knows after the previous round and the distances to them.
Match each of the statements or questions in the left column with the most appropriate response from the right column.
2

Transcribed Image Text:v Initially, before any updates, node U knows distances to what other nodes?
v After one round of updates, U knows distances to what other nodes?
A. 3
B. Nodes V, W, and X
C. Nodes V, X, and Y
What is the number of rounds needed for U to know distances to all other nodes in the
network?
D. 2
v What is the least-cost path from U to Y?
E. Nodes V, W, and Y
F. Node V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Operations Research : Applications and Algorithms
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780534380588
Author:
Wayne L. Winston
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Operations Research : Applications and Algorithms
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780534380588
Author:
Wayne L. Winston
Publisher:
Brooks Cole