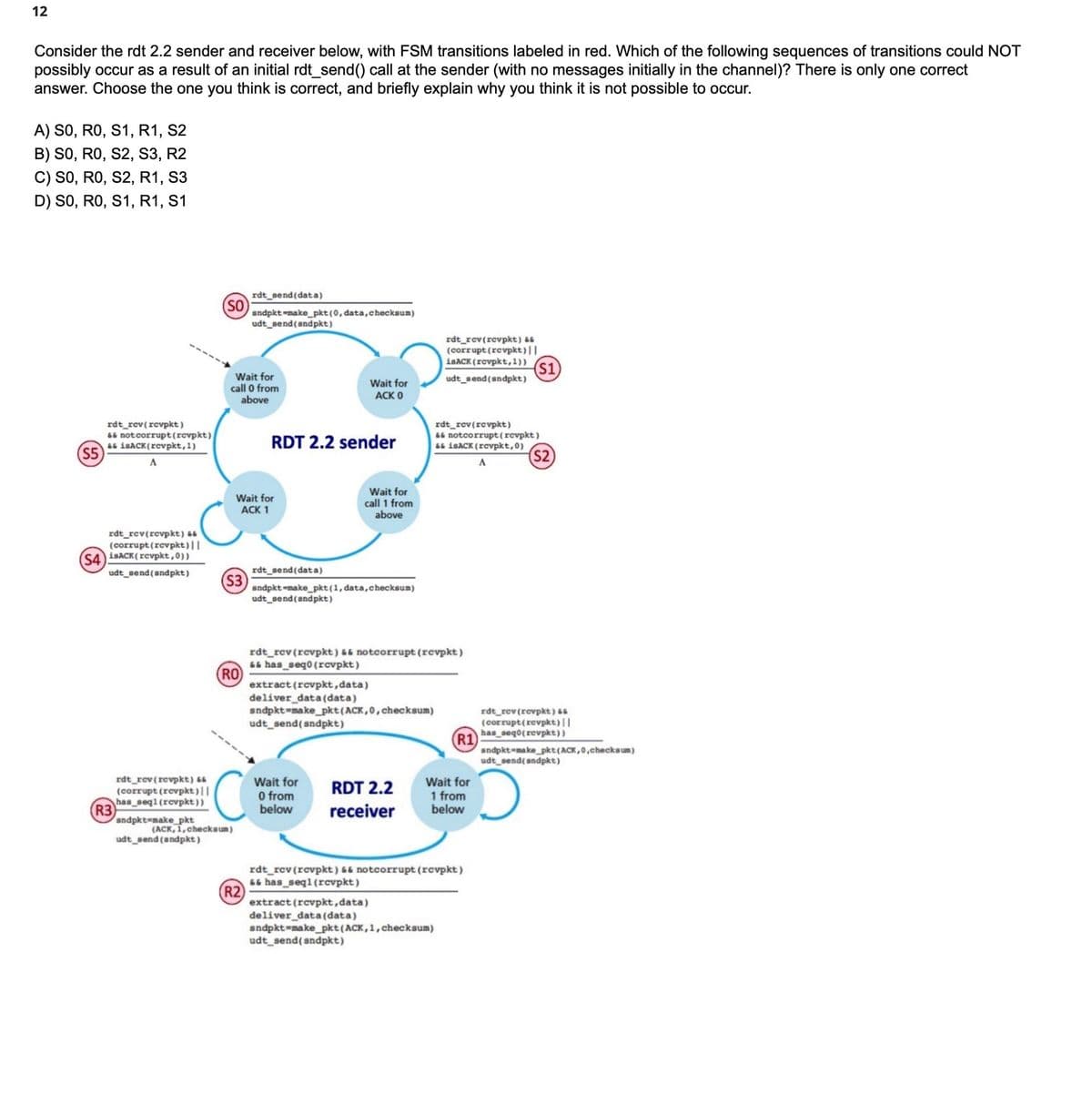
Consider the rdt 2.2 sender and receiver below, with FSM transitions labeled in red. Which of the following sequences of transitions could NOT possibly occur as a result of an initial rdt_send() call at the sender (with no messages initially in the channel)? There is only one correct answer. Choose the one you think is correct, and briefly explain why you think it is not possible to occur. A) SO, RO, S1, R1, S2 B) SO, RO, S2, S3, R2 C) SO, RO, S2, R1, S3 D) SO, RO, S1, R1, S1
Consider the rdt 2.2 sender and receiver below, with FSM transitions labeled in red. Which of the following sequences of transitions could NOT possibly occur as a result of an initial rdt_send() call at the sender (with no messages initially in the channel)? There is only one correct answer. Choose the one you think is correct, and briefly explain why you think it is not possible to occur. A) SO, RO, S1, R1, S2 B) SO, RO, S2, S3, R2 C) SO, RO, S2, R1, S3 D) SO, RO, S1, R1, S1
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PE
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:12
Consider the rdt 2.2 sender and receiver below, with FSM transitions labeled in red. Which of the following sequences of transitions could NOT
possibly occur as a result of an initial rdt_send() call at the sender (with no messages initially in the channel)? There is only one correct
answer. Choose the one you think is correct, and briefly explain why you think it is not possible to occur.
A) SO, RO, S1, R1, S2
B) SO, RO, S2, S3, R2
C) SO, RO, S2, R1, S3
D) SO, RO, S1, R1, S1
rdt_send(data)
sndpkt-make_pkt (0, data, checksum)
udt_send(sndpkt)
rdt_rev(revpkt) &&
(corrupt (revpkt)||
isACK (revpkt,1)) (S1)
udt_send(sndpkt)
Wait for
ACK 0
rdt_rev(revpkt)
&& not corrupt (revpkt)
&&isACK(revpkt, 1)
RDT 2.2 sender
A
Wait for
call 1 from
above
rdt_rev(revpkt) &&
(corrupt (revpkt)||
(S4) isACK(revpkt,0))
udt_send(sndpkt)
rdt_send(data)
sndpkt-make_pkt (1, data, checksum)
udt_send(sndpkt)
rdt_rev (revpkt) && notcorrupt (revpkt)
&&has_seq0 (revpkt)
extract (revpkt, data)
deliver_data (data)
sndpkt-make_pkt (ACK, 0, checksum)
udt_send(sndpkt)
Wait for
Wait for
RDT 2.2
rdt_rev(revpkt) &&
(corrupt (revpkt)||
has_seql (revpkt))
sndpkt-make_pkt
(ACK, 1, checksum)
udt_send (sndpkt)
0 from
below
1 from
below
receiver
rdt_rev (revpkt) && notcorrupt (revpkt)
&&has_seql (revpkt)
extract (revpkt, data)
deliver_data(data)
sndpkt-make_pkt (ACK, 1, checksum)
udt_send(sndpkt)
(S5)
(R3)
(SO)
Wait for
call 0 from
above
Wait for
ACK 1
(S3)
(RO)
C
(R2)
rdt_rev(revpkt)
&& notcorrupt (revpkt)
&& isACK (revpkt,0)
A
(R1)
(S2)
rdt_rev (revpkt) &&
(corrupt (revpkt) ||
has_seq0(revpkt))
sndpkt-make_pkt (ACK, 0, checksum)
udt_send(sndpkt)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780078022159
Author:
Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780134444321
Author:
Tony Gaddis
Publisher:
PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780132737968
Author:
Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:
PEARSON

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780078022159
Author:
Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780134444321
Author:
Tony Gaddis
Publisher:
PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780132737968
Author:
Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:
PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780133976892
Author:
Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337627900
Author:
Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education