Consider these three reactions as the elementary steps in the mechanism for a chemical reaction. (i) Cl2 (g) + Pt (s) à 2Cl (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 1550 kJ ∆H = – 950 kJ (ii) Cl (g)+ CO (g) + Pt (s) à ClCO (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 2240 kJ ∆H = 575 kJ (iii) Cl (g) + ClCO (g) à Cl2CO (g) Ea = 2350 kJ ∆H = – 825 kJ
Consider these three reactions as the elementary steps in the mechanism for a
(i) Cl2 (g) + Pt (s) à 2Cl (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 1550 kJ ∆H = – 950 kJ
(ii) Cl (g)+ CO (g) + Pt (s) à ClCO (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 2240 kJ ∆H = 575 kJ
(iii) Cl (g) + ClCO (g) à Cl2CO (g) Ea = 2350 kJ ∆H = – 825 kJ
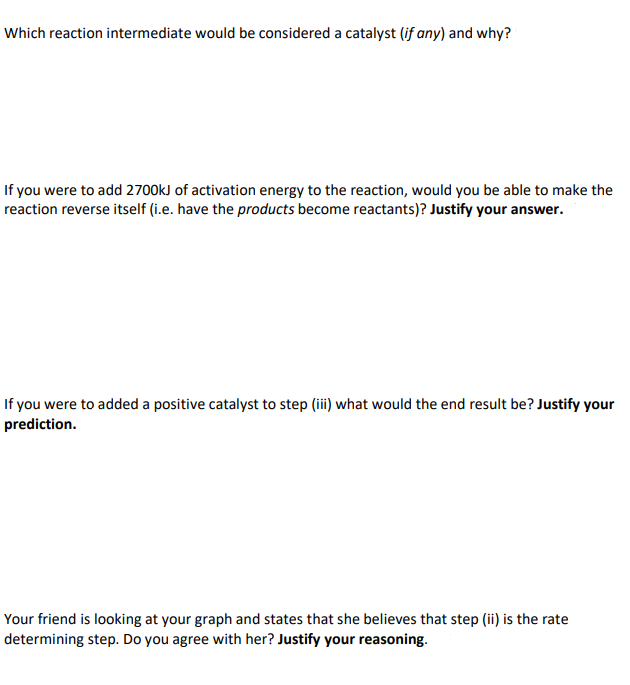
e. Which reaction intermediate would be considered a catalyst (if any) and why?
f. If you were to add 2700kJ of activation energy to the reaction, would you be able to make the
reaction reverse itself (i.e. have the products become reactants)? Justify your answer.
g. If you were to added a positive catalyst to step (iii) what would the end result be? Justify your
prediction.
h. Your friend is looking at your graph and states that she believes that step (ii) is the rate
determining step. Do you agree with her? Justify your reasoning.
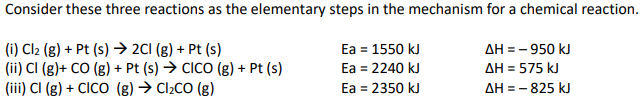
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









