d) How does the observed sound intensity compare between parts (a), (b), and (c)? Rank situations a, b, and c from loudest to quietest. e) From this point, how much farther would you have to move up the sliding section to reach the next minimum intensity situation?
Answer part D and E
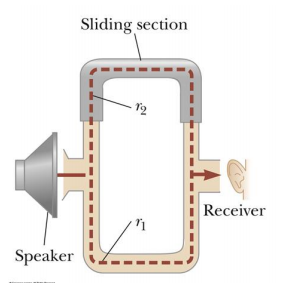
1) A sound wave of wavelength 20 cm is split into two equal parts that later recombine at the ear of the observer, as shown in the figure.
a) Initially, the upper path is the same length as the lower path, such that r2 – r1 = 0. At this point, is the interference between the two sound waves constructive, destructive, or something in between?
b) Now the sliding section is moved up by 5 cm (which extends path r2 by twice that). Is the interference between the two sound waves constructive, destructive, or something in between?
c) Next the sliding section is moved up by an additional 2.5 cm. Is the interference between the two sound waves constructive, destructive, or something in between?
d) How does the observed sound intensity compare between parts (a), (b), and (c)? Rank situations a, b, and c from loudest to quietest.
e) From this point, how much farther would you have to move up the sliding section to reach the next minimum intensity situation?
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps
