damaged. Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in c I with the following information for Dempsey Inc. for the month of January 2020. te y 1 y 5 y 8 y 10 15 Description Beginning inventory Purchase Sale Sale return Purchase Quantity 100 140 110 10 55 Unit Cost or Selling Price $15 18 28 28 20
damaged. Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in c I with the following information for Dempsey Inc. for the month of January 2020. te y 1 y 5 y 8 y 10 15 Description Beginning inventory Purchase Sale Sale return Purchase Quantity 100 140 110 10 55 Unit Cost or Selling Price $15 18 28 28 20
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
23rd Edition
ISBN:9781337794756
Author:HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:HEINTZ, James A.
Chapter12: Special Journals
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CE
Related questions
Question
P6.8, Can this question be done in excel? Thank you.
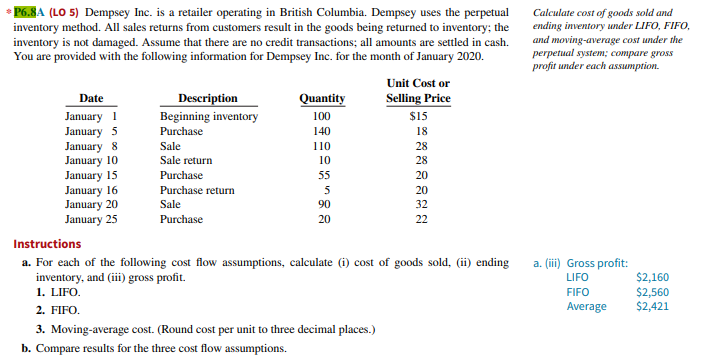
Transcribed Image Text:*P6.8A (LO 5) Dempsey Inc. is a retailer operating in British Columbia. Dempsey uses the perpetual
inventory method. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being returned to inventory; the
inventory is not damaged. Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in cash.
You are provided with the following information for Dempsey Inc. for the month of January 2020.
Date
January 1
January 5
January 8
January 10
January 15
January 16
January 20
January 25
Description
Beginning inventory
Purchase
Sale
Sale return
Purchase
Purchase return
Sale
Purchase
Quantity
100
140
110
10
55
5
90
20
Unit Cost or
Selling Price
3. Moving-average cost. (Round cost per unit to three decimal places.)
b. Compare results for the three cost flow assumptions.
$15
18
28
28
20
20
32
22
Instructions
a. For each of the following cost flow assumptions, calculate (i) cost of goods sold, (ii) ending
inventory, and (iii) gross profit.
1. LIFO.
2. FIFO.
Calculate cost of goods sold and
ending inventory under LIFO, FIFO,
and moving-average cost under the
perpetual system; compare gross
profit under each assumption.
a. (iii) Gross profit:
LIFO
FIFO
Average
$2,160
$2,560
$2,421
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,