Distinguish between active and passive sensors in terms of energy sour Hiagrams. A rotameter uses a cylindrical float of 3.5 cm height, 3.5 cm diameter a f the maximum inside diameter of the metering tube is 5 cm, calculat
Distinguish between active and passive sensors in terms of energy sour Hiagrams. A rotameter uses a cylindrical float of 3.5 cm height, 3.5 cm diameter a f the maximum inside diameter of the metering tube is 5 cm, calculat
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter7: Forced Convection Inside Tubes And Ducts
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.1P: 7.1 To measure the mass flow rate of a fluid in a laminar flow through a circular pipe, a...
Related questions
Question
Don't copy and paste chegg answers please
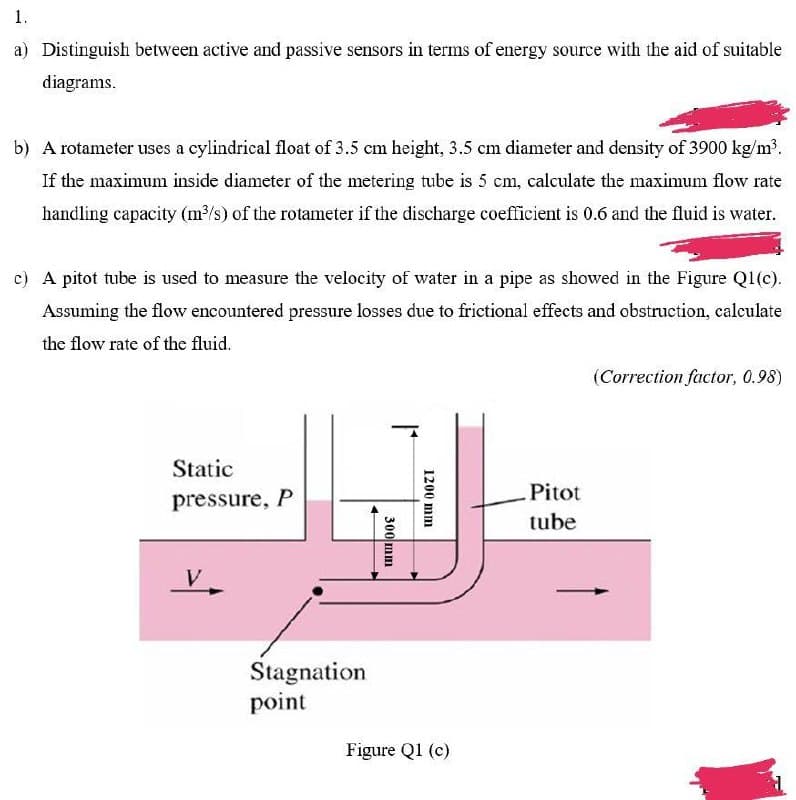
Transcribed Image Text:1.
a) Distinguish between active and passive sensors in terms of energy source with the aid of suitable
diagrams.
b) A rotameter uses a cylindrical float of 3.5 cm height, 3.5 cm diameter and density of 3900 kg/m³.
If the maximum inside diameter of the metering tube is 5 cm, calculate the maximum flow rate
handling capacity (m/s) of the rotameter if the discharge coefficient is 0.6 and the fluid is water.
c) A pitot tube is used to measure the velocity of water in a pipe as showed in the Figure Q1(c).
Assuming the flow encountered pressure losses due to frictional effects and obstruction, calculate
the flow rate of the fluid.
(Correction factor, 0.98)
Static
Pitot
pressure, P
tube
Stagnation
point
Figure Q1 (c)
1200 mm
300 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning