During inspiration, the volume of the lungs is actively increased by the action of the diaphragm. As the volume of the lungs increases, the pressure within the lungs falls about 1 mmHg below atmospheric pressure. Air rushes into the lungs due to this pressure difference. Bronchi, Bronchial Tree, and Lungs Larynx Primary bronchi Secondary bronchi Tertiary bronchi Bronchioles Cardiac notch Pulmonary artery Trachea Pulmonary vein Alveolar duct Alveoli This image is part of the Public Domain: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/db/Illu_bronchi lungs.jpg Fig. 1: The bronchi, bronchial trees, and the lungs. (a) The diameter of the trachea (windpipe) is about 17 mm. What net force does the air experience during inhalation? F = 0.03026 N net L (b) The flow rate of air entering the lungs is about 1.1 . What is the velocity of air moving S through the windpipe? ст windpipe 398.31 S
During inspiration, the volume of the lungs is actively increased by the action of the diaphragm. As the volume of the lungs increases, the pressure within the lungs falls about 1 mmHg below atmospheric pressure. Air rushes into the lungs due to this pressure difference. Bronchi, Bronchial Tree, and Lungs Larynx Primary bronchi Secondary bronchi Tertiary bronchi Bronchioles Cardiac notch Pulmonary artery Trachea Pulmonary vein Alveolar duct Alveoli This image is part of the Public Domain: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/db/Illu_bronchi lungs.jpg Fig. 1: The bronchi, bronchial trees, and the lungs. (a) The diameter of the trachea (windpipe) is about 17 mm. What net force does the air experience during inhalation? F = 0.03026 N net L (b) The flow rate of air entering the lungs is about 1.1 . What is the velocity of air moving S through the windpipe? ст windpipe 398.31 S
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter14: Fluid Mechanics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 92P: The arterioles (small arteries) leading to organ constrict in order to decrease flow to the organ....
Related questions
Question
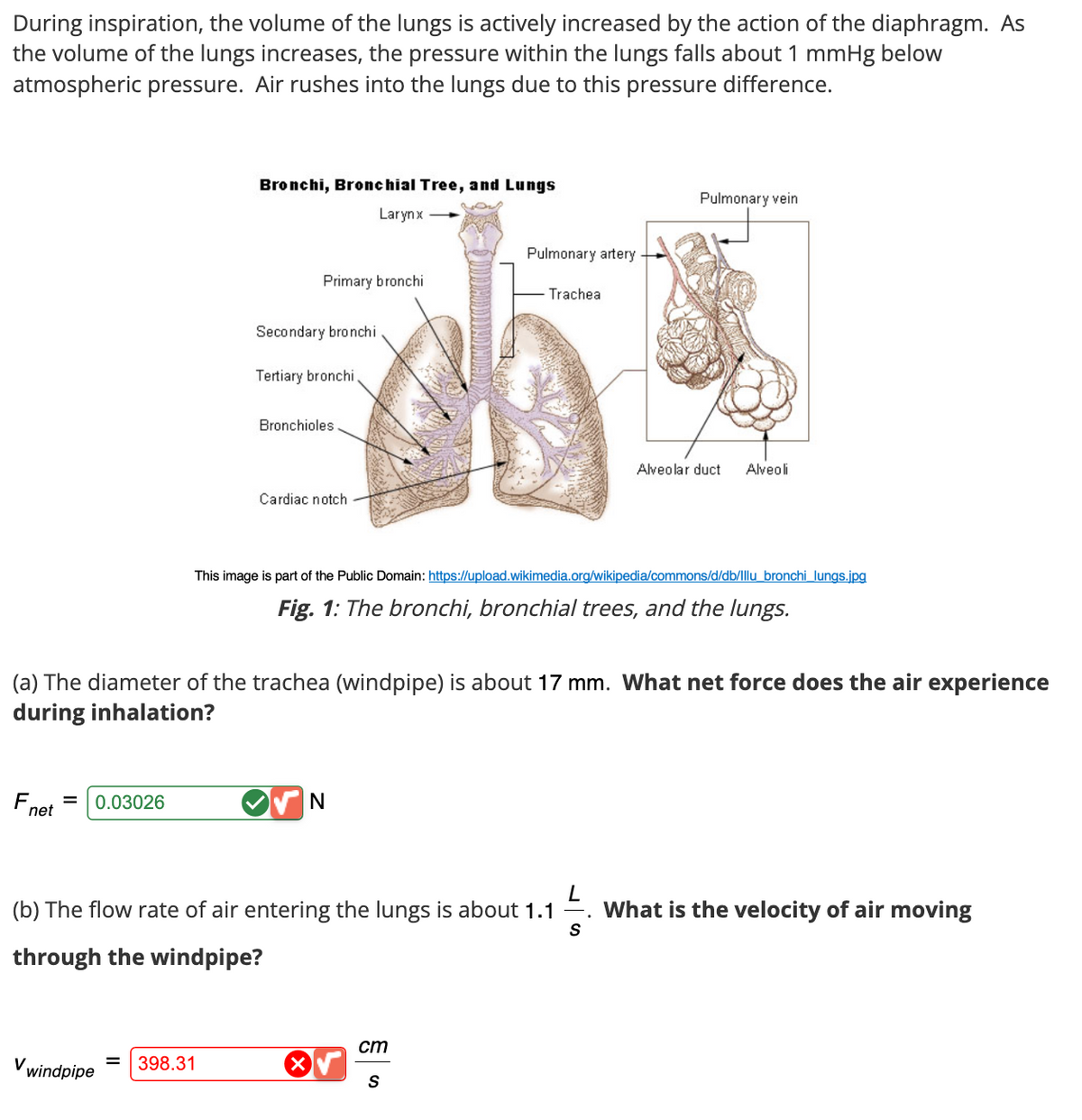
Transcribed Image Text:During inspiration, the volume of the lungs is actively increased by the action of the diaphragm. As
the volume of the lungs increases, the pressure within the lungs falls about 1 mmHg below
atmospheric pressure. Air rushes into the lungs due to this pressure difference.
Bronchi, Bronchial Tree, and Lungs
Larynx
Primary bronchi
Secondary bronchi
Tertiary bronchi
Bronchioles
Cardiac notch
Pulmonary artery
Trachea
Pulmonary vein
Alveolar duct
Alveoli
This image is part of the Public Domain: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/db/Illu_bronchi lungs.jpg
Fig. 1: The bronchi, bronchial trees, and the lungs.
(a) The diameter of the trachea (windpipe) is about 17 mm. What net force does the air experience
during inhalation?
F
=
0.03026
N
net
L
(b) The flow rate of air entering the lungs is about 1.1
.
What is the velocity of air moving
S
through the windpipe?
ст
windpipe
398.31
S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 1 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University