Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305071742
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter2: Functions
Section2.4: Average Rate Of Change Of A Function
Problem 4.2E: bThe average rate of change of the linear function f(x)=3x+5 between any two points is ________.
Related questions
Question
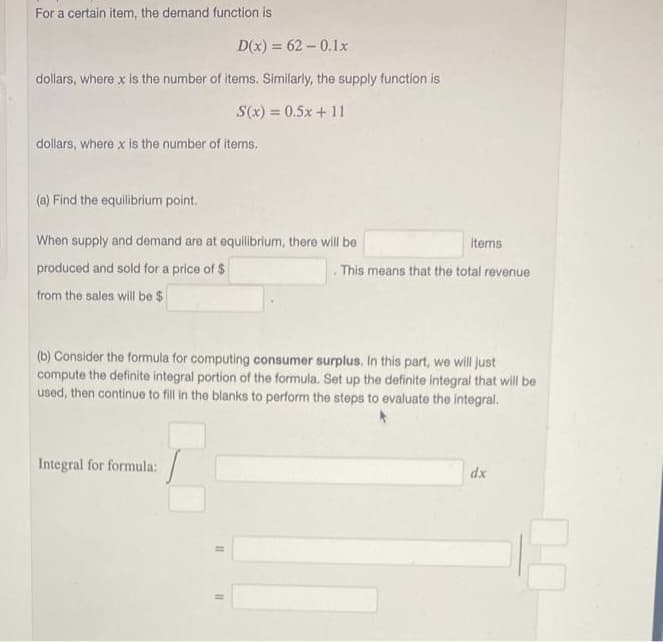
Transcribed Image Text:For a certain item, the demand function is
D(x) = 62-0.1x
dollars, where x is the number of items. Similarly, the supply function is
S(x) = 0.5x + 11
dollars, where x is the number of items.
(a) Find the equilibrium point.
When supply and demand are at equilibrium, there will be
items
produced and sold for a price of $
. This means that the total revenue
from the sales will be $
(b) Consider the formula for computing consumer surplus. In this part, we will just
compute the definite integral portion of the formula. Set up the definite integral that will be
used, then continue to fill in the blanks to perform the steps to evaluate the integral.
Integral for formula:
dx
11
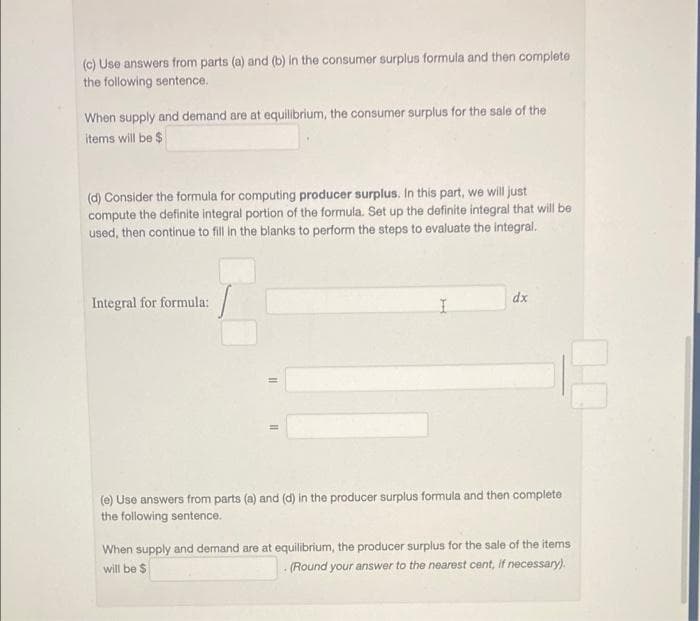
Transcribed Image Text:(c) Use answers from parts (a) and (b) in the consumer surplus formula and then complete
the following sentence.
When supply and demand are at equilibrium, the consumer surplus for the sale of the
items will be $
(d) Consider the formula for computing producer surplus. In this part, we will just
compute the definite integral portion of the formula. Set up the definite integral that will be
used, then continue to fill in the blanks to perform the steps to evaluate the integral.
Integral for formula:
dx
=
(e) Use answers from parts (a) and (d) in the producer surplus formula and then complete
the following sentence.
When supply and demand are at equilibrium, the producer surplus for the sale of the items
will be $
(Round your answer to the nearest cent, if necessary).
14
11
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning