e charged metal disks are arranged as shown (cutaway view). The disks are held apart by insulating supports not shown in the diagram. Each disk has an area of 2.5 m2 (this is the area of one flat surface of the disk). Use the value 8.85e-12 c/(N-m?) for co. The charge Q - 7e-8 coulombs, and the ge Q2- 4e-7 coulombs. 0.02 0.02 0.02 mm 4 mm mm 1.7 mm mm FG -Q 0: +Q; Disk 1 Disk 2 Disk 3 What is the magnitude of the electric field in the region between disks 1 and 27 IE - V/m What is the direction of the electric field between disks 1 and 27 x Which of the following statements are true? Choose all that apply. O Va - VA - -((Q/2.5)/e"(0.003) volts O Along a path from A to 8ELAÎ a va - VA -0 To calculate Ve - Va, which path should you choose? O A path starting at C and ending at B A path starting at B and ending at C O It doesn't matter whether the path starts or ends at B The sign of Ve - Va should be: O zero - no sign. • Negative, because Al is in the same direction as E O Positive, because Al is opposite to the direction of Ể What is the potential difference Ve- Va? volts What is the potential difference Vo - Vc? Vo Vc-0 v volts What is the potential difference Vy - Vo? Ve - Vo - What is the potential difference Va- V? VG - Vị -0 volts v volts
e charged metal disks are arranged as shown (cutaway view). The disks are held apart by insulating supports not shown in the diagram. Each disk has an area of 2.5 m2 (this is the area of one flat surface of the disk). Use the value 8.85e-12 c/(N-m?) for co. The charge Q - 7e-8 coulombs, and the ge Q2- 4e-7 coulombs. 0.02 0.02 0.02 mm 4 mm mm 1.7 mm mm FG -Q 0: +Q; Disk 1 Disk 2 Disk 3 What is the magnitude of the electric field in the region between disks 1 and 27 IE - V/m What is the direction of the electric field between disks 1 and 27 x Which of the following statements are true? Choose all that apply. O Va - VA - -((Q/2.5)/e"(0.003) volts O Along a path from A to 8ELAÎ a va - VA -0 To calculate Ve - Va, which path should you choose? O A path starting at C and ending at B A path starting at B and ending at C O It doesn't matter whether the path starts or ends at B The sign of Ve - Va should be: O zero - no sign. • Negative, because Al is in the same direction as E O Positive, because Al is opposite to the direction of Ể What is the potential difference Ve- Va? volts What is the potential difference Vo - Vc? Vo Vc-0 v volts What is the potential difference Vy - Vo? Ve - Vo - What is the potential difference Va- V? VG - Vị -0 volts v volts
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter19: Electric Forces And Electric Fields
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11CQ
Related questions
Question
Please solve the three parts that remain
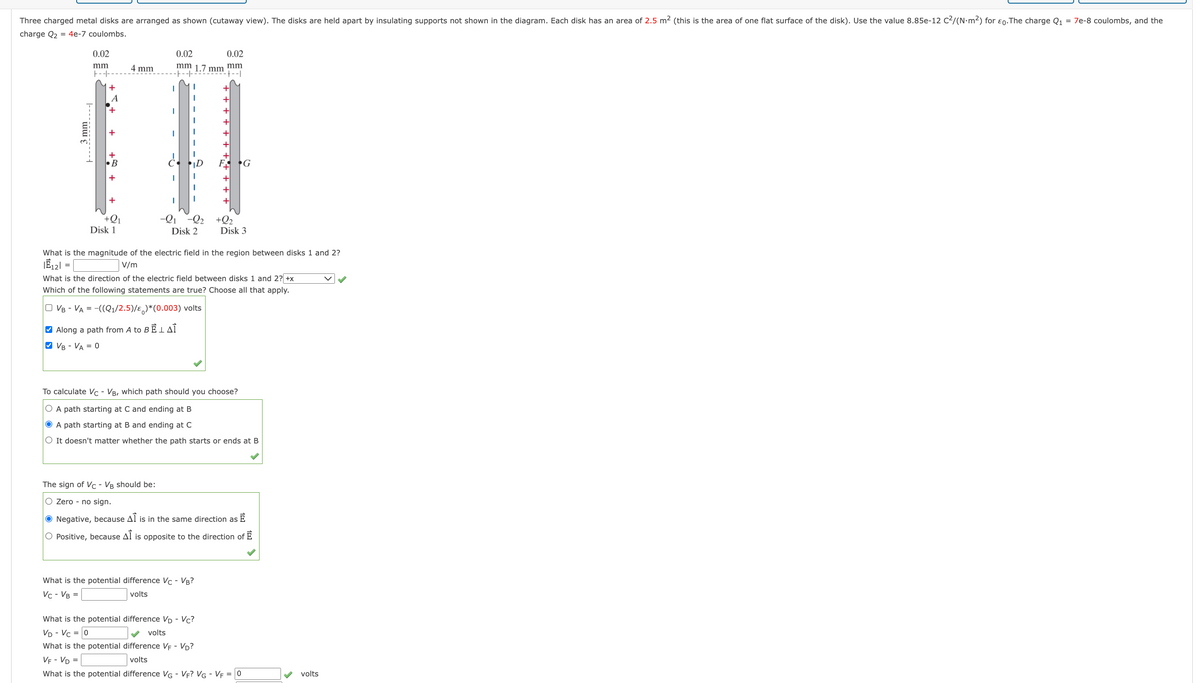
Transcribed Image Text:Three charged metal disks are arranged as shown (cutaway view). The disks are held apart by insulating supports not shown in the diagram. Each disk has an area of 2.5 m² (this is the area of one flat surface of the disk). Use the value 8.85e-12 C2/(N-m2) for ɛ0.The charge Q1 = 7e-8 coulombs, and the
charge Q2 = 4e-7 coulombs.
0.02
0.02
0.02
mm 1.7 mm mm
-- --
mm
4 mm
E--
+
A
•B
G
+
+
+Q1
Disk 1
-Q1 -Q2 +Q2
Disk 2
Disk 3
What is the magnitude of the electric field in the region between disks 1 and 2?
V/m
What is the direction of the electric field between disks 1 and 2? +x
Which of the following statements are true? Choose all that apply.
O VB - VA = -((Q1/2.5)/ɛ)*(0.003) volts
V Along a path from A to BĒLAĪ
O VB - VA = 0
To calculate Vc - VB, which path should you choose?
O A path starting at C and ending at B
O A path starting at B and ending at C
O It doesn't matter whether the path starts or ends at B
The sign of c - VB should be:
O Zero - no sign.
O Negative, because Al is in the same direction as E
O Positive, because Al is opposite to the direction of E
What is the potential difference Vc - VB?
Vc - VB =
volts
What is the potential difference Vp - Vc?
VD - Vc =
volts
What is the potential difference VF - Vp?
VE - Vp =
volts
What is the potential difference VG - VF? VG - VF = 0
volts
3 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning