7.0% 6.5% 6.0% 5.5% 5.0% 4.5% 4.0% 3.5% 3.0% 2.5% LL 2.0% 1.5% 1.0% 0.5% 0.0% $0 $10 $20 $30 $40 $50 $60 $70 $80 $90 $100 $110 $120 $130 $140 $150 $160 Bank Excess Reserves ($Billion) The model of the federal funds market that we have learned is sometimes called the corridor model. This is because, in this model the equilibrium fed funds rate fluctuates between the discount rate and the interest on reserves. This gives the Fed a tool to control the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds rate. Let's see how. Assume that the supply of federal funds equals $70 billion. Suppose that currently the discount rate is 4.5 percent and the interest on reserves equals 1.5 percent. In this case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars, the equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to percent, and if it decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to percent. Now suppose the Fed wants to reduce the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds rate. So it changes the discount rate to 3.5 percent and the interest on reserves to 2.5 percent. In that case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars, the equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to percent, and if it decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to percent. Federal Funds Rate
7.0% 6.5% 6.0% 5.5% 5.0% 4.5% 4.0% 3.5% 3.0% 2.5% LL 2.0% 1.5% 1.0% 0.5% 0.0% $0 $10 $20 $30 $40 $50 $60 $70 $80 $90 $100 $110 $120 $130 $140 $150 $160 Bank Excess Reserves ($Billion) The model of the federal funds market that we have learned is sometimes called the corridor model. This is because, in this model the equilibrium fed funds rate fluctuates between the discount rate and the interest on reserves. This gives the Fed a tool to control the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds rate. Let's see how. Assume that the supply of federal funds equals $70 billion. Suppose that currently the discount rate is 4.5 percent and the interest on reserves equals 1.5 percent. In this case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars, the equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to percent, and if it decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to percent. Now suppose the Fed wants to reduce the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds rate. So it changes the discount rate to 3.5 percent and the interest on reserves to 2.5 percent. In that case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars, the equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to percent, and if it decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to percent. Federal Funds Rate
Microeconomics A Contemporary Intro
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285635101
Author:MCEACHERN
Publisher:MCEACHERN
Chapter13: Capital, Interest, Entrepreneurship, And Corporate Finance
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13PAE
Related questions
Question
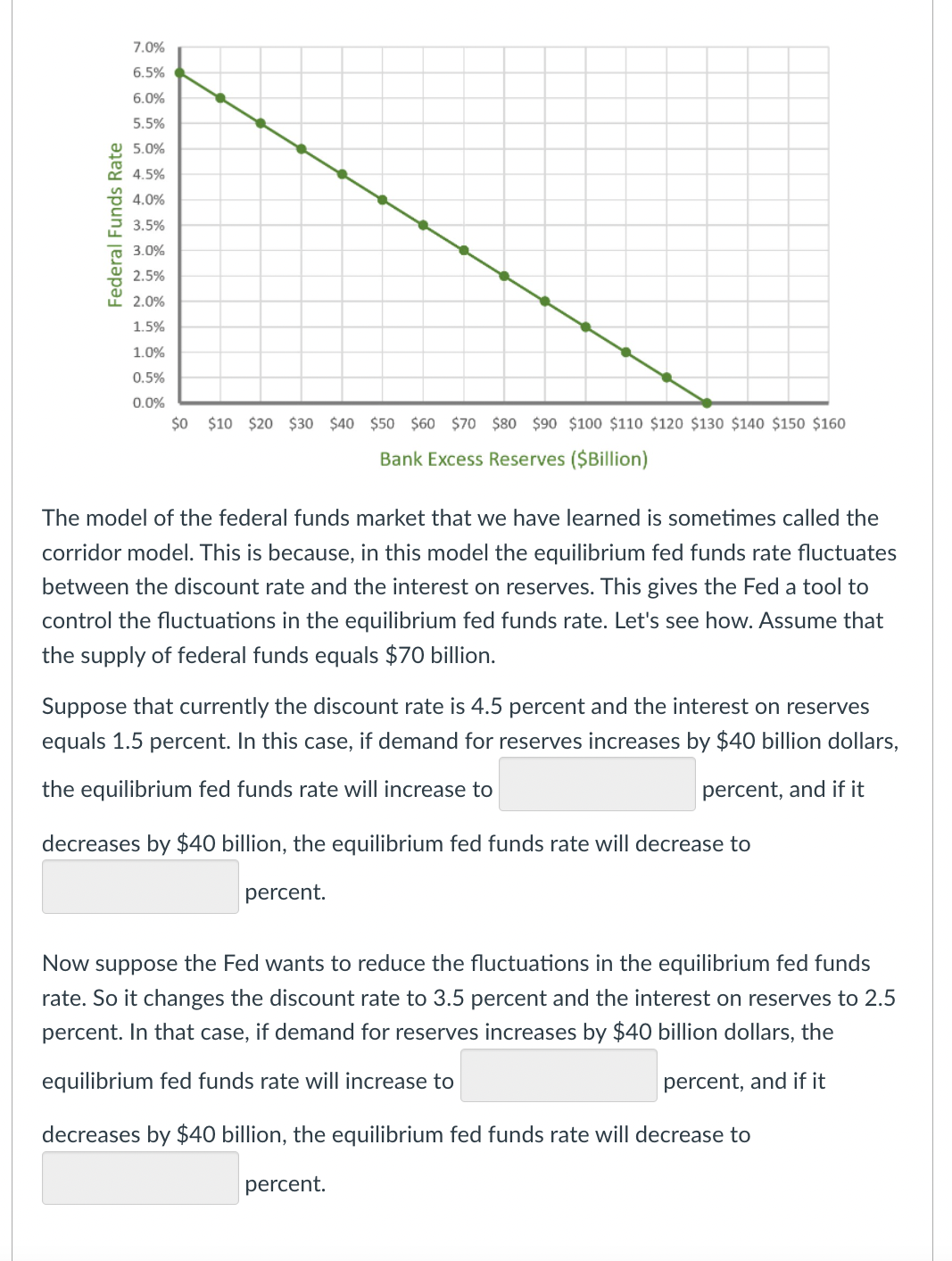
Transcribed Image Text:7.0%
6.5%
6.0%
5.5%
5.0%
4.5%
4.0%
3.5%
3.0%
2.5%
LL 2.0%
1.5%
1.0%
0.5%
0.0%
$0 $10 $20 $30 $40 $50 $60 $70 $80 $90 $100 $110 $120 $130 $140 $150 $160
Bank Excess Reserves ($Billion)
The model of the federal funds market that we have learned is sometimes called the
corridor model. This is because, in this model the equilibrium fed funds rate fluctuates
between the discount rate and the interest on reserves. This gives the Fed a tool to
control the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds rate. Let's see how. Assume that
the supply of federal funds equals $70 billion.
Suppose that currently the discount rate is 4.5 percent and the interest on reserves
equals 1.5 percent. In this case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars,
the equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to
percent, and if it
decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to
percent.
Now suppose the Fed wants to reduce the fluctuations in the equilibrium fed funds
rate. So it changes the discount rate to 3.5 percent and the interest on reserves to 2.5
percent. In that case, if demand for reserves increases by $40 billion dollars, the
equilibrium fed funds rate will increase to
percent, and if it
decreases by $40 billion, the equilibrium fed funds rate will decrease to
percent.
Federal Funds Rate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax