Elements of group 16 form hydrides with the generic formula H,X. When gaseous H,X is bubbled through a solution containing 0.30 Mhydrochloric acid, the solution becomes saturated and (H,X) - 0.10 M. The following equilibria exist in this solution: H,X(aq) +H,0(1) HX (aq) + H,0"(aq) K - 8.3 x 10 HX (ag) + H,0(/) x (ag) + H,0" (ag) K2- 10 x 10 14 4th attempt lal See Periodic Table O See Hint Feedback When the concentration of species at equilibrium is large relative to the equilibrium constant, it can be assumed that the starting concentrations will not be significantly changed during the reaction. x 10-10 M Calculate the concentration of X2 in the solution. 9.50
Elements of group 16 form hydrides with the generic formula H,X. When gaseous H,X is bubbled through a solution containing 0.30 Mhydrochloric acid, the solution becomes saturated and (H,X) - 0.10 M. The following equilibria exist in this solution: H,X(aq) +H,0(1) HX (aq) + H,0"(aq) K - 8.3 x 10 HX (ag) + H,0(/) x (ag) + H,0" (ag) K2- 10 x 10 14 4th attempt lal See Periodic Table O See Hint Feedback When the concentration of species at equilibrium is large relative to the equilibrium constant, it can be assumed that the starting concentrations will not be significantly changed during the reaction. x 10-10 M Calculate the concentration of X2 in the solution. 9.50
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Chapter12: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12.ACP
Related questions
Question
100%
its not 1.0 x 10^-14 either
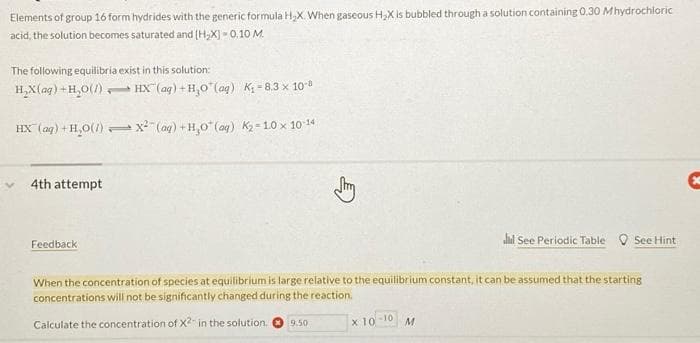
Transcribed Image Text:Elements of group 16 form hydrides with the generic formula H,X. When gaseous H,X is bubbled through a solution containing 0.30 Mhydrochloric
acid, the solution becomes saturated and (H,X) - 0.10 M.
The following equilibria exist in this solution:
H,X(aq) +H,0(1) HX (ag) + H,0"(aq) K = 8.3 x 100
HX (ag) + H,0() x (ag) + H,0" (ag) K2- 10 x 10 14
4th attempt
alial See Periodic Table O See Hint
Feedback
When the concentration of species at equilibrium is large relative to the equilibrium constant, it can be assumed that the starting
concentrations will not be significantly changed during the reaction.
x 10-10
M
Calculate the concentration of X in the solution.
9.50
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199030
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning