Examine the image that shows an inactive signaling pathway. When the signaling molecule binds to the G protein-coupled receptor, which of the following will be triggered? Signaling molecule G protein-coupled Plasma receptor membrane CYTOPLASM G protein (inactive) Enzyme The receptor will remain in an inactive state. But the G protein will become activated, binding to and activating the enzyme which will cause a cellular response. The receptor will be activated. Without contacting the receptor, the G protein will activate and bind to the inactive enzyme, making it active. This results in a cellular response. The receptor will be activated. The G protein will bind to the receptor, becoming activated by binding of GTP. The activated G protein will bind to and activate the inactive enzyme, triggering a cellular response. The receptor will be activated and will directly bind to and activate the enzyme, resulting in a cellular response.
Please answer with an explanation thank you!!
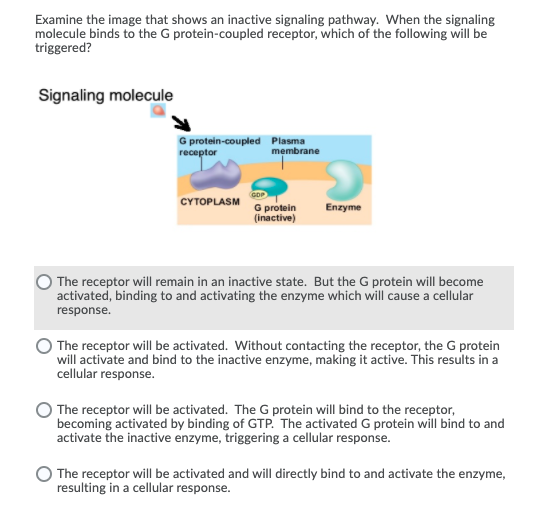
Signaling molecules and receptors mediate the signaling process in a cell. The cell surface receptors are classified into G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR), ion channel linked receptors, and enzyme-linked receptors. GPCR is a seven-transmembrane receptor.
Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins or G proteins are part of GPCR. G proteins are classified into small G protein and heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The heterotrimeric G protein consists of three subunits - α, β, and γ subunit.
When a signaling molecule binds to GPCR, the receptor gets activated by the induced conformational changes. The activated receptor function as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GEF helps in the exchange of GDP with GTP in the α subunit of intracellular G protein. The activated α-GTP subunit gets separated from the β-γ subunit complex. Both α-GTP and β-γ subunit complex activate signal transduction cascades, including enzymes and various other molecules in the cytosol. This cascade of signals will finally end up in a cellular response.
Therefore, option (3) is correct
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps




