Exercise 1: Rolling cylinder A homogenous cylinder is rolling down a plane (inclination a towards the horizontal plane) without sliding. The moment of inertia of the cylinder for rotations about its symmetry axis is given by I = mr²/2. Find the equations of motion.
Exercise 1: Rolling cylinder A homogenous cylinder is rolling down a plane (inclination a towards the horizontal plane) without sliding. The moment of inertia of the cylinder for rotations about its symmetry axis is given by I = mr²/2. Find the equations of motion.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Exercise 3: Sliding rope
A rope of length l and mass p per length unit slides down over the edge of a table after
being released without friction (cp. Figure).
Solve the equation of motion for the initial values:
r(0) = a with a <l and i(0) = 0.
Exercise 4: Unrolling Cylinders
homogenous cylinders
tia I = mırf/2, 12 = mrf/2 are wrapped by a thread (see figure). The first
mass m1, m2:
ri, ra and mome
iner-
cylinder is rotating on a fixed axis without friction. The second cylinder is falling
down vertically in the gravitational field. Derive the equations
calculate the thread tension.
motion and
x-Achse
Exercise 5: Bead on rotating wire
On a parabola-like wire (cp Example 2 in the lectures) a bead is moving un-
der the constraint z = ar? (in cylindrical coordinates). The wire rotates with
constant angular velocity w about the z-axis. Gravity is acting in the negative
z-direction.
a) Find the Lagrange function L and show that for
w = V2ag
the sum of centrifugal and gravitational force is perpendicular to the wire.
b) Solve the equation of motion.
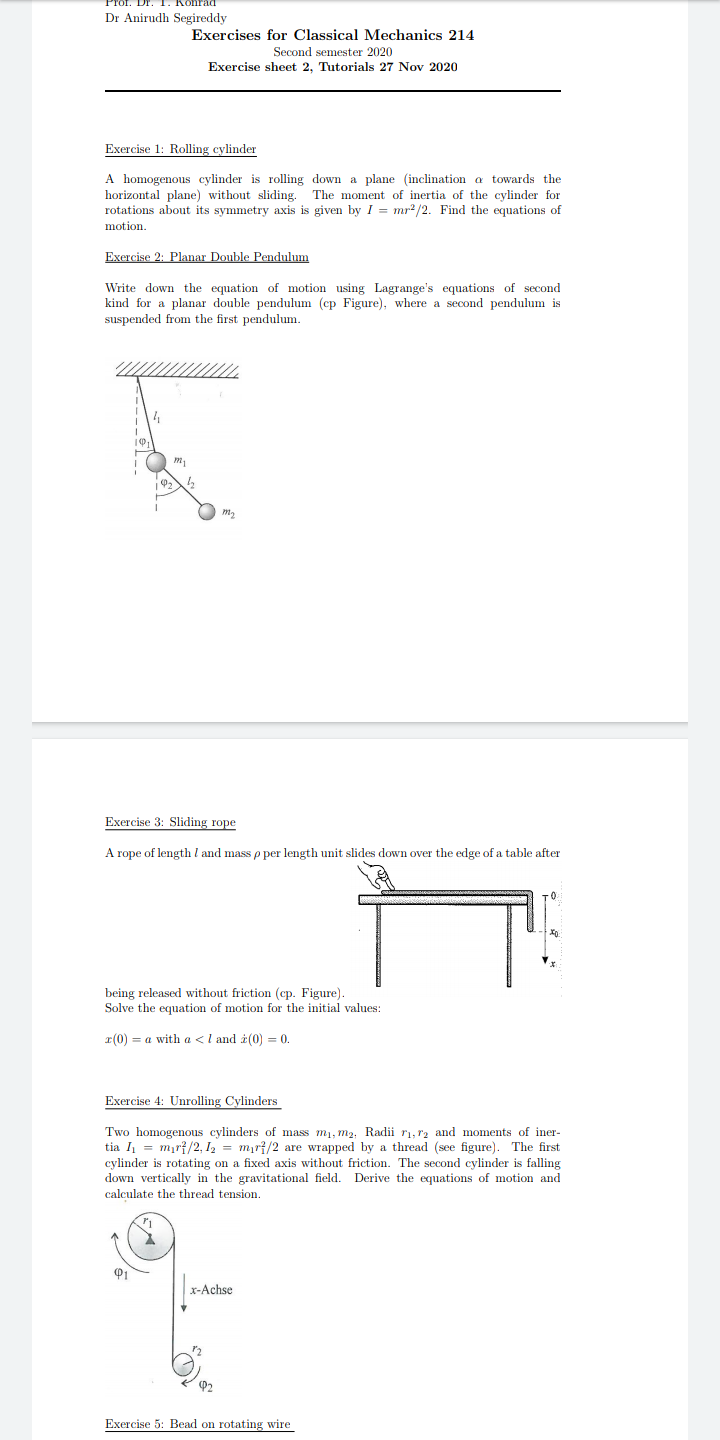
Transcribed Image Text:Kohrad
Dr Anirudh Segireddy
Exercises for Classical Mechanics 214
Second semester 2020
Exercise sheet 2, Tutorials 27 Nov 2020
Exercise 1: Rolling cylinder
A homogenous cylinder is rolling down a plane (inclination a towards the
horizontal plane) without sliding. The moment of inertia of the cylinder for
rotations about its symmetry axis is given by I = mr2/2. Find the equations of
motion.
Exercise 2: Planar Double Pendulum
Write down the equation of motion using Lagrange's equations of second
kind for a planar double pendulum (cp Figure), where a second pendulum is
suspended from the first pendulum.
Exercise 3: Sliding rope
A rope of length l and mass p per length unit slides down over the edge of a table after
being released without friction (cp. Figure).
Solve the equation of motion for the initial values:
r(0) = a with a <l and i(0) = 0.
Exercise 4: Unrolling Cylinders
Two homogenous cylinders of mass m1, m2, Radii ri, r2 and moments of iner-
tia I = mır{/2, I2 = mır{/2 are wrapped by a thread (see figure). The first
cylinder is rotating on a fixed axis without friction. The second cylinder is falling
down vertically in the gravitational field.
calculate the thread tension.
Derive the equations of motion and
x-Achse
P2
Exercise 5: Bead on rotating wire
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 6 images
