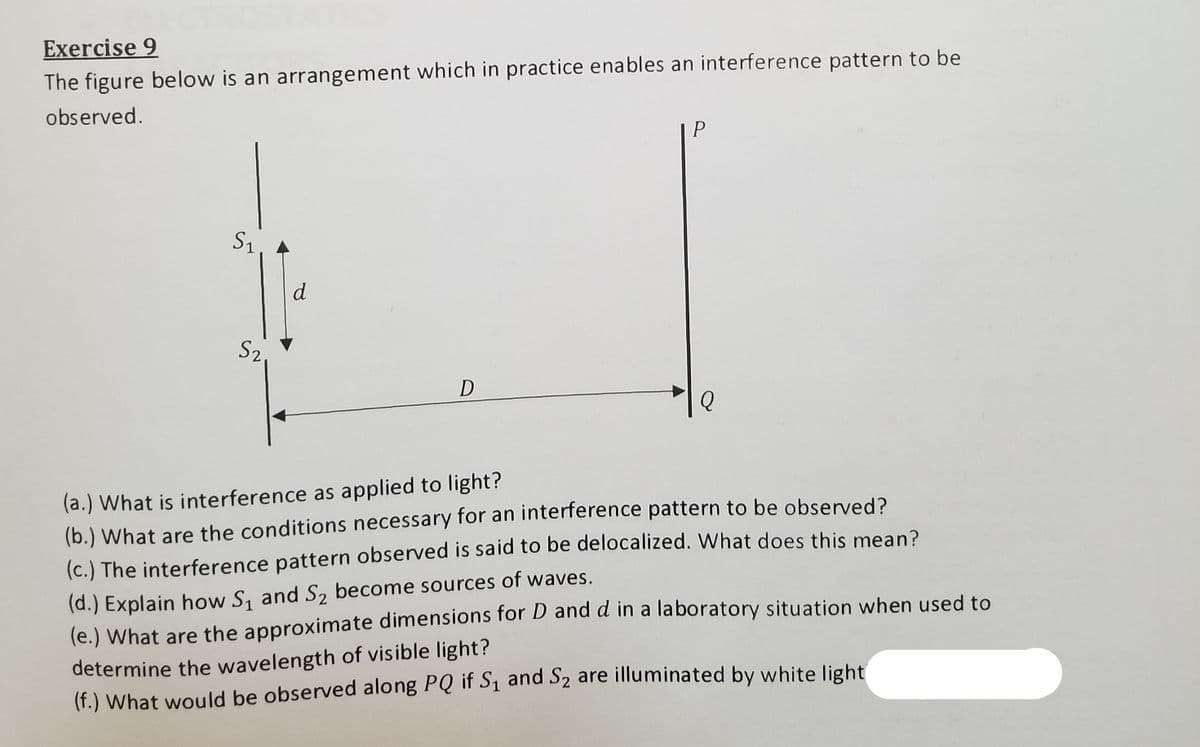
Exercise 9 The figure below is an arrangement which in practice enables an interference pattern to be observed. D (a.) What is interference as applied to light? (b.) What are the conditions necessary for an interference pattern to be observed? (c.) The interference pattern observed is said to be delocalized. What does this mean? (d.) Explain how S, and S2 become sources of waves. (e.) What are the approximate dimensions for D and d in a laboratory situation when used to determine the wavelength of visible light? (f.) What would be observed along PQ if Sı and S2 are illuminated by white light
Exercise 9 The figure below is an arrangement which in practice enables an interference pattern to be observed. D (a.) What is interference as applied to light? (b.) What are the conditions necessary for an interference pattern to be observed? (c.) The interference pattern observed is said to be delocalized. What does this mean? (d.) Explain how S, and S2 become sources of waves. (e.) What are the approximate dimensions for D and d in a laboratory situation when used to determine the wavelength of visible light? (f.) What would be observed along PQ if Sı and S2 are illuminated by white light
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter34: The Nature Of Light And The Principles Of Ray Optics
Section34.4: Analysis Model: Wave Under Refraction
Problem 34.2QQ: If beam is the incoming beam in Figure 34.10b, which of the other four red lines are reflected...
Related questions
Question
Answer Exercise 9 (d), (e) & (f)
Transcribed Image Text:determine the wavelength of visible light?
Exercise 9
The figure below is an arrangement which in practice enables an interference pattern to be
observed.
S1
S2
D
(a.) What is interference as applied to light?
(b.) What are the conditions necessary for an interference pattern to be observed?
(c.) The interference pattern observed is said to be delocalized. What does this mean?
(d.) Explain how S, and S2 become sources of waves.
(e.) What are the approximate dimensions for D and d in a laboratory situation when used to
(f.) What would be observed along PQ if S1 and S2 are illuminated by white light|
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning