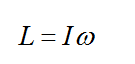1 Introduction And Vectors 2 Motion In One Dimension 3 Motion In Two Dimensions 4 The Laws Of Motion 5 More Applications Of Newton’s Laws 6 Energy Of A System 7 Conservation Of Energy 8 Momentum And Collisions 9 Relativity 10 Rotational Motion 11 Gravity, Planetary Orbits, And The Hydrogen Atom 12 Oscillatory Motion 13 Mechanical Waves 14 Superposition And Standing Waves 15 Fluid Mechanics 16 Temperature And The Kinetic Theory Of Gases 17 Energy In Thermal Processes: The First Law Of Thermodynamics 18 Heat Engines, Entropy, And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics 19 Electric Forces And Electric Fields 20 Electric Potential And Capacitance 21 Current And Direct Current Circuits 22 Magnetic Forces And Magnetic Fields 23 Faraday’s Law And Inductance 24 Electromagnetic Waves 25 Reflection And Refraction Of Light 26 Image Formation By Mirrors And Lenses 27 Wave Optics 28 Quantum Physics 29 Atomic Physics 30 Nuclear Physics 31 Particle Physics Chapter10: Rotational Motion
10.1 Angular Position, Speed, And Acceleration 10.2 Analysis Model: Rigid Object Under Constant Angular Acceleration 10.3 Relations Between Rotational And Translational Quantities 10.4 Rotational Kinetic Energy 10.5 Torque And The Vector Product 10.6 Analysis Model: Rigid Object In Equilibrium 10.7 Analysis Model: Rigid Object Under A Net Torque 10.8 Energy Considerations In Rotational Motion 10.9 Analysis Model: Nonisolated System (angular Momentum) 10.10 Analysis Model: Isolated System (angular Momentum) 10.11 Precessional Motion Of Gyroscopes 10.12 Rolling Motion Of Rigid Objects 10.13 Context Connection: Turning The Spacecraft Chapter Questions Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1OQ: A cyclist rides a bicycle with a wheel radius of 0.500 m across campus. A piece of plastic on the... Problem 2OQ Problem 3OQ Problem 4OQ Problem 5OQ: Assume a single 300-N force is exerted on a bicycle frame as shown in Figure OQ10.5. Consider the... Problem 6OQ: Consider an object on a rotating disk a distance r from its center, held in place on the disk by... Problem 7OQ: Answer yes or no to the following questions. (a) Is it possible to calculate the torque acting on a... Problem 8OQ: Figure OQ10.8 shows a system of four particles joined by light, rigid rods. Assume a = b and M is... Problem 9OQ: As shown in Figure OQ10.9, a cord is wrapped onto a cylindrical reel mounted on a fixed,... Problem 10OQ Problem 11OQ Problem 12OQ: A constant net torque is exerted on an object. Which of the following quantities for the object... Problem 13OQ: Let us name three perpendicular directions as right, up, and toward you as you might name them when... Problem 14OQ: A rod 7.0 m long is pivoted at a point 2.0 m from the left end. A downward force of 50 N acts at the... Problem 15OQ Problem 16OQ: A 20.0-kg horizontal plank 4.00 m long rests on two supports, one at the left end and a second 1.00... Problem 1CQ: (a) What is the angular speed of the second hand of a clock? (b) What is the direction of as you... Problem 2CQ Problem 3CQ Problem 4CQ: Which of the entries in Table 10.2 applies to finding the moment of inertia (a) of a long, straight... Problem 5CQ Problem 6CQ Problem 7CQ Problem 8CQ Problem 9CQ: Three objects of uniform densitya solid sphere, a solid cylinder, and a hollow cylinderare placed at... Problem 10CQ Problem 11CQ: If the torque acting on a particle about an axis through a certain origin is zero, what can you say... Problem 12CQ Problem 13CQ: Stars originate as large bodies of slowly rotating gas. Because of gravity, these clumps of gas... Problem 14CQ Problem 15CQ Problem 16CQ Problem 17CQ Problem 1P: During a certain time interval, the angular position of a swinging door is described by = 5.00 +... Problem 2P: A bar on a hinge starts from rest and rotates with an angular acceleration = 10 + 6t, where is in... Problem 3P Problem 4P Problem 5P: The tub of a washer goes into its spin cycle, starting from rest and gaining angular speed steadily... Problem 6P: Why is the following situation impossible? Starting from rest, a disk rotates around a fixed axis... Problem 7P: An electric motor rotating a workshop grinding wheel at 1.00 102 rev/min is switched off. Assume... Problem 8P Problem 9P Problem 10P: A wheel 2.00 m in diameter lies in a vertical plane and rotates about its central axis with a... Problem 11P: A disk 8.00 cm in radius rotates at a constant rate of 1200 rev/min about its central axis.... Problem 12P: Make an order-of-magnitude estimate of the number of revolutions through which a typical automobile... Problem 13P: A car traveling on a flat (unbanked), circular track accelerates uniformly from rest with a... Problem 14P Problem 15P: A digital audio compact disc carries data, each bit of which occupies 0.6 m along a continuous... Problem 16P: Figure P10.16 shows the drive train of a bicycle that has wheels 67.3 cm in diameter and pedal... Problem 17P: Big Ben, the Parliament tower clock in London, has an hour hand 2.70 m long with a mass of 60.0 kg... Problem 18P: Rigid rods of negligible mass lying along the y axis connect three particles (Fig. P10.18). The... Problem 19P: A war-wolf, or trebuchet, is a device used during the Middle Ages to throw rocks at castles and now... Problem 20P Problem 21P: Review. Consider the system shown in Figure P10.21 with m1 = 20.0 kg, m2 = 12.5 kg, R = 0.200 m, and... Problem 22P: The fishing pole in Figure P10.22 makes an angle of 20.0 with the horizontal. What is the torque... Problem 23P: Find the net torque on the wheel in Figure P10.23 about the axle through O, taking a = 10.0 cm and b... Problem 24P Problem 25P Problem 26P Problem 27P: A force of F=(2.00i+3.00j) N is applied to an object that is pivoted about a fixed axle aligned... Problem 28P: A uniform beam resting on two pivots has a length L = 6.00 m and mass M = 90.0 kg. The pivot under... Problem 29P Problem 30P Problem 31P: Figure P10.31 shows a claw hammer being used to pull a nail out of a horizontal board. The mass of... Problem 32P Problem 33P: A 15.0-m uniform ladder weighing 500 N rests against a frictionless wall. The ladder makes a 60.0... Problem 34P: A uniform ladder of length L and mass m1 rests against a frictionless wall. The ladder makes an... Problem 35P: BIO The arm in Figure P10.35 weighs 41.5 N. The gravitational force on the arm acts through point A.... Problem 36P: A crane of mass m1 = 3 000 kg supports a load of mass m2 = 10 000 kg as shown in Figure P10.36. The... Problem 37P: An electric motor turns a flywheel through a drive belt that joins a pulley on the motor and a... Problem 38P Problem 39P Problem 40P: In Figure P10.40, the hanging object has a mass of m1 = 0.420 kg; the sliding block has a mass of m2... Problem 41P: A potters wheela thick stone disk of radius 0.500 in and mass 100 kgis freely rotating at 50.0... Problem 42P: A model airplane with mass 0.750 kg is tethered to the ground by a wire so that it flies in a... Problem 44P: Consider two objects with m1 m2 connected by a light string that passes over a pulley having a... Problem 45P: Review. An object with a mass of m = 5.10 kg is attached to the free end of a light string wrapped... Problem 46P: A playground merry-go-round of radius R = 2.00 m has a moment of inertia I = 250 kg m2 and is... Problem 47P: The position vector of a particle of mass 2.00 kg as a function of time is given by... Problem 48P Problem 49P: Big Ben (Fig. P10.17), the Parliament tower clock in London, has hour and minute hands with lengths... Problem 50P: A disk with moment of inertia I1 rotates about a frictionless, vertical axle with angular speed i. A... Problem 51P Problem 52P: A space station is constructed in the shape of a hollow ring of mass 5.00 104 kg. Members of the... Problem 53P Problem 54P: Why is the following situation impossible? A space station shaped like a giant wheel has a radius of... Problem 55P: The puck in Figure 10.25 has a mass of 0.120 kg. The distance of the puck from the center of... Problem 56P: A student sits on a freely rotating stool holding two dumbbells, each of mass 3.00 kg (Fig. P10.56).... Problem 57P Problem 58P Problem 59P: A cylinder of mass 10.0 kg rolls without slipping on a horizontal surface. At a certain instant, its... Problem 60P: A uniform solid disk and a uniform hoop are placed side by side at the top of an incline of height... Problem 61P: A metal can containing condensed mushroom soup has mass 215 g, height 10.8 cm, and diameter 6.38 cm.... Problem 62P: A tennis ball is a hollow sphere with a thin wall. It is set rolling without slipping at 4.03 m/s on... Problem 63P Problem 64P: Review. A mixing beater consists of three thin rods, each 10.0 cm long. The rods diverge from a... Problem 65P: A long, uniform rod of length L and mass M is pivoted about a frictionless, horizontal pin through... Problem 66P: The hour hand and the minute hand of Big Ben, the Parliament tower clock in London, are 2.70 m and... Problem 67P: Two astronauts (Fig. P10.67), each having a mass of 75.0 kg, are connected by a 10.0-m rope of... Problem 68P: Two astronauts (Fig. P10.67), each having a mass M, are connected by a rope of length d having... Problem 69P Problem 70P Problem 71P: The reel shown in Figure P10.71 has radius R and moment of inertia I. One end of the block of mass m... Problem 72P: Review. A block of mass m1 = 2.00 kg and a block of mass m2 = 6.00 kg are connected by a massless... Problem 73P: A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P10.73, with AC = BC = = 4.00... Problem 74P: A stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P10.73, with AC = BC = ℓ. A... Problem 75P: A wad of sticky clay with mass m and velocity vi is fired at a solid cylinder of mass M and radius R... Problem 76P Problem 77P Problem 78P: Review. A string is wound around a uniform disk of radius R and mass M. The disk is released from... Problem 79P Problem 80P Problem 81P: A projectile of mass m moves to the right with a speed vi (Fig. P10.81a). The projectile strikes and... Problem 82P: Figure P10.82 shows a vertical force applied tangentially to a uniform cylinder of weight Fg. The... Problem 83P: A solid sphere of mass m and radius r rolls without slipping along the track shown in Figure P10.83.... Problem 84P Problem 85P: BIO When a gymnast performing on the rings executes the iron cross, he maintains the position at... Problem 2CQ
Related questions
Explain about Torque, rotational dynamics, and angular momentum .
Definition Definition Product of the moment of inertia and angular velocity of the rotating body: (L) = Iω Angular momentum is a vector quantity, and it has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of angular momentum is represented by the length of the vector, and the direction is the same as the direction of angular velocity.
Expert Solution
Dynamics: The branch of physics which involves the study of cause of a motion or and their effect on that motion.
Rotational Dynamics: When the cause of motion involves terms such as Torque or angular momentum, it is studied under Rotational Dynamics. It is analogous to the dynamics in translational motion. The quantities in rotational motion are mentioned with their translational analogue below,
Inertia (Mass)
Angular momentum (Momentum )
Torque (Force)
Translational Kinetic energy (Rotational Kinetic Energy)
Angular acceleration (Acceleration)
Under this branch we study the rotational motion of various systems like,
Motion of planets around the sun
Spinning top
Motion of wheels and gears.
Spinning of dancing ice skaters.
Angular Momentum: It is the rotational analogue of the quantity momentum in the translational motion. It is defined as the product of moment of inertia of a rotating body about a fixed axis and its angular velocity. It is a conserved quantity for system isolated to external torque. It can be expressed as,
Where I is the moment of inertia of a rotating body about its axis and ω is the angular velocity.
Example: When a ice skaters spin with hands and legs streched away from the body, takes its hands and legs closer to the rotating axis(body) its moment of inertia lowers and hence angular velocity increase to conserve the total angular momentum. Since there was no external torque acting on the skater.
It is the amount of motion a body have in rotating states such as spinning and orbiting. Hence a body can have two type of momentum while rotational motion,
Orbital angular momentum
Spin angular momentum
The total angular momentum of a body is the sum of the spin angular momentum and the orbital angular momentum of a body.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images
UNLOCK THE REST