Extend the Array class adding the following two new methods: A) the method called min that returns the smallest number in the array. E.g., applying min to the array [−3, 2, 0, −10, 9, 7], we get −10. B) the method called reverse that reverses the array. E.g., applying reverse to the array [−3, 2, 0, −10, 9, 7], we change it to [7, 9, −10, 0, 2, −3].
Extend the Array class adding the following two new
methods:
A) the method called min that returns the smallest number
in the array.
E.g., applying min to the array [−3, 2, 0, −10, 9, 7], we get −10.
B) the method called reverse that reverses the array.
E.g., applying reverse to the array [−3, 2, 0, −10, 9, 7], we change it
to [7, 9, −10, 0, 2, −3].
USE THE JAVA CODE BELOW TO ADD ON PLEASE
public class Array {
private int[] elems;
private int nElems;
public Array(int size) {
if (size < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
elems = new int[size];
}
public void print() {
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = 0; i < nElems; ++i)
if (i < nElems - 1) {
System.out.print(elems[i] + ", ");
} else {
System.out.print(elems[i]);
}
System.out.println("]");
}
public void insert(int element) {
// if the array is full, increases its size
if (elems.length == 0) {
int[] extendedElems = new int[1];
elems = extendedElems;
}
if (elems.length == nElems) {
int[] extendedElems = new int[nElems * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < nElems; ++i) {
extendedElems[i] = elems[i];
}
elems = extendedElems;
}
// otherwise, adds a new element at the end
elems[nElems] = element;
nElems++;
}
public void removeAt(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= nElems) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
} else {
for (int i = index; i < nElems; ++i) {
elems[i] = elems[i + 1];
}
nElems--;
}
}
public int indexOf(int element) {
for (int i = 0; i < nElems; ++i) {
if (elems[i] == element) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public boolean contains(int element) {
return (indexOf(element) != -1);
}
}
ANSWER:
(A) Smallest Number in Array:
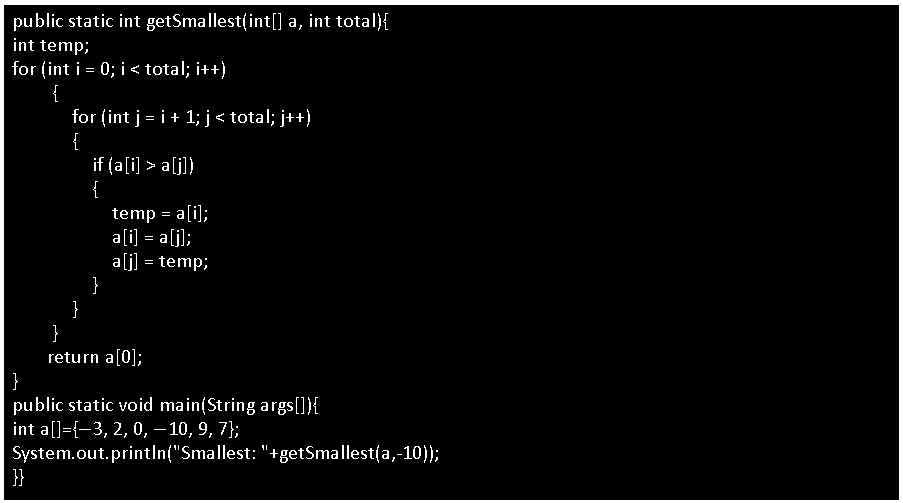
Output:

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images









