f: X→ Y and g: Y→V be bijective functions. Show the following: ) gof: X→V is injective. ) gof: X→ V is surjective. ) (gof)-¹ = f¹og-¹
f: X→ Y and g: Y→V be bijective functions. Show the following: ) gof: X→V is injective. ) gof: X→ V is surjective. ) (gof)-¹ = f¹og-¹
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.5: The Kernel And Range Of A Linear Transformation
Problem 30EQ
Related questions
Question
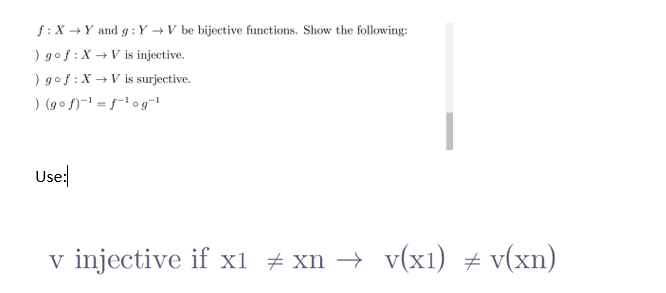
Transcribed Image Text:f: X→ Y and g: Y→V be bijective functions. Show the following:
) gof: X → V is injective.
) gof: X → V is surjective.
) (gof)-¹=f-¹og=¹
Use:
v injective if x1 ‡xn → v(x1) = v(xn)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage