F3² || Two forces of F₁ = 112. (i-j) √2 N and F₂ = 388 √2 What is the resultant force in terms of the force vectors F₁ and F2? What is the magnitude of an equal and opposite force, F3, which balances the first two forces? । N act on an object.
F3² || Two forces of F₁ = 112. (i-j) √2 N and F₂ = 388 √2 What is the resultant force in terms of the force vectors F₁ and F2? What is the magnitude of an equal and opposite force, F3, which balances the first two forces? । N act on an object.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter14: Static Equilibrium, Elasticity, And Fracture
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8PQ
Related questions
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Two forces of F₁ = 112
√2
N and F₂ = 388
√2
What is the resultant force in terms of the force vectors F₁ and F2?
What is the magnitude of an equal and opposite force, F3, which balances the first two forces?
sin()
cos()
tan()
T
HOME
cotan()
acos
EM4
asin()
atan() acotan() sinh()
7 8 9
5 6
1 2 3
*
0
END
cosh() tanh() cotanh()
ⒸDegrees O Radians
VO BACKSPACE DEL CLEAR
Submit
Hint
Feedback
I give up!
Given your observations from parts a and b, if working with vectors in 3 dimensions (i, j, k); what will the normalizing term n be for
(i- j+ k)
(i − j+ k)
the two vectors F₁ = C₁
N and F₂ = 0₂
N.
√T
| Fren |
Given the normalizing term n found in the previous part in 3 dimensions (i, j, k); what will the magnitude of the resultant vector
be in terms of the constants c₁ and ₂.
(i − j+ k)
(i- j+k)
The vectors in question are F₁:
N and F₂ = 0₂
√√T
√π
F3 =
= C1
N act on an object.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
What is the magnitude of the resultant vector in terms of the constants, given then normalizing term n?
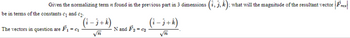
Transcribed Image Text:Given the normalizing term found in the previous part in 3 dimensions (i, j, k); what will the magnitude of the resultant vector = | Fres||
(i-j+ k)
(i-j+ k)
N and F₂-0₂
√π
be in terms of the constants c₁ and ₂.
The vectors in question are F₁ = C₁
Solution
Follow-up Question
How would the last part of this problem be solved (finding the magnitude of the resultant

Transcribed Image Text:, (1-2) N and Pr - 388 -
Two forces of F₁-112-
What is the resultant force in terms of the force vectors F₁ and F₂?
What is the magnitude of an equal and opposite force, F3, which balances the first two forces?
sin()
cos)
tan =(
acos E
cotan()
asin()
789
456
123
0
atan() acotan
sinh
cosh)
tan
cotart()
Degrees O Radians
NO BACKSPACE
Submit
Feedback
Given your observations from parts a and b, if working with vectors in 3 dimensions (i, j, k); what will the normalizing term befor
(1-3+k).
(²-3+k).
the two vectors F₁ -
-N and F₂-₂
N.
√₁
Given the normalizing term found in the previous part in 3 dimensions (i, j, k); what will the magnitude of the resultant vector
be in terms of the constants and c
The vectors in question are F₁ - ₁ ¸ (î −3+ k) N and ³ − c (î− 3 + k)
F₂-₂
√₁
√₁
Fy-
(1-5) Nact on an object.
Solution
Follow-up Question
Is normalizing in this case creating a unit vector or a vector perpendicular to F1 and F2?
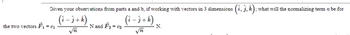
Transcribed Image Text:Given your observations from parts a and b, if working with vectors in 3 dimensions (i, j, k); what will the normalizing term be for
(i-j+k)
(i-j+k).
-G
N and F₂ = 0
N.
√₁
the two vectors F₁-
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University