Figure 1.0 below is a diagram showing two cars, A & B, travelling along a straight road, and also a person standing on the pavement at the side of the road (in bottom left-hand corner). Assume that moving from the left to the right along the road is in the positive direction and that moving from right to left the negative direction. Car A travels on the road with an absolute velocity 50km/h to the right, while Car B travels down the same street with an absolute velocity 60km/h to the right. Both velocities are relative to a stationary observer on earth. 50km/h 1 A 60km/h B Figure 1.0 Cars travelling along a road
Figure 1.0 below is a diagram showing two cars, A & B, travelling along a straight road, and also a person standing on the pavement at the side of the road (in bottom left-hand corner). Assume that moving from the left to the right along the road is in the positive direction and that moving from right to left the negative direction. Car A travels on the road with an absolute velocity 50km/h to the right, while Car B travels down the same street with an absolute velocity 60km/h to the right. Both velocities are relative to a stationary observer on earth. 50km/h 1 A 60km/h B Figure 1.0 Cars travelling along a road
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter1: Introduction To Statics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.19P: Plot the earths gravitational acceleration g(m/s2) against the height h (km) above the surface of...
Related questions
Question
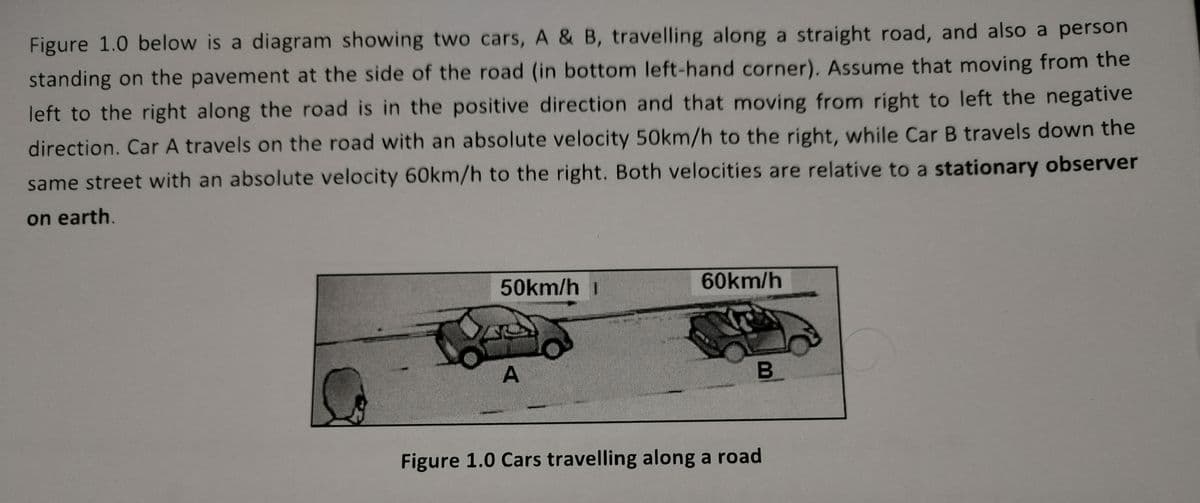
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 1.0 below is a diagram showing two cars, A & B, travelling along a straight road, and also a person
standing on the pavement at the side of the road (in bottom left-hand corner). Assume that moving from the
left to the right along the road is in the positive direction and that moving from right to left the negative
direction. Car A travels on the road with an absolute velocity 50km/h to the right, while Car B travels down the
same street with an absolute velocity 60km/h to the right. Both velocities are relative to a stationary observer
on earth.
50km/h 1
A
60km/h
B
Figure 1.0 Cars travelling along a road
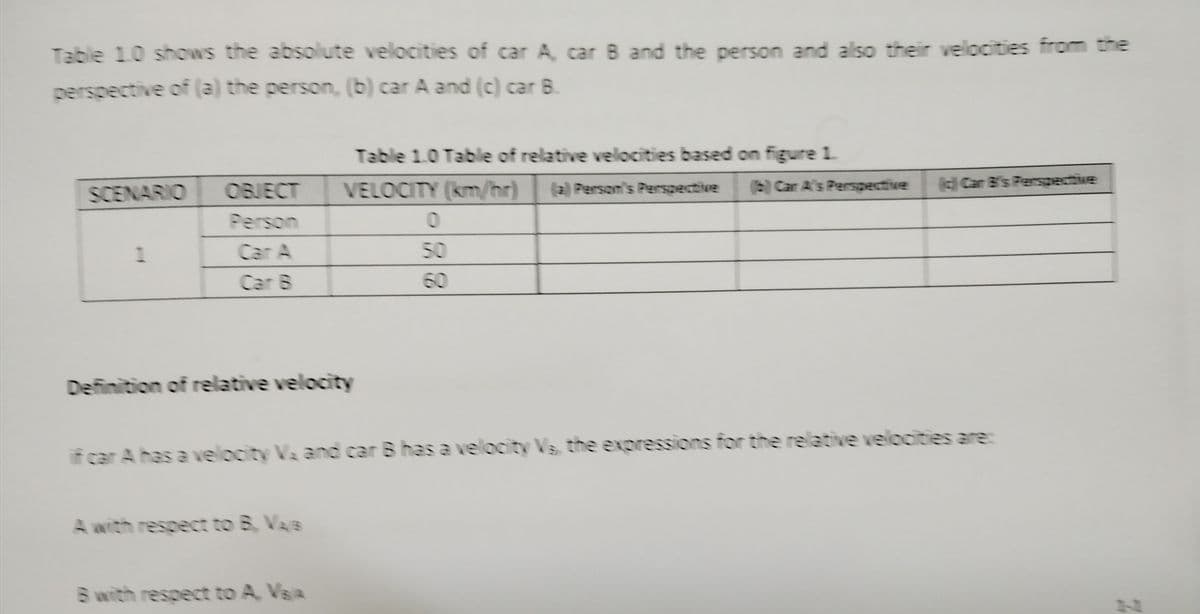
Transcribed Image Text:Table 1.0 shows the absolute velocities of car A, car B and the person and also their velocities from the
perspective of (a) the person, (b) car A and (c) car B
SCENARIO
1
OBJECT
Car A
Definition of relative velocity
Table 1.0 Table of relative velocities based on figure 1.
VELOCITY (km/hr)
A with respect to B. Vaja
B with respect to A, VSA
0
50
60
(c) Car B's Perspective
if car A has a velocity Vs and car B has a velocity Vs, the expressions for the relative velocities are:
(b) Car A's Perspective
(a) Person's Perspective
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L