Figure 2 shows a countershaft carrying two V-belt pulleys. Pulley A receives power from a motor through a belt with the belt tensions shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and delivered to the belt on pulley B. Assume the belt tension on the loose side at B is 15 percent of the tension on the tight side. a) Determine the tensions in the belt on pulley B, assuming the shaft is running at a constant speed. b) Find the magnitudes of the bearing reaction forces, assuming the bearings act as simple supports. c) Draw shear-force and bending-moment diagrams in X-Y plane for the shaft. d) At the point of maximum bending moment, determine the bending stress and the torsional shear stress. 230 mm 280 mm 30-mm dia. 300 mm 250-mm dia. 400-mm đia. 270 N 1800 N
Figure 2 shows a countershaft carrying two V-belt pulleys. Pulley A receives power from a motor through a belt with the belt tensions shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and delivered to the belt on pulley B. Assume the belt tension on the loose side at B is 15 percent of the tension on the tight side. a) Determine the tensions in the belt on pulley B, assuming the shaft is running at a constant speed. b) Find the magnitudes of the bearing reaction forces, assuming the bearings act as simple supports. c) Draw shear-force and bending-moment diagrams in X-Y plane for the shaft. d) At the point of maximum bending moment, determine the bending stress and the torsional shear stress. 230 mm 280 mm 30-mm dia. 300 mm 250-mm dia. 400-mm đia. 270 N 1800 N
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter11: Columns
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.3.10P: Repeat Problem 11.3-9. Use two C 150 × 12.2 steel shapes and assume that E = 205 GPa and L = 6 m.
Related questions
Question
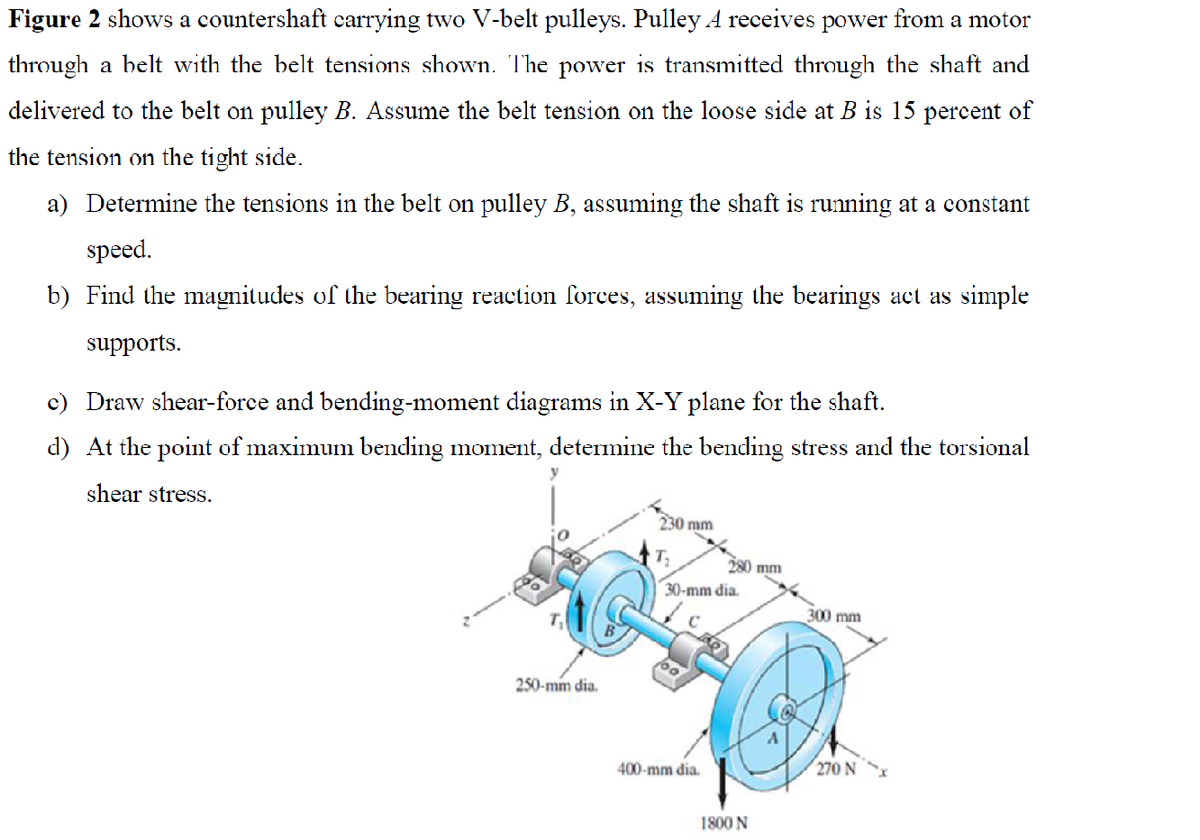
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 2 shows a countershaft carrying two V-belt pulleys. Pulley A receives power from a motor
through a belt with the belt tensions shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and
delivered to the belt on pulley B. Assume the belt tension on the loose side at B is 15 percent of
the tension on the tight side.
a) Determine the tensions in the belt on pulley B, assuming the shaft is running at a constant
speed.
b) Find the magnitudes of the bearing reaction forces, assuming the bearings act as simple
supports.
c) Draw shear-force and bending-moment diagrams in X-Y plane for the shaft.
d) At the point of maximum bending moment, determine the bending stress and the torsional
shear stress.
230 mm
280 mm
30-mm dia.
300 mm
250-mm dia.
400-mm đia.
270 N
1800 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning