FIGURE 24.6 Helicobacter pylori Pathogenesis Neutrophils are common in the early inflammatory response to H. pylori. Lymphocytes and other cells appear later. Urease CO(NH2)2 + H,0 CO2 + 2 NH3 How does urease allow Urea Ammonia H. pylori to live in the stomach? Helicobacter pylori Bacteria 2 Thinning of mucus layer due to mucosal damage Acidic environment of stomach penetrate and multiply in mucus layer Epithelium destroyed Mucus layer Mucus- Ulcer secreting cell mar Epithelium lining the stomach Basement membrane Connective Red blood cell Neutrophil Plasma Lymphocyte cell tissue Dilated capillary Capillary- Red blood cell- Inflammatory response Bacterial cells use their flagella to penetrate the mucus layer, and then attach to the mucus- secreting epithelium or multiply adjacent to it. Helicobacter survives the acidic environment of the stomach by secreting urease, which breaks urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. Bacterial toxins and inflammation damage epithelial cells, decreasing mucus production; acidic stomach juices damage the exposed tissue, causing a peptic ulcer. Ammonia neutralizes stomach acid.
FIGURE 24.6 Helicobacter pylori Pathogenesis Neutrophils are common in the early inflammatory response to H. pylori. Lymphocytes and other cells appear later. Urease CO(NH2)2 + H,0 CO2 + 2 NH3 How does urease allow Urea Ammonia H. pylori to live in the stomach? Helicobacter pylori Bacteria 2 Thinning of mucus layer due to mucosal damage Acidic environment of stomach penetrate and multiply in mucus layer Epithelium destroyed Mucus layer Mucus- Ulcer secreting cell mar Epithelium lining the stomach Basement membrane Connective Red blood cell Neutrophil Plasma Lymphocyte cell tissue Dilated capillary Capillary- Red blood cell- Inflammatory response Bacterial cells use their flagella to penetrate the mucus layer, and then attach to the mucus- secreting epithelium or multiply adjacent to it. Helicobacter survives the acidic environment of the stomach by secreting urease, which breaks urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. Bacterial toxins and inflammation damage epithelial cells, decreasing mucus production; acidic stomach juices damage the exposed tissue, causing a peptic ulcer. Ammonia neutralizes stomach acid.
Biomedical Instrumentation Systems
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133478294
Author:Chatterjee
Publisher:Chatterjee
Chapter17: Instrumentation In Intensive Care Units
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RT
Related questions
Question
How does urease allow H. pylori to live in the stomach?
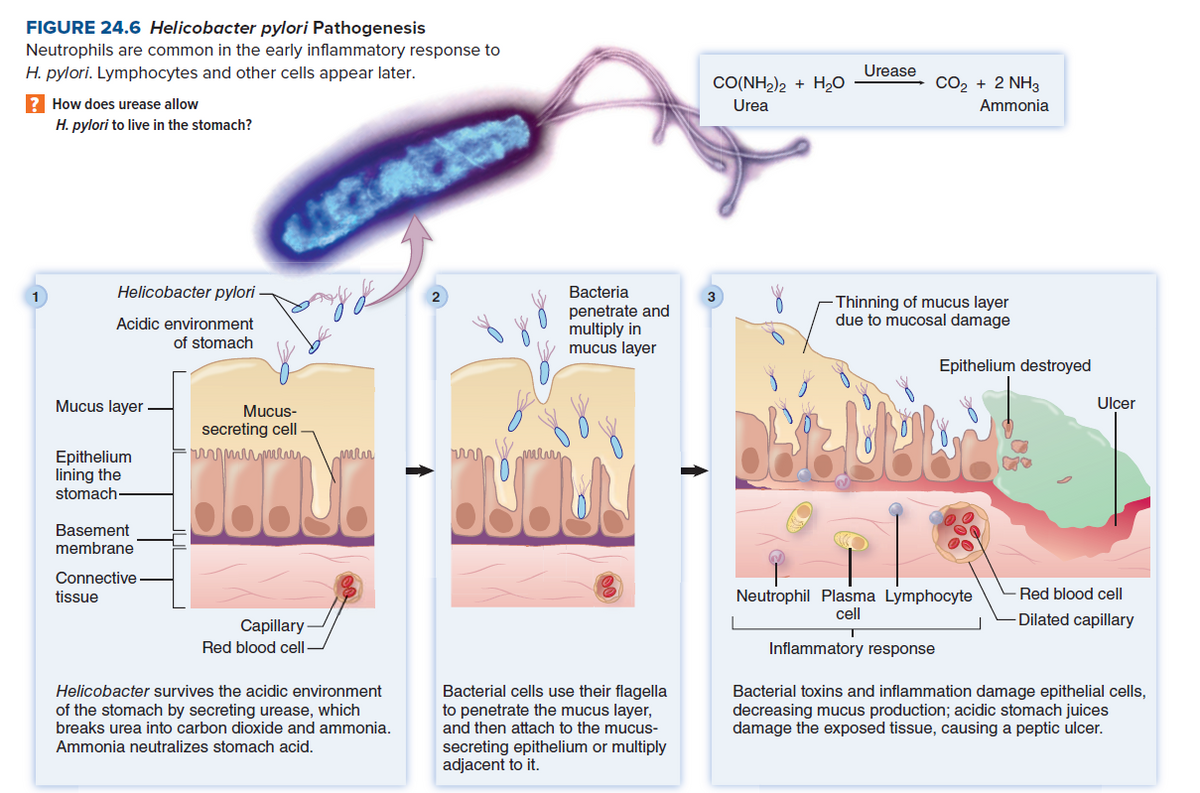
Transcribed Image Text:FIGURE 24.6 Helicobacter pylori Pathogenesis
Neutrophils are common in the early inflammatory response to
H. pylori. Lymphocytes and other cells appear later.
Urease
CO(NH2)2 + H,0
CO2 + 2 NH3
How does urease allow
Urea
Ammonia
H. pylori to live in the stomach?
Helicobacter pylori
Bacteria
2
Thinning of mucus layer
due to mucosal damage
Acidic environment
of stomach
penetrate and
multiply in
mucus layer
Epithelium destroyed
Mucus layer
Mucus-
Ulcer
secreting cell
mar
Epithelium
lining the
stomach
Basement
membrane
Connective
Red blood cell
Neutrophil Plasma Lymphocyte
cell
tissue
Dilated capillary
Capillary-
Red blood cell-
Inflammatory response
Bacterial cells use their flagella
to penetrate the mucus layer,
and then attach to the mucus-
secreting epithelium or multiply
adjacent to it.
Helicobacter survives the acidic environment
of the stomach by secreting urease, which
breaks urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia.
Bacterial toxins and inflammation damage epithelial cells,
decreasing mucus production; acidic stomach juices
damage the exposed tissue, causing a peptic ulcer.
Ammonia neutralizes stomach acid.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781111306663
Author:
Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781111306663
Author:
Margaret Rodriguez, Paul Price
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira…
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781305634350
Author:
Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. Schroeder
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

