Figure 8.11 (Example 8.8) A block sliding on a fric- tionless, horizontal surface collides with a light spring. (a) Initially, the block slides to the right, approaching the spring. (b) The block strikes the spring and begins to compress it. (c) The block stops momen- tarily at the maximum compression of the spring. (d) The spring pushes the block to the left. As the x= 0 ww- E = mu a b ® WWW E = mv + kx E = kxmax spring returns to its equilib- rium length, the block con- tinues moving to the left. The energy equations at the right show the energies of the system in the friction- less case in part (A). max d
Figure 8.11 (Example 8.8) A block sliding on a fric- tionless, horizontal surface collides with a light spring. (a) Initially, the block slides to the right, approaching the spring. (b) The block strikes the spring and begins to compress it. (c) The block stops momen- tarily at the maximum compression of the spring. (d) The spring pushes the block to the left. As the x= 0 ww- E = mu a b ® WWW E = mv + kx E = kxmax spring returns to its equilib- rium length, the block con- tinues moving to the left. The energy equations at the right show the energies of the system in the friction- less case in part (A). max d
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter5: Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 46P: A child of mass m starts from rest and slides without friction from a height h along a curved...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
A block having a mass of 0.80 kg is given an initial velocity υⒶ = 1.2 m/s to the right and collides with a spring whose mass is negligible and whose force constant is k = 50 N/m as shown.
(A) Assuming the surface to be frictionless, calculate the maximum compression of the spring after the collision. (B) Suppose a constant
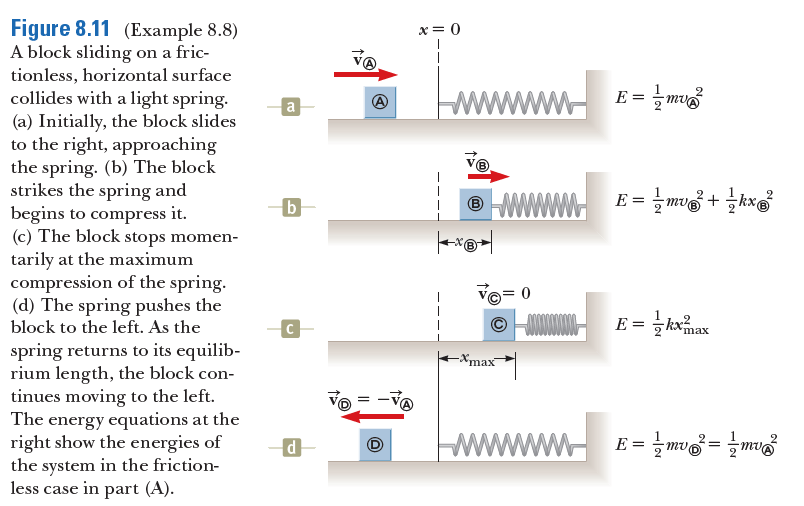
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 8.11 (Example 8.8)
A block sliding on a fric-
tionless, horizontal surface
collides with a light spring.
(a) Initially, the block slides
to the right, approaching
the spring. (b) The block
strikes the spring and
begins to compress it.
(c) The block stops momen-
tarily at the maximum
compression of the spring.
(d) The spring pushes the
block to the left. As the
x= 0
ww-
E = mu
a
b
® WWW
E = mv + kx
E = kxmax
spring returns to its equilib-
rium length, the block con-
tinues moving to the left.
The energy equations at the
right show the energies of
the system in the friction-
less case in part (A).
max
d
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill