Figure Q20-1 Cumulative risk of lung cancer mortality for nonsmokers, smokers, and former smokers (Problem 20-6). Cumulative risk is the running total of deaths, as a percentage, for each group. Thus, for continuing smokers, 1% died of lung cancer between ages 45 and 55; an additional 4% died between never 15 stopped 10 stopped age 50 5 55 and 65 (giving a cumulative risk of 5%); and 11% more died between 65 and 75 (for a cumulative risk of 16%). stopped - age 30 never smoked 45 55 65 75 85 age (years) lung cancer mortality, cumulative risk (%)
Figure Q20-1 Cumulative risk of lung cancer mortality for nonsmokers, smokers, and former smokers (Problem 20-6). Cumulative risk is the running total of deaths, as a percentage, for each group. Thus, for continuing smokers, 1% died of lung cancer between ages 45 and 55; an additional 4% died between never 15 stopped 10 stopped age 50 5 55 and 65 (giving a cumulative risk of 5%); and 11% more died between 65 and 75 (for a cumulative risk of 16%). stopped - age 30 never smoked 45 55 65 75 85 age (years) lung cancer mortality, cumulative risk (%)
Chapter13: Addictive Behavior
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7AYK
Related questions
Question
Mortality due to lung cancer was followed in
groups of males in the United Kingdom for 50 years. Figure
Q20–1 shows the cumulative risk of dying from lung can-
cer as a function of age and smoking habits for four groups
of males: those who never smoked, those who stopped at
age 30, those who stopped at age 50, and those who contin-
ued to smoke. These data show clearly that individuals can
substantially reduce their cumulative risk of dying from
lung cancer by stopping smoking. What do you suppose is
the biological basis for this observation?
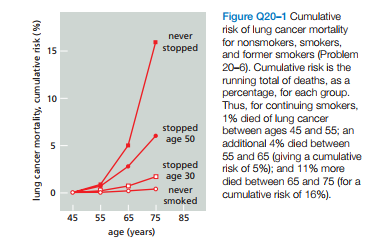
Transcribed Image Text:Figure Q20-1 Cumulative
risk of lung cancer mortality
for nonsmokers, smokers,
and former smokers (Problem
20-6). Cumulative risk is the
running total of deaths, as a
percentage, for each group.
Thus, for continuing smokers,
1% died of lung cancer
between ages 45 and 55; an
additional 4% died between
never
15
stopped
10
stopped
age 50
5
55 and 65 (giving a cumulative
risk of 5%); and 11% more
died between 65 and 75 (for a
cumulative risk of 16%).
stopped
- age 30
never
smoked
45
55
65 75 85
age (years)
lung cancer mortality, cumulative risk (%)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Lifetime Physical Fitness & Wellness
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781337677509
Author:
HOEGER
Publisher:
Cengage

Lifetime Physical Fitness & Wellness
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781337677509
Author:
HOEGER
Publisher:
Cengage