Find the absolute extrema of the given function on the indicated closed and bounded set R. f(x, y) = xy – x – 5y; Ris the triangular region with vertices (0, 0), (0, 30), and (5, 0) Absolute maximum: i Absolute minimum: i
Find the absolute extrema of the given function on the indicated closed and bounded set R. f(x, y) = xy – x – 5y; Ris the triangular region with vertices (0, 0), (0, 30), and (5, 0) Absolute maximum: i Absolute minimum: i
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Chapter3: Functions
Section3.3: More On Functions; Piecewise-defined Functions
Problem 99E: Determine if the statemment is true or false. If the statement is false, then correct it and make it...
Related questions
Question
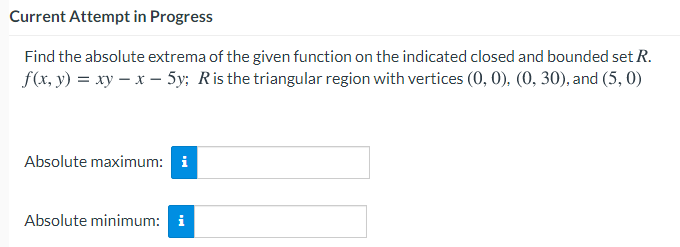
Transcribed Image Text:Current Attempt in Progress
Find the absolute extrema of the given function on the indicated closed and bounded set R.
f(x, y) = xy – x – 5y; Ris the triangular region with vertices (0, 0), (0, 30), and (5, 0)
Absolute maximum: i
Absolute minimum: i

Transcribed Image Text:Hint
Assistance Used
A point (xo, yo) in the domain of a function f(x, y) is called a critical point of the function if f, (xo, yo) = 0 andf, (xo, Yo) = 0 or
if one or both partial derivatives do not exist at (xo, yo).
The Second Partials Test:
Let f be a function of two variables with continuous second-order partial derivatives in some disk centered at a critical point
(xo. Yo), and let
D = fr (x0, Yo )fyy (xo, Yo) – f, (xo, Yo)
(a) If D > 0 and f (xo, Yo) > 0, thenf has a relative maximum at (xo, Yo).
(b) If D > 0 and fr (xo, Yo) < 0, thenf has a relative minimum at (xo, yo).
(c) If D < 0, thenf has a saddle point at (xo, Yo).
(d) If D = 0, then no conclusion can be drawn.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning