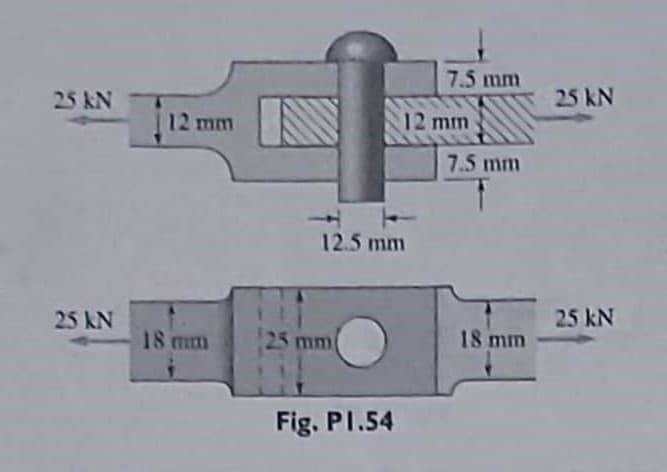
1.54 For the joint shown in the figure, calculate (a) the largest bearing stress between the pin and the members; (b) the average shear stress in the pin; and (c) the largest average normal stress in the members. 11 the rivets in
Answer the problem question and store value and then use 4 decimal places as final answer then box the final answer. Don’t forget the unit.
Write it on a piece of paper, handwritten showing the correct answer.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Answer the problem question and store value and then use 2 decimal places as final answer then box the final answer. Don’t forget the unit.
Take note: Write it on a paper, hand written showing correct answer.
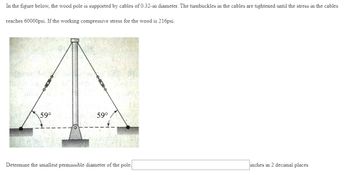
Answer the problem question and store value and then use 2 decimal places as final answer then box the final answer. Don’t forget the unit.
Take note: Write it on a paper, hand written showing correct answer.

Answer the problem question and store value and then use 2 decimal places as final answer then box the final answer. Don’t forget the unit.
Take note: Write it on a paper, hand written showing correct answer.









