Firm 1 must decide whether to enter an industry in which firm 2 is an incumbent. To enter this industry, firm
Firm 1 must decide whether to enter an industry in which firm 2 is an incumbent. To enter this industry, firm
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course List)
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305627734
Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Chapter15: Decision Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5P: Hudson Corporation is considering three options for managing its data warehouse: continuing with its...
Related questions
Question
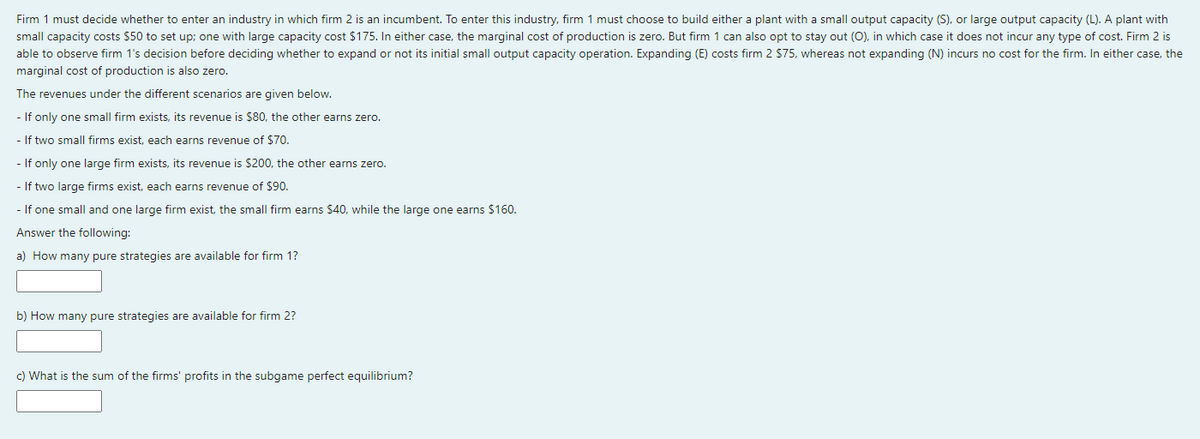
Transcribed Image Text:Firm 1 must decide whether to enter an industry in which firm 2 is an incumbent. To enter this industry, firm 1 must choose to build either a plant with a small output capacity (S), or large output capacity (L). A plant with
small capacity costs $50 to set up; one with large capacity cost $175. In either case, the marginal cost of production is zero. But firm 1 can also opt to stay out (O), in which case it does not incur any type of cost. Firm 2 is
able to observe firm 1's decision before deciding whether to expand or not its initial small output capacity operation. Expanding (E) costs firm 2 $75, whereas not expanding (N) incurs no cost for the firm. In either case, the
marginal cost of production is also zero.
The revenues under the different scenarios are given below.
- If only one small firm exists, its revenue is $80, the other earns zero.
- If two small firms exist, each earns revenue of $70.
- If only one large firm exists, its revenue is $200, the other earns zero.
- If two large firms exist, each earns revenue of $90.
- If one small and one large firm exist, the small firm earns $40, while the large one earns $160.
Answer the following:
a) How many pure strategies are available for firm 1?
b) How many pure strategies are available for firm 2?
c) What is the sum of the firms' profits in the subgame perfect equilibrium?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course …
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305627734
Author:
Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course …
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305627734
Author:
Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning