Flying Circus of Physics Continuation of Problem 8 and Problem 37. Another explanation for the sliding stones of Racetrack Playa in Death Valley, California is that the stones move only when the water dumped on the playa during a storm freezes into a large, thin sheet of ice. The stones are trapped in place in the ice. Then, as air flows across the ice during a wind, the air-drag forces on the ice and stones move them both, with the stones gouging out the trails. The magnitude of the air-drag force on this horizontal "ice sail" is given by Dice = 4CicepAicev², where Cice is the drag coefficient (2.0 x 10-³), p is the air density (1.21 kg/m³), Aice is the horizontal area of the ice, and v is the wind speed along the ice. Assume the following: The ice sheet measures 210 m by 540 m by 4.8 mm and has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15 with the ground and a density of 917 kg/m³. Also assume that 100 stones of mass 17 kg are trapped in the ice. To maintain the motion of the sheet, what is the required wind speed near the sheet? Number i Units
Flying Circus of Physics Continuation of Problem 8 and Problem 37. Another explanation for the sliding stones of Racetrack Playa in Death Valley, California is that the stones move only when the water dumped on the playa during a storm freezes into a large, thin sheet of ice. The stones are trapped in place in the ice. Then, as air flows across the ice during a wind, the air-drag forces on the ice and stones move them both, with the stones gouging out the trails. The magnitude of the air-drag force on this horizontal "ice sail" is given by Dice = 4CicepAicev², where Cice is the drag coefficient (2.0 x 10-³), p is the air density (1.21 kg/m³), Aice is the horizontal area of the ice, and v is the wind speed along the ice. Assume the following: The ice sheet measures 210 m by 540 m by 4.8 mm and has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15 with the ground and a density of 917 kg/m³. Also assume that 100 stones of mass 17 kg are trapped in the ice. To maintain the motion of the sheet, what is the required wind speed near the sheet? Number i Units
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter5: The Laws Of Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.23CQ
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
100%
The tolerance is -+2%
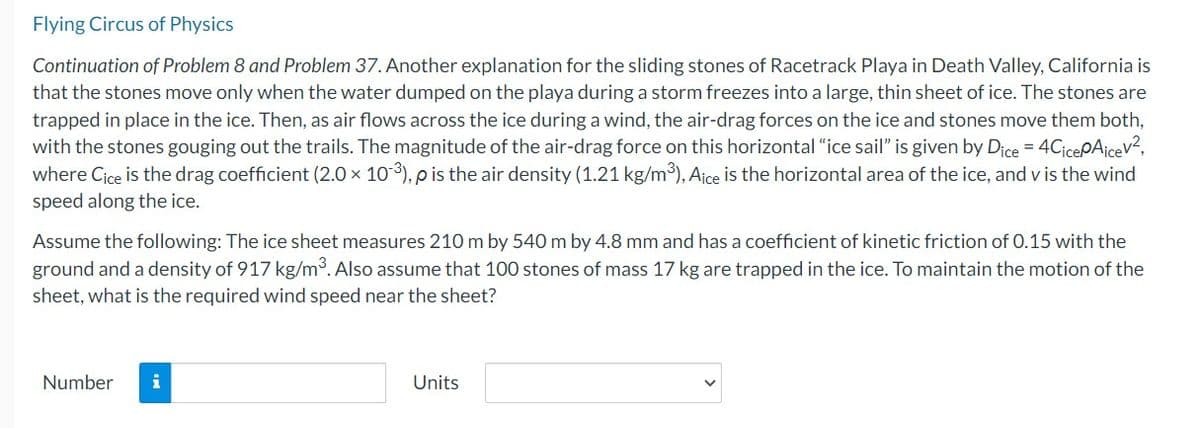
Transcribed Image Text:Flying Circus of Physics
Continuation of Problem 8 and Problem 37. Another explanation for the sliding stones of Racetrack Playa in Death Valley, California is
that the stones move only when the water dumped on the playa during a storm freezes into a large, thin sheet of ice. The stones are
trapped in place in the ice. Then, as air flows across the ice during a wind, the air-drag forces on the ice and stones move them both,
with the stones gouging out the trails. The magnitude of the air-drag force on this horizontal "ice sail" is given by Dice = 4CicepAicev²,
where Cice is the drag coefficient (2.0 × 103), p is the air density (1.21 kg/m³), Aice is the horizontal area of the ice, and v is the wind
speed along the ice.
Assume the following: The ice sheet measures 210 m by 540 m by 4.8 mm and has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15 with the
ground and a density of 917 kg/m³. Also assume that 100 stones of mass 17 kg are trapped in the ice. To maintain the motion of the
sheet, what is the required wind speed near the sheet?
Number i
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning