For every polyhedron there is a construction for a so called dual polyhedron by connecting together the centres of the faces. The diagram on the left below shows this construction for a cube that constructs an octahedron inside it. 2²³ B .O Choose an origin O to be the centre of the base of the cube and choose the i, j and k directions to be parallel to the faces of the cube. Let A be the centre of the face with positive i-coordinate and B be the centre of the face with positive j- coordinate, as shown in the right-hand diagram. Let the cube have a side length 2. (a) Write down OA and OB in terms of the unit vectors i, j and k. (b) Calculate OÀ OB and hence calculate the angle AOB. (c) Calculate OÀ X OB and hence calculate the ratio of the surface area of the octahedron to the surface area of the cube.
For every polyhedron there is a construction for a so called dual polyhedron by connecting together the centres of the faces. The diagram on the left below shows this construction for a cube that constructs an octahedron inside it. 2²³ B .O Choose an origin O to be the centre of the base of the cube and choose the i, j and k directions to be parallel to the faces of the cube. Let A be the centre of the face with positive i-coordinate and B be the centre of the face with positive j- coordinate, as shown in the right-hand diagram. Let the cube have a side length 2. (a) Write down OA and OB in terms of the unit vectors i, j and k. (b) Calculate OÀ OB and hence calculate the angle AOB. (c) Calculate OÀ X OB and hence calculate the ratio of the surface area of the octahedron to the surface area of the cube.
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Chapter9: Surfaces And Solids
Section9.2: Pyramids, Area, And Volume
Problem 6E
Related questions
Question
100%
q28
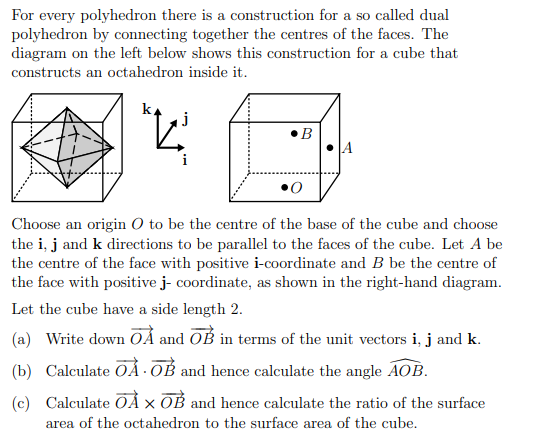
Transcribed Image Text:For every polyhedron there is a construction for a so called dual
polyhedron by connecting together the centres of the faces. The
diagram on the left below shows this construction for a cube that
constructs an octahedron inside it.
j
"K³
B
i
0
Choose an origin O to be the centre of the base of the cube and choose
the i, j and k directions to be parallel to the faces of the cube. Let A be
the centre of the face with positive i-coordinate and B be the centre of
the face with positive j- coordinate, as shown in the right-hand diagram.
Let the cube have a side length 2.
(a) Write down OA and OB in terms of the unit vectors i, j and k.
(b) Calculate ŌÀ OB and hence calculate the angle AOB.
(c) Calculate OÀ X OB and hence calculate the ratio of the surface
area of the octahedron to the surface area of the cube.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL