For the acceleration equation, when the term VdV/ds-2 m/s² that means the flow is: In a horizontal 0 time Steady Uniform any flowing fluid Unsteady Non- uniform
For the acceleration equation, when the term VdV/ds-2 m/s² that means the flow is: In a horizontal 0 time Steady Uniform any flowing fluid Unsteady Non- uniform
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
pllllllllllllease solve question 3
Transcribed Image Text:9
11
4
5
6
7
3
2
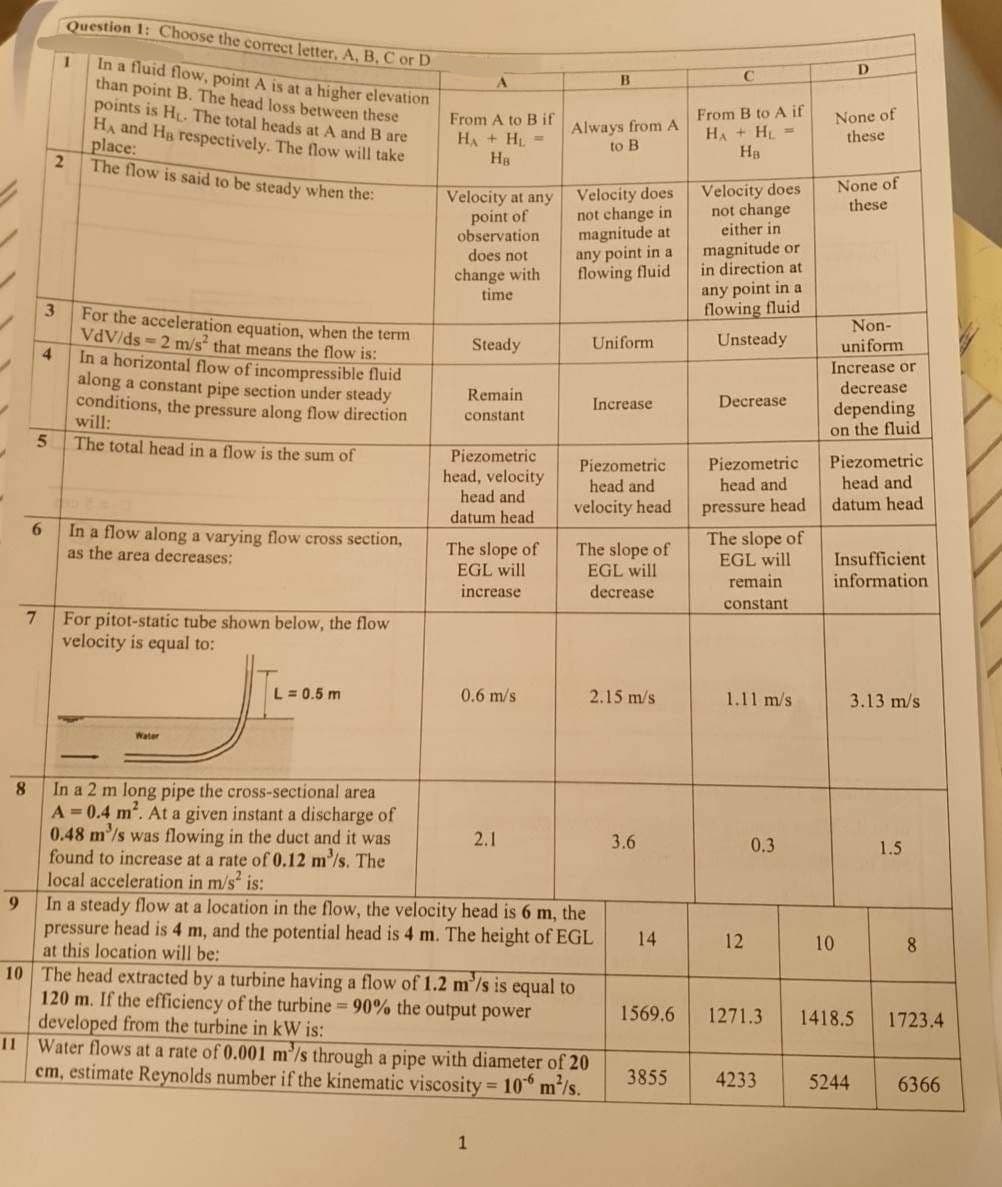
Question 1: Choose the correct letter, A, B, C or D
In a fluid flow, point A is at a higher elevation
than point B. The head loss between these
points is H. The total heads at A and B are
HA and Ha respectively. The flow will take
place:
The flow is said to be steady when the:
1
For the acceleration equation, when the term
VdV/ds=2 m/s² that means the flow is:
In a horizontal flow of incompressible fluid
along a constant pipe section under steady
conditions, the pressure along flow direction
will:
The total head in a flow is the sum of
In a flow along a varying flow cross section,
as the area decreases:
For pitot-static tube shown below, the flow
velocity is equal to:
Water
8
In a 2 m long pipe the cross-sectional area
A=0.4 m². At a given instant a discharge of
0.48 m/s was flowing in the duct and it was
found to increase at a rate of 0.12 m³/s. The
local acceleration in m/s² is:
L = 0.5 m
From A to B if
HA + H₂=
На
Velocity at any
point of
observation
does not
change with
time
Steady
Remain
constant
Piezometric
head, velocity
head and
datum head
The slope of
EGL will
increase
0.6 m/s
2.1
1
Always from A
to B
Velocity does
not change in
magnitude at
any point in a
flowing fluid
B
10 The head extracted by a turbine having a flow of 1.2 m/s is equal to
120 m. If the efficiency of the turbine = 90% the output power
developed from the turbine in kW is:
Uniform
Piezometric
head and
velocity head
Increase
The slope of
EGL will
decrease
In a steady flow at a location in the flow, the velocity head is 6 m, the
pressure head is 4 m, and the potential head is 4 m. The height of EGL
at this location will be:
Water flows at a rate of 0.001 m/s through a pipe with diameter of 20
cm, estimate Reynolds number if the kinematic viscosity = 106 m²/s.
2.15 m/s
3.6
14
1569.6
3855
C
From B to A if
HA+HL=
На
Velocity does
not change
either in
magnitude or
in direction at
any point in a
flowing fluid
Unsteady
Decrease
Piezometric
head and
pressure head
The slope of
EGL will
remain
constant
1.11 m/s
12
0.3
1271.3
4233
D
None of
these
None of
these
10
Non-
uniform
Increase or
decrease
depending
on the fluid
Piezometric
head and
datum head
Insufficient
information
3.13 m/s
5244
1.5
8
1418.5 1723.4
6366
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY